Exam Code: 1D0-520
Exam Name: CIW v5 Site Designer
Certification Provider: CIW
Corresponding Certifications: CIW Web Design Professional, CIW Web Design Specialist, Master CIW Designer
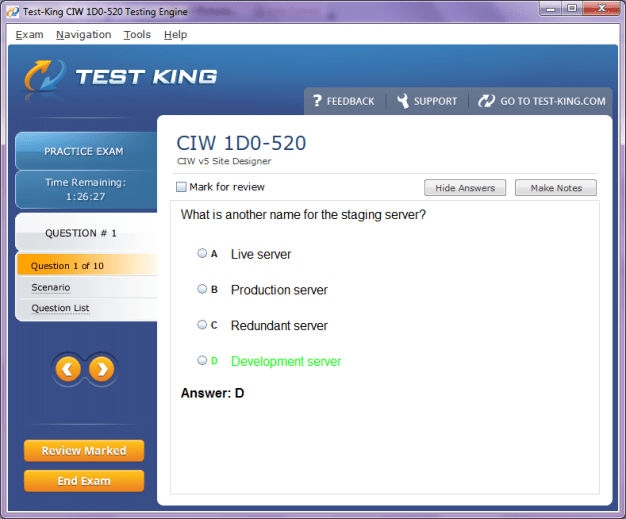
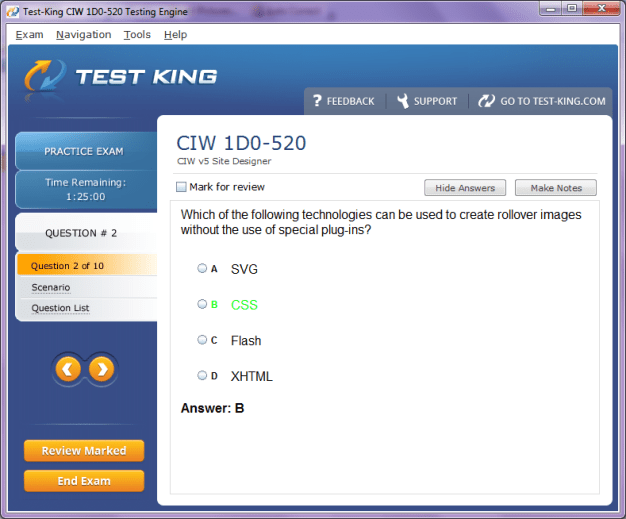
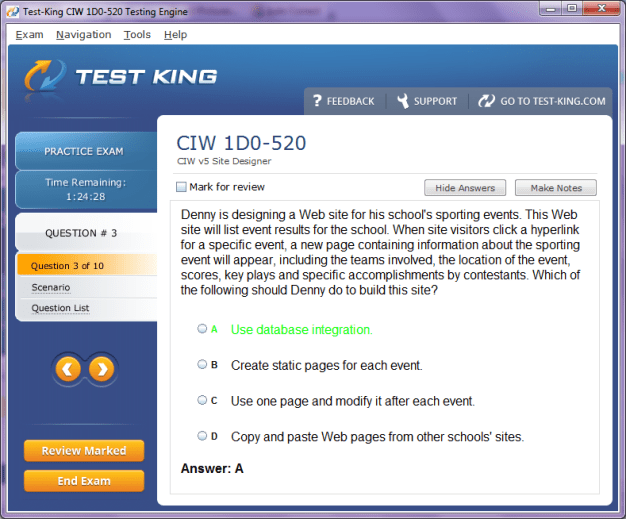
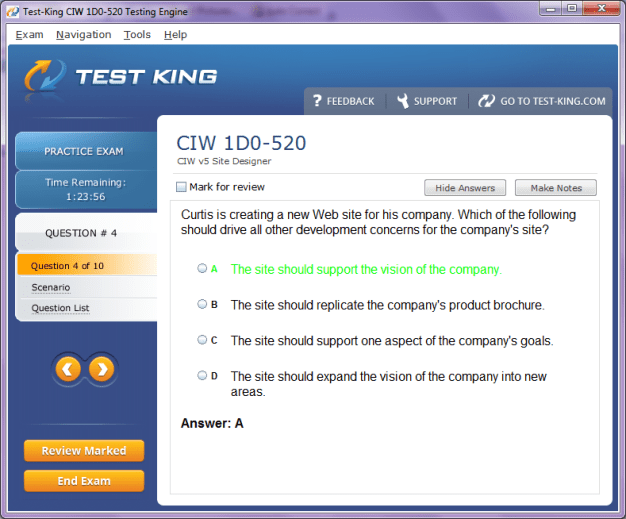
1D0-520 Exam Product Screenshots
Product Reviews
Kudos test-king
"I am a working person with a profession of design specialist. I really was worried about my exam 1D0-520 as I was having a huge problem with the topic site development essentials. I mean I wasn't getting much time to prepare for it and I felt like I needed more than books this time to prepare for the exam. Then I found test-king QnA which was amazing and helped me so well that in less than a week's preparation I was ready to give my exam.
Omar
Cairo, Egypt"
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get the products after purchase?
All products are available for download immediately from your Member's Area. Once you have made the payment, you will be transferred to Member's Area where you can login and download the products you have purchased to your computer.
How long can I use my product? Will it be valid forever?
Test-King products have a validity of 90 days from the date of purchase. This means that any updates to the products, including but not limited to new questions, or updates and changes by our editing team, will be automatically downloaded on to computer to make sure that you get latest exam prep materials during those 90 days.
Can I renew my product if when it's expired?
Yes, when the 90 days of your product validity are over, you have the option of renewing your expired products with a 30% discount. This can be done in your Member's Area.
Please note that you will not be able to use the product after it has expired if you don't renew it.
How often are the questions updated?
We always try to provide the latest pool of questions, Updates in the questions depend on the changes in actual pool of questions by different vendors. As soon as we know about the change in the exam question pool we try our best to update the products as fast as possible.
How many computers I can download Test-King software on?
