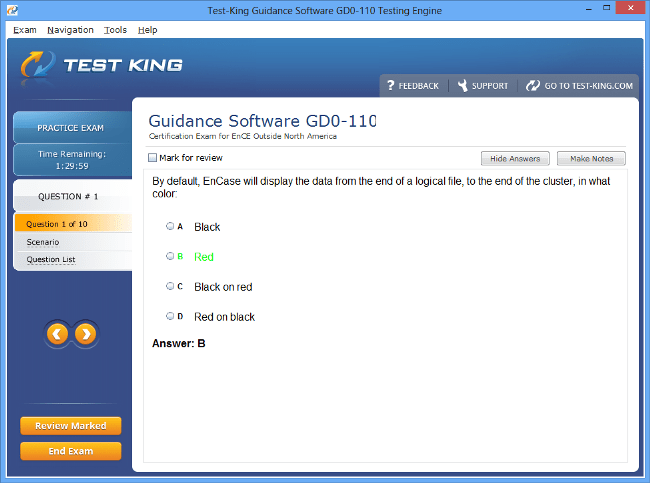
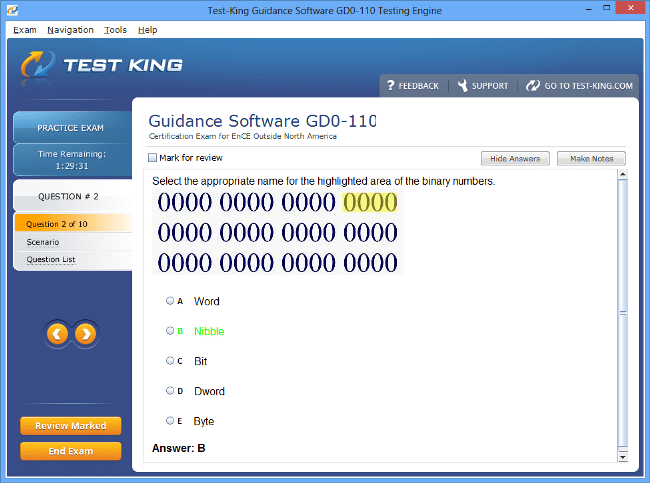
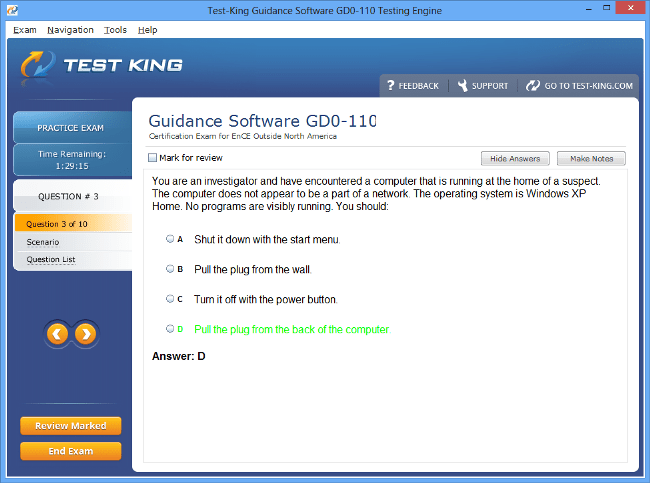
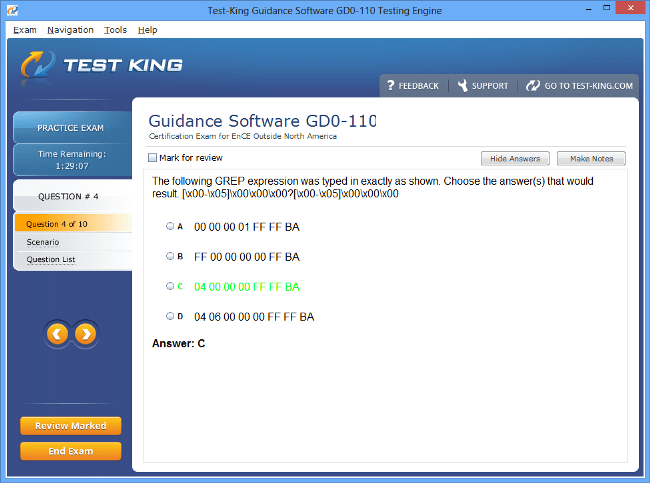
Exam Code: GD0-110
Exam Name: Certification for EnCE Outside North America
Certification Provider: Guidance Software
Corresponding Certification: EnCE
GD0-110 Exam Product Screenshots
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get the products after purchase?
All products are available for download immediately from your Member's Area. Once you have made the payment, you will be transferred to Member's Area where you can login and download the products you have purchased to your computer.
