Windows Server 2008 and RADIUS
Exam: Microsoft 70-649 - TS: Upgrading Your MCSE on Windows Server 2003 to Windows Server 2008, Technology Specialist
Windows Server 2008 can act as a RADIUS server, proxy or client using the Network Policy Server role. In the case of Windows Server 2003, the function was performed by the Internet Authentication Service (IAS). The role of Windows Server 2008 in all three roles is:
- As a RADIUS server - It provides authentication services for RADIUS clients;
- As a RADIUS client - It sends authenticated traffic to a designated RADIUS server and
- As a RADIUS proxy - It sends authentication traffic from RADIUS clients to RADIUS servers.
The figure given below represents a basic RADIUS infrastructure where authentication is provided directly for the VPN server and indirectly through the dial-up server.
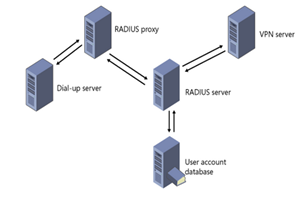
Basic RADIUS infrastructure
Windows Server 2008 Enterprise and Datacenter enable configuring RADIUS clients unlimited in number and remote server groups. RADIUS clients can be specified by hostname, IP and address range. This enables configuration of multiple RADIUS clients. In Windows Server 2008 Standard the number of radius clients is limited to 50 and number of server groups is limited to two.
While using Windows Server 2008 Standard with NPS, RADIUS clients can be defined by the host name or the IP address but not by the address range. RADIUS clients can be defined by the address range with Windows Server 2008 Enterprise or Datacenter editions.
RADIUS Client
Windows Server 2008 can act like a RADIUS client. Other servers and network devices can also be configured to act as RADIUS clients of a system running Windows Server 2008 along with Network Policy Server role service which is installed in conjunction with the Network Policy and Access Services server role.
Dial-up servers, VPN servers, WLAN access points, 802.1x compliant switches, RADIUS proxies are included in RADIUS clients. The working of a RADIUS client need not be specified while adding a RADIUS client. RADIUS clients act in the same manner irrespective of the fact that they are wireless access points or dial-up servers. Follow the steps mentioned below for configuring a system running Windows Server 2008 with a RADIUS client.
- The first step is to open the Network Policy Server console.
- The next step is to move to the NPS (Local)\RADIUS Clients And Servers\RADIUS Clients node. On the RADIUS Clients node press the right click, followed by selecting New RADIUS Client. This opens the New RADIUS Client dialog box.
- The last step is to enter the details of the RADIUS client, and then clicking on OK.
RADIUS servers and clients authenticate one another by using a shared secret which can be generated automatically by Windows Server 2008.
RADIUS Server
When Windows Server 2008 is configured to function as a RADIUS server, it carries out authentication by itself and does not forward authentication to another RADIUS server. Two different instances are possible here:
- RADIUS server is a member of a domain: In this case authentication can be performed by using AD DS, LDAP or a local account database.
- RADIUS server is not a member of a domain: In this case authentication can be performed by the local account database or an LDAP.
Authentication traffic that is forwarded to RADIUS servers is accepted by them. Authentication decisions are made on the basis of network policies that are configured on the RADIUS server. RADIUS clients can access servers like VPN, dial-up servers, RADIUS proxies that are capable of routing authentication traffic from access servers to the RADIUS server which further authenticate the clients based depending on a shared secret.
RADIUS Proxy
RADIUS proxies are involved in the process of routing RADIUS authentication requests between RADIUS clients and servers. It is the RADIUS proxy that decides where to route the RADIUS connection requests based on information that is contained in the RADIUS message. Multiple RADIUS proxies are possible between a RADIUS client and a server. When connection requests are to be forwarded to a remote NPS or RADIUS server, a remote RADIUS server group has to be created and connection request policy has to be configured for forwarding requests to a remote server group that is dependent on the properties of the connection request. This way, you can have multiple RADIUS server groups with the RADIUS proxy routing connection requests to each one, based on the connection request policies that you configured.
For a system running on Windows Server 2008 it is possible to act as a RADIUS server and a proxy, authenticating some requests while forwarding the remaining to remote RADIUS server group. This is based on configured connection request policies. A proxy group can be configured using the following points:
- As the first step, click on Network Policy Server console to open it. Expand the Radius Clients And Servers node.
- Right click on the Remote RADIUS Server Groups node, and then click on New. This will start the New Remote Radius Server Group dialog box.
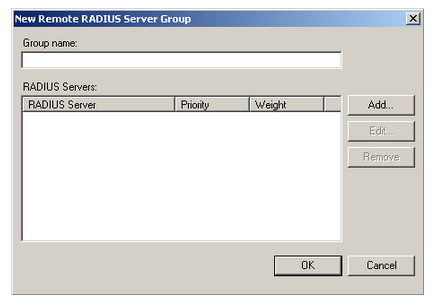
New Remote RADIUS server group
- The next step is to enter the name for the RADIUS server group followed by clicking on Add. This will open the Add RADIUS Server dialog box.
- The last step is to enter the host name or the IP address of the remote RADIUS server. The shared secret on the is also required to be entered on the for using between the RADIUS proxy and server.