You can download the Test-King products on the maximum number of 2 (two) computers or devices. If you need to use the software on more than two machines, you can purchase this option separately. Please email support@test-king.com if you need to use more than 5 (five) computers.
What is a PDF Version?
PDF Version is a pdf document of Questions & Answers product. The document file has standart .pdf format, which can be easily read by any pdf reader application like Adobe Acrobat Reader, Foxit Reader, OpenOffice, Google Docs and many others.
Can I purchase PDF Version without the Testing Engine?
PDF Version cannot be purchased separately. It is only available as an add-on to main Question & Answer Testing Engine product.
What operating systems are supported by your Testing Engine software?
Our testing engine is supported by Windows. Andriod and IOS software is currently under development.
Top CIW Exams
1D0-520: The Foundation of Modern Web Design and the Significance of CIW Certification
In the fast-moving world of technology, the craft of web design has emerged as one of the most vital disciplines shaping the modern digital landscape. From the earliest days of the internet, when websites were rudimentary collections of static text and limited images, to today’s immersive, dynamic, and highly responsive digital platforms, the journey of web design reflects the evolution of human interaction with technology itself. The importance of this progression lies not merely in aesthetics but in how users engage, communicate, and make decisions in a digital-first society. Every website that captures attention, builds trust, or drives action is the result of carefully crafted design principles interwoven with technical mastery. In this sphere, the CIW Web Design Professional Exam, coded as 1D0-520, has cemented itself as a recognized benchmark for validating expertise in designing functional, visually pleasing, and user-centered websites.
Understanding the Roots and Relevance of Digital Craftsmanship
The CIW Web Design Professional certification is not a mere embellishment on a resume; it is an emblem of mastery, credibility, and readiness to meet industry demands. The Certified Internet Web Professional program is internationally respected for its ability to measure a professional’s competence in areas that matter most for success in the ever-shifting world of digital design. In contrast to certificates that remain narrowly focused or stagnant, CIW has gained prestige for ensuring its content evolves alongside industry standards. This means that individuals who hold this certification are not only equipped with foundational knowledge but also prepared to adapt to new design paradigms and technological advances. For organizations searching for skilled professionals, this certification represents a seal of assurance that the candidate understands both the artistry and engineering involved in creating high-functioning websites.
The rise of certifications like CIW stems from the need for standardized recognition of skills in an industry where self-taught designers, academic programs, and on-the-job learners coexist. Employers face the challenge of discerning which candidates can actually transform theory into practice. The CIW Web Design Professional Exam addresses this ambiguity by focusing on real-world application of knowledge. Unlike traditional academic examinations that may reward rote memorization, this assessment emphasizes comprehension, adaptability, and the demonstration of skill in practical contexts. This pragmatic approach ensures that certification holders are not only conversant with terminologies but are also capable of delivering solutions in a professional environment.
When delving into the historical underpinnings of web design, it is clear that what began as a largely technical endeavor has steadily matured into a multidisciplinary practice. In its infancy, creating a website required only basic knowledge of HTML, which determined the structure of a page. Over time, the incorporation of cascading style sheets allowed designers to separate structure from style, paving the way for far more elaborate and nuanced digital creations. The addition of multimedia elements such as images, animations, and eventually interactive graphics signaled a transformative period in which websites were no longer static repositories of information but vibrant spaces for engagement. This trajectory highlights why modern web design professionals require both technical literacy and creative ingenuity, a balance that the CIW Web Design Professional Exam aims to instill.
The exam codified as 1D0-520 embodies the philosophy that proficiency in web design is multifaceted. It tests knowledge across several domains essential to crafting websites that not only look appealing but also perform effectively under diverse circumstances. This includes understanding the principles of responsive design, where websites must adapt seamlessly across devices with different screen sizes. As mobile devices and tablets increasingly dominate online interactions, the ability to design platforms that remain fluid and accessible has transitioned from optional to indispensable. Equally important is expertise in user interface and user experience design, where the goal is not merely to make a site visually attractive but to ensure that it fosters intuitive navigation, reduces friction, and enhances satisfaction for its visitors. In this sense, the certification reflects the industry’s shift toward valuing the overall experience as much as the underlying architecture.
Another essential area encompassed within the exam is proficiency in HTML5 and CSS3. While the untrained eye might consider these technologies elementary, their complexity and versatility remain the foundation upon which the majority of modern websites are constructed. HTML5 has expanded the possibilities of structuring and presenting content, while CSS3 has provided designers with the capability to achieve sophisticated styling, animations, and responsive layouts without depending heavily on external plugins. By requiring mastery of these tools, the exam ensures that candidates can build from the ground up, understanding not just pre-designed templates but the underlying frameworks that empower them. This grounding in code, when coupled with design intuition, equips professionals to handle projects ranging from minimalistic corporate portals to multimedia-heavy entertainment sites.
The importance of graphics and multimedia integration in web design cannot be understated. A well-placed image, thoughtfully chosen typography, or seamlessly embedded video can elevate a website from ordinary to memorable. However, the challenge lies in maintaining equilibrium between aesthetics and performance. An excessive use of graphics can slow down load times, frustrate users, and even impact search engine visibility. Conversely, a sparse design that neglects visual storytelling can feel sterile and uninspiring. The CIW Web Design Professional Exam acknowledges this delicate balance by ensuring that candidates understand not only how to incorporate multimedia elements but also how to optimize them for efficiency. Such considerations extend to accessibility, where designers must account for individuals with diverse abilities by ensuring that their websites remain navigable through screen readers, alt text, and adaptable color contrasts.
Beyond the technical specifics, one of the most striking features of the certification is its emphasis on practical application. In an industry where theory often diverges from practice, the CIW approach ensures that certified professionals can transition seamlessly into workplace demands. Candidates are challenged to simulate real-world tasks, from coding pages to crafting user-centric interfaces, demonstrating their ability to solve tangible problems. This method mirrors the daily responsibilities of professionals who may be asked to design for clients with unique brand requirements, troubleshoot performance issues, or innovate solutions within constrained budgets and timelines. For individuals who earn the certification, this experience fosters confidence, adaptability, and resilience—traits highly sought after by employers navigating an unpredictable digital economy.
The global recognition of the CIW Web Design Professional Exam also contributes to its significance. In an interconnected economy where businesses often operate across borders, professionals with credentials that are universally respected gain an advantage. A web designer certified in one region can seamlessly market their skills in another, broadening career prospects and enabling mobility. The credential carries weight not only with employers but also with clients who seek assurance that their digital investments are entrusted to competent hands. This universality distinguishes CIW from other programs that may hold regional relevance but lack international resonance.
In addition to validating skills, the certification also serves as a catalyst for personal growth and continuous learning. The field of web design is not static; it evolves constantly as new technologies emerge and user expectations shift. Artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and voice interfaces are no longer futuristic concepts but increasingly integral elements of modern design. Designers must remain agile, continuously expanding their skill sets to remain competitive. The CIW framework prepares professionals for this dynamism by encouraging a mindset of adaptability and forward thinking. Rather than training candidates for a single moment, it instills in them the capacity to anticipate, absorb, and implement new trends as they arise.
For many aspirants, the decision to pursue certification stems from a blend of professional ambition and personal passion. Some may be drawn by the prospect of career advancement, envisioning roles such as front-end developer, user interface architect, or creative strategist. Others may seek the intrinsic satisfaction of mastering a craft that combines artistry with problem-solving. Regardless of motivation, the certification provides a structured pathway toward achieving these goals. It validates effort, enhances credibility, and fosters a sense of accomplishment that can propel individuals toward greater milestones. In industries characterized by intense competition and rapid change, such validation can make the difference between stagnation and progression.
The CIW Web Design Professional Exam represents more than just a test; it symbolizes the convergence of technical precision, creative ingenuity, and professional recognition. Its presence in the digital landscape underscores the growing importance of web design as a discipline that not only supports but shapes the way the world communicates, learns, and conducts commerce. By demanding both theoretical knowledge and practical skill, it produces professionals capable of creating digital environments that are not only aesthetically compelling but also functional, accessible, and forward-looking. As web design continues to evolve alongside advances in technology, this certification ensures that those who pursue it are well-positioned to remain at the forefront of innovation and impact in the digital domain.
Mastering the Pillars of Web Design
The craft of web design is a delicate interplay between technical precision and aesthetic sensibility, demanding an understanding that spans multiple domains. The 1D0-520 exam is meticulously structured to evaluate this breadth of knowledge, ensuring that individuals are not merely conversant with superficial concepts but possess a comprehensive grasp of the foundational elements that underpin modern digital experiences. From the principles of layout to the nuances of coding and responsive adaptation, the exam encompasses every facet essential for the creation of functional, visually harmonious websites.
At the outset, grasping the fundamentals of web design is crucial. This domain introduces candidates to the core philosophies that govern layout, hierarchy, and usability. Design principles such as balance, contrast, alignment, and proximity are not arbitrary rules but critical tools that shape user perception and interaction. Candidates learn how to guide a visitor’s attention, create intuitive pathways through information, and establish a visual rhythm that fosters engagement. The exam emphasizes that a web designer’s role extends beyond ornamentation; it is about orchestrating an experience that is coherent, accessible, and memorable. This holistic approach ensures that the foundation of any digital project is both functional and artistically informed.
Integral to web design is proficiency in HTML5 and CSS3, technologies that constitute the scaffolding of digital content. HTML5 provides the structural framework, allowing designers to define elements such as headings, paragraphs, forms, and multimedia containers with semantic clarity. Understanding semantic tags, proper nesting, and the hierarchy of elements ensures that content is not only presented accurately but is accessible to diverse audiences, including those relying on assistive technologies. CSS3, on the other hand, imbues the structure with visual life. Mastery of selectors, properties, and cascading rules enables designers to apply styles with precision, control layout responsiveness, and introduce animations that enhance user experience without detracting from performance. The exam assesses candidates’ ability to translate design concepts into code, demonstrating fluency in creating pages that are both aesthetically compelling and technically sound.
Responsive design constitutes another critical domain, reflecting the necessity of adaptability in an era dominated by varied devices and screen resolutions. Websites must render fluidly across desktops, tablets, smartphones, and emerging wearable technologies. The 1D0-520 exam evaluates strategies for achieving this adaptability, including fluid grids, flexible images, and media queries that adjust layout based on device characteristics. Candidates must understand that responsive design is not merely a convenience; it is a mandate for accessibility, engagement, and search engine performance. By mastering this domain, designers ensure that the integrity of their creations persists regardless of the environment in which they are viewed, thereby maintaining usability, brand consistency, and user satisfaction.
Equally paramount is the domain of user interface and user experience design, which focuses on the interaction between humans and digital systems. Candidates explore methodologies for crafting interfaces that are intuitive, aesthetically harmonious, and conducive to efficient navigation. Understanding cognitive load, visual hierarchy, and affordances allows designers to anticipate user behavior and reduce friction in interactions. The exam encourages candidates to consider the holistic journey of a visitor, integrating visual cues, interactive elements, and feedback mechanisms to create environments that are engaging yet unobtrusive. This domain underscores the principle that effective web design is not merely about decoration; it is about shaping experiences that are seamless, satisfying, and aligned with user expectations.
In addition to interface design, the integration of graphics and multimedia constitutes a vital component of professional web creation. The 1D0-520 exam assesses candidates’ ability to incorporate visual elements that enhance comprehension and appeal without compromising functionality. From optimizing images for performance to embedding audio, video, and vector graphics, designers must achieve a delicate equilibrium between richness and efficiency. Knowledge of file formats, compression techniques, and visual storytelling strategies enables candidates to create immersive experiences while mitigating latency, bandwidth constraints, and accessibility challenges. Mastery of multimedia integration also demands an understanding of aesthetic principles, ensuring that images, typography, and interactive elements coalesce into a coherent visual narrative.
Typography, while sometimes overlooked, is an essential element within the web design domain. Candidates are evaluated on their ability to select typefaces, establish hierarchy, and manage spacing to enhance readability and convey appropriate tone. The interplay of font style, size, weight, and line spacing can significantly influence user perception, guiding emotions and comprehension. The exam highlights that typography is not a superficial choice but a functional instrument that can improve usability, reinforce branding, and enrich the overall digital experience.
Another key aspect involves understanding accessibility and compliance standards. Web design is inherently a responsibility toward diverse audiences, including individuals with disabilities. Candidates are expected to demonstrate knowledge of accessibility guidelines, such as ensuring proper color contrast, providing alternative text for images, and enabling keyboard navigation. These considerations are not ancillary but essential for inclusivity, legal compliance, and ethical practice. Mastery of accessibility principles ensures that websites serve the broadest possible audience, reflecting the societal and professional obligations of a competent designer.
The interplay between functionality and aesthetics is further tested through practical application scenarios embedded within the exam. Candidates are presented with challenges that require the simultaneous application of multiple domains: coding a responsive page that adheres to design principles, integrating multimedia elements that enhance engagement, and ensuring accessibility compliance. These scenarios mirror the realities of professional web design, where technical expertise, creative judgment, and problem-solving abilities converge. By successfully navigating these exercises, candidates exhibit the capacity to transform conceptual knowledge into tangible digital assets.
Color theory is another nuanced domain explored within the exam. Understanding the psychological impact of color, the balance between complementary and contrasting hues, and the use of color to guide attention is vital. Candidates learn to employ palettes that align with brand identity, enhance readability, and evoke the desired emotional response. The subtlety of color choice underscores the designer’s role as a communicator, not merely a technician, highlighting the intersection of art and science that defines web design.
Furthermore, the domain of usability testing and iterative improvement is emphasized. Candidates are introduced to methodologies for evaluating design effectiveness through user feedback, analytics, and behavioral observation. The iterative process ensures that designs evolve in response to actual user interactions, optimizing performance, navigation, and satisfaction. Understanding how to interpret data, identify pain points, and implement refinements distinguishes competent designers from those who rely solely on intuition, reinforcing the exam’s emphasis on evidence-based practice.
An often-overlooked area is cross-browser compatibility, which addresses the challenges posed by disparate rendering engines and platform idiosyncrasies. Candidates must demonstrate awareness of how different browsers interpret HTML, CSS, and scripts, ensuring that websites maintain consistent functionality and appearance across environments. This technical knowledge complements creative skills, illustrating that mastery of web design encompasses both expressive and operational proficiency.
Search engine optimization, while not purely a design consideration, is entwined with the structure and accessibility of content. The exam evaluates candidates’ understanding of how semantic markup, proper headings, metadata, and responsive design contribute to discoverability. Designers who integrate these principles create websites that are not only user-friendly but also visible to the broader digital ecosystem, highlighting the interconnectedness of design, content, and technical strategy.
Throughout the examination, candidates encounter concepts that require them to synthesize knowledge across domains. Each task is an opportunity to demonstrate that they can balance aesthetic judgment with functional requirements, technical execution with user-centric principles. By cultivating versatility, analytical thinking, and creative problem-solving, the exam ensures that those who succeed are prepared for the multifaceted demands of the professional web design environment.
The 1D0-520 assessment also subtly instills the importance of continuous learning. With rapid technological evolution, a proficient designer must adapt to emerging frameworks, innovative coding techniques, and evolving user expectations. The breadth of the exam reinforces that knowledge is interconnected; understanding coding principles, design aesthetics, multimedia integration, and accessibility is insufficient if considered in isolation. Excellence in web design arises from harmonizing these domains into a coherent, functional, and engaging digital experience.
Candidates are encouraged to develop both meticulous attention to detail and a macro-level perspective. The precision required in coding, styling, and element placement complements the broader vision of how a website functions as a cohesive ecosystem. The integration of each knowledge domain forms the substratum upon which effective, resilient, and elegant web experiences are constructed.
By thoroughly examining these core domains, the 1D0-520 exam distinguishes between superficial familiarity and deep comprehension. It nurtures professionals who can approach a design challenge with methodical reasoning, technical dexterity, and aesthetic sensibility. Those who emerge successfully from this rigorous assessment possess not only a certification but also the capacity to contribute meaningfully to digital projects, shaping experiences that resonate with users while adhering to industry best practices.
The multifaceted domains assessed by the exam underscore the central truth of modern web design: it is an endeavor that requires simultaneous fluency in art, technology, and human psychology. Designers must navigate the intricate choreography of layout, code, multimedia, interaction, and accessibility while anticipating the behaviors and expectations of users across contexts. The CIW Web Design Professional Exam ensures that candidates are adept in each of these domains, establishing a comprehensive framework of knowledge that serves as a foundation for professional excellence and ongoing innovation.
Translating Knowledge into Functional Web Design
The true measure of a web designer’s proficiency extends far beyond theoretical comprehension. In the dynamic environment of digital creation, practical application is paramount. The CIW Web Design Professional Exam (1D0-520) places significant emphasis on the candidate’s ability to operationalize principles, turning abstract concepts into tangible, functional, and aesthetically compelling websites. This approach ensures that professionals who earn the certification are not merely familiar with terminology or design theory, but are fully capable of navigating real-world design challenges with skill, creativity, and technical precision.
Understanding the practical dimension begins with the recognition that web design is an applied art. While knowledge of HTML5, CSS3, and responsive frameworks provides the foundation, the true challenge lies in orchestrating these elements within a live environment. Candidates are evaluated on their ability to construct pages that are structurally sound, visually balanced, and adaptable across devices. The examination tasks require them to integrate content, styling, navigation, and interactive features cohesively, reflecting the realities of professional projects where multiple constraints converge simultaneously. This methodology bridges the gap between learning and doing, cultivating a mindset that prioritizes both function and user experience.
One of the central objectives of practical evaluation is to assess problem-solving acumen. Designers frequently encounter unexpected constraints, such as conflicting client requirements, limitations of legacy systems, or performance issues arising from high-resolution multimedia. The 1D0-520 exam replicates these conditions, prompting candidates to apply analytical reasoning, iterative testing, and adaptive strategies. This process nurtures resilience, resourcefulness, and the capacity to devise solutions that are both innovative and effective. By confronting realistic scenarios, candidates develop confidence in their ability to translate design concepts into operational, user-friendly websites.
The integration of responsive design principles is a recurrent theme within practical tasks. With the proliferation of diverse screen sizes, from large monitors to handheld devices, designers must ensure that layouts remain coherent and accessible. Practical exercises demand mastery of flexible grids, fluid images, and media queries, compelling candidates to reconcile aesthetic intentions with functional adaptability. Through repeated engagement with these challenges, professionals internalize the strategies required to maintain consistency, usability, and performance across multiple environments, thereby fostering versatility and technical dexterity.
User interface and user experience considerations are equally critical in applied evaluation. Candidates must demonstrate an understanding of how navigational elements, interactive components, and visual hierarchy influence user behavior. Practical tasks emphasize creating interfaces that minimize cognitive load, provide intuitive feedback, and encourage exploration without confusion. By simulating scenarios such as e-commerce portals, informational sites, or multimedia-rich platforms, the exam tests the candidate’s ability to craft seamless interactions that elevate engagement while satisfying both functional and aesthetic objectives.
Another domain that receives considerable attention is multimedia integration. The inclusion of images, audio, video, and interactive graphics introduces both creative opportunities and technical challenges. Practical evaluation requires candidates to optimize media elements for performance while maintaining clarity, visual appeal, and responsiveness. Knowledge of compression techniques, file formats, and load optimization becomes essential, reinforcing the principle that compelling design must coexist with efficiency. Candidates learn to balance richness of content with speed, usability, and accessibility, reflecting the multifaceted nature of contemporary web projects.
Typography, a subtle yet powerful component of web aesthetics, is also woven into practical exercises. Candidates are tasked with selecting fonts that enhance readability, establish hierarchy, and align with the intended tone and brand identity. Attention to spacing, line height, and alignment is critical, as minor deviations can significantly affect legibility and user perception. The exam ensures that designers appreciate typography not as a decorative afterthought but as an integral element of functional, user-centered design.
Accessibility considerations further underscore the practical emphasis of the exam. Candidates must ensure that websites are navigable by individuals with varying abilities, incorporating elements such as keyboard-accessible controls, proper labeling, alt text for images, and color contrast optimization. By embedding these principles into applied exercises, the exam reinforces ethical responsibility, inclusivity, and adherence to established web standards, preparing candidates to produce designs that are equitable and universally navigable.
The practical component also includes scenarios requiring iterative refinement. Candidates are encouraged to review their work critically, identify areas for improvement, and implement enhancements based on user interaction or simulated feedback. This process mirrors professional practice, where ongoing evaluation and iteration are essential to achieving optimal usability and engagement. The ability to assess one’s own work and adjust accordingly cultivates a mindset of continuous improvement, fostering both technical competence and creative insight.
Cross-browser compatibility presents another layer of complexity in applied evaluation. Candidates must anticipate discrepancies in rendering across different platforms and browsers, ensuring that functionality, appearance, and interactivity remain consistent. Tasks may involve troubleshooting inconsistencies, adjusting styles, and implementing fallbacks for unsupported features. This technical rigor emphasizes that practical expertise encompasses not only creation but also maintenance and problem resolution, reflecting the comprehensive skill set demanded by modern web development.
Performance optimization is a recurring theme in applied tasks. Candidates must demonstrate awareness of strategies to minimize load times, manage bandwidth, and reduce server requests, all while maintaining visual and functional integrity. Practical exercises integrate these considerations seamlessly, compelling candidates to adopt a holistic perspective that balances creative ambition with operational efficiency. This aspect of evaluation ensures that certified professionals can deliver websites that are both beautiful and performant, meeting the expectations of users and stakeholders alike.
The exam also integrates tasks that test the ability to synthesize multiple knowledge domains simultaneously. Candidates might be asked to construct a page that combines responsive design, multimedia elements, typography, and accessibility considerations, requiring a coordinated application of diverse skills. Success in these exercises indicates that a designer can navigate complex project requirements, prioritize conflicting demands, and execute a coherent, polished solution. This multidimensional assessment cultivates adaptability, critical thinking, and the capacity to orchestrate disparate elements into a unified digital experience.
Project planning and workflow management are subtly incorporated into practical evaluation. Candidates must demonstrate an understanding of how to structure design processes, sequence tasks, and manage resources efficiently. This aspect mirrors real-world scenarios where deadlines, client expectations, and collaborative dynamics influence the outcome of web projects. By emphasizing planning alongside execution, the exam reinforces that practical competence is not confined to technical skill alone but includes strategic organization and foresight.
The integration of analytical skills is evident in tasks that require evaluation of usability, navigation efficiency, and visual coherence. Candidates are expected to interpret feedback, identify pain points, and implement modifications that enhance overall experience. This analytical rigor fosters a disciplined approach to design, ensuring that solutions are not only attractive but also functional, user-centric, and sustainable over time. The ability to translate observation into actionable improvement is a hallmark of a proficient web designer.
In addition, the practical focus encourages the development of creative problem-solving capabilities. Candidates often face scenarios where constraints challenge conventional solutions, requiring innovative approaches that respect technical limitations while achieving aesthetic and functional goals. These exercises nurture ingenuity, adaptability, and resourcefulness, equipping designers to address the unpredictable complexities encountered in professional environments.
The interplay of aesthetics and functionality is consistently emphasized throughout practical evaluation. Candidates learn that visual appeal cannot exist in isolation; it must harmonize with usability, performance, and accessibility. This principle guides the creation of websites that are not only engaging but also intuitive and efficient. The exam’s applied approach ensures that candidates internalize this balance, cultivating a design philosophy that values the user’s experience as much as technical sophistication.
Practical application also extends to problem anticipation and proactive planning. Candidates are encouraged to foresee potential challenges, such as compatibility issues, performance bottlenecks, or accessibility concerns, and implement preventive measures. This forward-thinking approach mirrors professional expectations, where preemptive solutions mitigate risk and enhance overall quality. The ability to anticipate and address issues before they arise is a critical differentiator for skilled designers in competitive environments.
Collaboration and communication, while not directly tested, are implied through scenarios that simulate team-based or client-driven projects. Candidates must create deliverables that could be interpreted and implemented by others, emphasizing clarity, documentation, and coherence. This indirect assessment ensures that practical skills are complemented by professional sensibilities, preparing candidates to operate effectively within multidisciplinary teams.
The cumulative effect of these practical exercises is the cultivation of a holistic, adaptable, and resilient professional. By requiring candidates to apply knowledge across multiple domains, the exam ensures that certification holders are not only technically proficient but also capable of approaching challenges with strategic insight and creative agility. Real-world readiness, therefore, is achieved not merely through familiarity with tools and concepts, but through demonstrated competence in executing projects that satisfy functional, aesthetic, and experiential criteria.
Through this intensive emphasis on practical application, the 1D0-520 exam shapes individuals into designers who can thrive in professional environments. Candidates emerge with the confidence, versatility, and critical thinking skills necessary to navigate complex web projects, adapt to evolving technologies, and meet the nuanced expectations of users and stakeholders. The assessment fosters a blend of technical dexterity, artistic judgment, and applied reasoning, ensuring that certified professionals are fully prepared to contribute meaningfully to the digital landscape.
Building Knowledge, Skills, and Confidence
Achieving proficiency in web design requires more than a conceptual understanding; it necessitates structured preparation, exposure to practical scenarios, and engagement with a community of like-minded professionals. The CIW Web Design Professional Exam (1D0-520) is designed to measure comprehensive competence, and candidates are encouraged to approach preparation as a multifaceted endeavor that encompasses theoretical study, hands-on practice, and collaborative learning. Success is built on a foundation of disciplined study habits, strategic use of resources, and the cultivation of both technical and creative acuity.
Central to preparation is the mastery of the core domains assessed by the exam. Candidates must develop fluency in HTML5 and CSS3, understanding how these technologies interact to create structurally sound and visually cohesive web pages. Repeated practice in coding, styling, and troubleshooting reinforces both muscle memory and conceptual clarity, ensuring that theoretical principles translate into accurate and efficient execution. For example, constructing layouts that respond fluidly to various screen dimensions requires repeated experimentation with fluid grids, media queries, and flexible images. This experiential learning solidifies the ability to design websites that are both visually appealing and technically resilient.
Responsive design, an essential competency, demands attention to detail and iterative practice. Candidates engage in exercises that require adjusting layouts dynamically, optimizing multimedia for multiple devices, and evaluating usability across different platforms. By simulating real-world conditions, learners cultivate an instinct for adaptive design, gaining insights into how subtle changes in code or styling affect the overall user experience. Preparation for this domain involves not only understanding technical frameworks but also internalizing principles of ergonomics, visual hierarchy, and interaction flow.
User interface and user experience design occupy a central role in preparation strategies. Candidates are encouraged to analyze existing websites critically, identifying strengths and weaknesses in navigation, layout, and engagement. Exercises often include designing wireframes, prototypes, and mockups, which serve as intermediaries between conceptual ideas and final implementation. By iteratively refining these prototypes, candidates enhance their ability to anticipate user needs, streamline interaction paths, and create intuitive digital environments. This practice also reinforces the understanding that usability is inseparable from aesthetic coherence; effective interfaces must harmonize functionality with visual communication.
Multimedia integration, encompassing images, audio, video, and animations, is another domain where hands-on preparation proves invaluable. Candidates experiment with file optimization, compression techniques, and embedding methods to maintain performance without sacrificing clarity or impact. Exposure to varied multimedia formats and delivery mechanisms cultivates a nuanced understanding of how each element influences load times, responsiveness, and user engagement. Through deliberate practice, designers learn to balance richness of content with efficiency, a skill essential for professional-grade websites.
Typography, a subtle yet pivotal aspect of preparation, involves mastering the selection of typefaces, establishing hierarchy, and ensuring legibility across devices. Exercises in font pairing, scaling, and spacing familiarize candidates with how textual elements influence readability, user perception, and visual rhythm. This meticulous attention to detail ensures that candidates appreciate the functional and emotional impact of typography, recognizing it as a powerful tool for guiding attention and reinforcing brand identity.
Accessibility and compliance considerations are integrated into preparation routines to ensure that candidates understand the broader social and ethical responsibilities of web design. Practicing the implementation of accessible features, such as alt text, proper labeling, keyboard navigation, and color contrast, fosters awareness of diverse user needs. Candidates learn to anticipate potential barriers and design inclusive solutions, aligning technical skills with principles of equity and ethical responsibility. This preparation ensures that certified professionals can deliver websites that are universally navigable, legally compliant, and socially responsible.
Structured study guides and practice assessments provided by CIW constitute the backbone of formal preparation. These materials offer comprehensive coverage of the exam’s domains, presenting information in a logical progression that scaffolds learning. Practice assessments allow candidates to gauge their comprehension, identify areas of weakness, and refine strategies before attempting the actual exam. By simulating test conditions, learners cultivate time management, attention to detail, and the ability to apply knowledge under pressure, reinforcing both confidence and competence.
Interactive labs and exercises further enhance readiness by providing controlled environments in which candidates can experiment with coding, layout, and design elements. These hands-on experiences bridge the gap between theory and practice, enabling learners to witness the immediate consequences of their choices and adjustments. Repeated engagement with lab exercises cultivates problem-solving skills, attention to nuance, and the ability to troubleshoot errors efficiently. This experiential preparation mirrors the iterative nature of professional web design, where refinement and adjustment are continuous processes.
Collaborative engagement with peers represents a crucial, though often underappreciated, component of preparation. Forums, discussion groups, and online communities facilitate the exchange of ideas, solutions, and insights. Candidates benefit from exposure to diverse perspectives, learning alternative approaches to common challenges and gaining feedback on their work. Interaction with a professional community fosters both accountability and motivation, while also providing access to collective knowledge that enriches individual learning. The social dimension of preparation reinforces the idea that web design, while technical, thrives on shared experiences, critique, and mentorship.
Time management and disciplined study routines are vital for comprehensive preparation. Candidates are encouraged to establish consistent schedules, allocating periods for reading, coding practice, multimedia experimentation, and review of accessibility principles. Integrating micro-goals within broader study objectives allows for measurable progress and sustained engagement. Reflective practices, such as reviewing completed exercises and analyzing mistakes, enhance retention and deepen understanding. By cultivating a structured approach, candidates maximize the effectiveness of their preparation while developing professional habits that extend beyond the exam.
Analytical skills are nurtured through exercises that require evaluation and iterative improvement. Candidates examine the usability of their designs, the efficiency of code, and the coherence of visual composition. This process emphasizes that preparation is not solely about producing outputs but about critically assessing their quality and optimizing outcomes. By learning to measure success against established criteria, candidates internalize professional standards and develop the capacity to elevate their work through informed adjustments.
Simulated real-world scenarios are integral to preparation, as they replicate the types of challenges designers encounter in professional contexts. Candidates may be asked to design a site for a hypothetical client, incorporating branding elements, multimedia content, responsive layouts, and accessibility features. These exercises encourage comprehensive application of knowledge, fostering integration across domains while demanding attention to deadlines, usability, and aesthetic cohesion. The experience builds both competence and confidence, preparing candidates to navigate complex projects with strategic insight.
Exposure to emerging trends and technologies further enriches preparation. Candidates explore the implications of artificial intelligence, evolving user interface paradigms, and novel interaction modalities such as voice or gesture control. Familiarity with these trends equips learners with a forward-looking perspective, ensuring that they are not only prepared for current industry standards but are also capable of adapting to the evolving demands of the digital landscape. This integration of contemporary insights into preparation reinforces the notion that proficiency in web design requires both mastery of fundamentals and anticipation of future developments.
Effective preparation also involves cultivating problem-solving agility. Candidates practice identifying potential conflicts between design intentions, technical constraints, and user requirements. Through iterative experimentation, they develop strategies to reconcile these tensions, creating functional and visually coherent solutions. This process mirrors professional practice, where designers must navigate competing priorities and devise innovative solutions under realistic constraints. The capacity to adapt and respond dynamically to unforeseen challenges is a distinguishing feature of highly skilled web professionals.
Documentation and reflective practice are subtly embedded in preparation strategies. Candidates are encouraged to record their design decisions, coding strategies, and troubleshooting approaches. This reflective practice allows learners to consolidate knowledge, track progress, and identify patterns in both successes and errors. By reviewing this documentation, candidates can refine their methods, enhance efficiency, and cultivate a deeper understanding of the interdependencies among design, code, and user experience.
Ultimately, the preparation pathway for the CIW Web Design Professional Exam is a convergence of structured study, practical engagement, iterative improvement, and collaborative learning. Candidates immerse themselves in both foundational and advanced domains, continually applying knowledge in simulated real-world contexts. By leveraging official resources, peer communities, and reflective practices, learners develop not only the technical skills necessary for exam success but also the professional judgment, adaptability, and creativity essential for sustained achievement in the field of web design.
Exploring Opportunities, Innovation, and the Path Ahead
The field of web design is a dynamic and ever-evolving domain, shaped by technological advances, shifting user expectations, and the continuous integration of new tools and methodologies. Professionals who achieve the CIW Web Design Professional Exam (1D0-520) certification find themselves uniquely positioned to navigate this landscape, equipped with a blend of technical proficiency, creative acumen, and applied problem-solving skills. The certification serves as a bridge between foundational knowledge and professional expertise, opening avenues for diverse career opportunities, fostering adaptability to emerging trends, and providing a platform for sustained growth and innovation in digital design.
Career prospects for certified individuals are expansive and multifaceted. Web designers with this credential are sought after for roles that range from front-end development to user interface and user experience design, with responsibilities encompassing the creation, maintenance, and optimization of digital environments. The certification signals to employers that the individual possesses a robust understanding of HTML5 and CSS3, is adept at crafting responsive layouts, and can integrate multimedia effectively while ensuring accessibility. This recognition enhances employability across a variety of organizations, from small creative studios to multinational corporations, and extends to freelance opportunities where demonstrated expertise attracts clients seeking high-quality, professional web solutions.
In addition to traditional roles, the credential opens doors to specialized positions where design intersects with emerging technologies. Opportunities exist in areas such as interactive design, motion graphics, and immersive experiences that leverage augmented reality, virtual reality, and AI-driven interfaces. As businesses increasingly seek innovative ways to engage users, designers who can blend technical proficiency with creative experimentation are positioned to lead initiatives that redefine digital interaction. The certification provides the conceptual and practical foundation needed to thrive in such environments, cultivating professionals capable of producing experiences that are both visually compelling and functionally sophisticated.
The evolution of web design is inextricably linked to technological trends that continue to reshape the digital landscape. Artificial intelligence, for example, is increasingly influencing design processes, enabling automation in layout adjustments, content personalization, and even generating design suggestions based on user behavior. Designers must remain conversant with these advancements, understanding how to incorporate AI tools without compromising the integrity of their creative vision or user experience. The CIW certification encourages an awareness of such innovations, preparing professionals to engage with them thoughtfully and strategically.
Accessibility and inclusivity remain central to the evolution of web design, reflecting both ethical imperatives and regulatory requirements. As digital platforms reach increasingly diverse audiences, designers must ensure that their creations accommodate varying abilities, devices, and contexts. Knowledge of accessibility standards, color contrast optimization, semantic structure, and assistive technology integration becomes critical. Certified professionals are equipped to balance creative ambition with inclusivity, producing websites that are universally navigable while maintaining aesthetic appeal. This capability enhances the reputation of designers, broadens audience engagement, and ensures alignment with legal and ethical standards.
User experience continues to be a driving force in shaping career trajectories. Designers who can anticipate user needs, streamline interactions, and create intuitive interfaces are in high demand. Emerging methodologies such as human-centered design, design thinking, and iterative prototyping have shifted the emphasis from static aesthetics to experiential quality. Professionals with the CIW certification possess the foundational understanding and practical skills necessary to employ these methodologies effectively, creating interfaces that are both engaging and efficient. The ability to analyze user behavior, interpret analytics, and iterate design solutions establishes designers as strategic contributors within multidisciplinary teams.
The integration of multimedia and interactivity has also expanded career horizons. Websites now often incorporate video, animation, audio, and interactive visualizations to enhance engagement. Designers who can optimize these elements for performance and accessibility while maintaining visual harmony are highly valued. Mastery of such skills ensures that certified professionals can handle complex projects where technical execution, creative design, and user experience intersect seamlessly. This versatility enhances career mobility, enabling designers to work across diverse industries, from e-commerce and entertainment to education and healthcare.
Entrepreneurial opportunities emerge as another significant facet of professional growth. Certification provides credibility that facilitates the establishment of independent web design ventures or consulting services. Freelance designers can leverage their recognized expertise to attract clients seeking high-quality digital solutions, negotiate competitive rates, and cultivate a personal brand that reflects professionalism and skill. This entrepreneurial avenue underscores the flexibility and autonomy available to certified individuals, complementing traditional employment opportunities.
Continuous professional development is an inherent expectation in the web design domain. Technologies, frameworks, and user expectations evolve rapidly, necessitating a mindset of lifelong learning. The CIW certification instills habits of ongoing engagement with emerging tools, trends, and best practices, ensuring that professionals remain relevant and innovative. Familiarity with new coding frameworks, design software, AI-assisted tools, and user experience methodologies positions certified designers to anticipate industry shifts and adapt proactively. This adaptability enhances career longevity and reinforces a reputation for competence and forward-thinking within professional networks.
The convergence of design, technology, and analytics represents a further avenue for career advancement. Certified professionals can specialize in optimizing websites for search engine visibility, analyzing user engagement metrics, and implementing data-driven improvements. This interdisciplinary capability enhances the strategic value of designers within organizations, enabling them to influence decision-making processes and contribute to broader digital initiatives. Mastery in these areas reflects the expanding role of web designers as not only creators but also analysts and strategists.
Networking and engagement within professional communities bolster career potential. Interaction with peers, mentors, and industry leaders facilitates knowledge exchange, exposure to innovative practices, and opportunities for collaboration. Participation in conferences, workshops, and forums reinforces both technical expertise and professional presence, enabling certified individuals to remain abreast of emerging trends, gain insights into industry standards, and cultivate connections that can lead to advancement or partnership opportunities.
In addition, the integration of design ethics and sustainability is becoming increasingly relevant. Professionals are expected to consider the environmental impact of digital practices, optimize resource usage, and promote sustainable user behaviors through design. Certified designers, equipped with both technical knowledge and ethical awareness, are well-positioned to advocate for and implement sustainable practices in their work. This perspective aligns with broader societal expectations and enhances the credibility and responsibility associated with professional web design.
The future of web design is poised for continued transformation. Innovations such as voice-assisted interfaces, augmented reality, immersive 3D environments, and AI-powered personalization are reshaping how users interact with digital content. Certified professionals must remain agile, integrating new capabilities while maintaining the foundational principles of usability, accessibility, and aesthetic integrity. The CIW certification ensures that designers possess a versatile toolkit that enables them to navigate these advancements with skill and discernment, positioning them as leaders in the evolving digital ecosystem.
Global demand for skilled web designers continues to expand. Organizations recognize the value of professionals who can synthesize design principles, coding proficiency, and user experience insights to produce compelling digital environments. The CIW certification provides a benchmark of quality, assuring employers and clients that certified individuals are capable of executing projects with both creativity and technical precision. This credibility enhances competitiveness in the job market and fosters opportunities for advancement, cross-functional collaboration, and international mobility.
By combining technical mastery, applied experience, and strategic awareness, certified professionals are uniquely equipped to seize the opportunities emerging within the digital landscape. Their skill set enables them to influence both the visual and functional aspects of web design, guiding user experiences while maintaining operational efficiency. In a profession defined by rapid change, these capabilities are invaluable, ensuring that certified designers remain not only relevant but also influential in shaping the future of digital interaction.
The cumulative impact of certification on career trajectories, adaptability to emerging trends, and preparedness for future innovation underscores its value. It empowers professionals to navigate complex challenges, leverage new technologies, and contribute meaningfully to both organizational goals and the broader field of web design. With a foundation built on knowledge, practical application, and strategic insight, certified individuals are positioned to lead, innovate, and elevate the standards of digital creation.
The CIW Web Design Professional Exam (1D0-520) serves as more than a credential; it is a gateway to a future defined by professional excellence, creative innovation, and continuous growth. By fostering mastery across technical, aesthetic, and user-centric domains, it prepares individuals to thrive in an environment where adaptability, foresight, and skill converge. Certified designers are not only equipped to meet current industry expectations but are also positioned to anticipate trends, integrate emerging technologies, and influence the evolution of digital experiences on a global scale.
Conclusion
In achieving the CIW Web Design Professional certification signifies the attainment of a comprehensive skill set, the capacity for applied innovation, and the readiness to engage with the rapidly transforming digital world. It enhances career opportunities, fosters professional growth, and instills the confidence necessary to navigate emerging trends and technological advancements. Certified professionals are poised to shape the future of web design, transforming user experiences, advancing industry standards, and contributing to a digital landscape that is inclusive, innovative, and enduring.