How long can I use my product? Will it be valid forever?
Test-King products have a validity of 90 days from the date of purchase. This means that any updates to the products, including but not limited to new questions, or updates and changes by our editing team, will be automatically downloaded on to computer to make sure that you get latest exam prep materials during those 90 days.
Can I renew my product if when it's expired?
Yes, when the 90 days of your product validity are over, you have the option of renewing your expired products with a 30% discount. This can be done in your Member's Area.
Please note that you will not be able to use the product after it has expired if you don't renew it.
How often are the questions updated?
We always try to provide the latest pool of questions, Updates in the questions depend on the changes in actual pool of questions by different vendors. As soon as we know about the change in the exam question pool we try our best to update the products as fast as possible.
How many computers I can download Test-King software on?
You can download the Test-King products on the maximum number of 2 (two) computers or devices. If you need to use the software on more than two machines, you can purchase this option separately. Please email support@test-king.com if you need to use more than 5 (five) computers.
What is a PDF Version?
PDF Version is a pdf document of Questions & Answers product. The document file has standart .pdf format, which can be easily read by any pdf reader application like Adobe Acrobat Reader, Foxit Reader, OpenOffice, Google Docs and many others.
Can I purchase PDF Version without the Testing Engine?
PDF Version cannot be purchased separately. It is only available as an add-on to main Question & Answer Testing Engine product.
What operating systems are supported by your Testing Engine software?
Our testing engine is supported by Windows. Andriod and IOS software is currently under development.
Understanding the Scope and Objectives of the GD0-110 Certification Exam
The GD0-110 certification exam is a specialized evaluation designed to validate the knowledge and skills of professionals in digital forensics outside North America. This examination, offered by Guidance Software, focuses on the EnCE certification, which is recognized globally as a benchmark for competence in forensic investigation, analysis, and data recovery. Candidates who pursue this exam are expected to demonstrate expertise in a variety of forensic techniques, evidence handling procedures, and investigative strategies. The exam is meticulously structured to assess both theoretical understanding and practical application, ensuring that successful candidates possess a holistic command of forensic methodologies.
Who Should Consider the GD0-110 Exam?
Professionals involved in law enforcement, corporate investigations, cybersecurity, or private forensic consultancy often seek the GD0-110 certification to establish credibility and enhance career prospects. This exam caters to individuals who have foundational knowledge in computer systems, networks, and investigative procedures, and who wish to attain advanced competence in digital forensic analysis. For candidates operating outside North America, this certification offers a means to gain international recognition and align with industry best practices that are accepted and respected worldwide. By pursuing this exam, individuals signal their dedication to professional growth and their ability to meet rigorous forensic standards.
Key Objectives of the GD0-110 Exam
The primary objectives of the GD0-110 certification are to ensure that candidates can competently acquire, preserve, analyze, and report digital evidence. This includes understanding the lifecycle of digital artifacts, employing forensic tools and techniques for data recovery, and presenting findings in a clear and legally defensible manner. Another crucial goal is to instill an understanding of ethical and legal considerations that govern digital investigations. Candidates are expected to demonstrate proficiency in identifying, extracting, and interpreting data from various storage media, operating systems, and network configurations, all while adhering to strict procedural and ethical guidelines. The exam also emphasizes critical thinking, problem-solving, and the ability to adapt methodologies to complex investigative scenarios.
Scope of Knowledge Required
The GD0-110 exam encompasses a broad spectrum of knowledge areas, reflecting the multifaceted nature of digital forensics. Candidates must have a solid grasp of file systems, operating system structures, and the nuances of data storage. Understanding how different operating systems handle data, including Windows, macOS, and Linux environments, is essential. The exam further explores network forensics, including the ability to trace data packets, identify anomalies, and understand the intricacies of various protocols. Investigative techniques, including timeline analysis, metadata examination, and the interpretation of log files, are also core components. Beyond technical acumen, candidates must appreciate the contextual relevance of evidence, ensuring that each piece of data is evaluated within the broader framework of an investigation.
Practical Skills and Forensic Techniques
A distinctive feature of the GD0-110 exam is its focus on practical application. Candidates are tested on their ability to handle forensic tools and software effectively, from acquiring disk images to analyzing volatile memory. They are expected to perform forensic examinations on diverse storage media, including hard drives, SSDs, removable media, and cloud-based environments. Techniques such as file carving, data recovery from damaged systems, and the reconstruction of deleted or corrupted data are fundamental. Additionally, candidates must demonstrate skill in using forensic suites to identify hidden or encrypted information, recover internet activity, and analyze email correspondence or other digital communications. Mastery of these skills ensures that professionals can translate technical findings into actionable intelligence.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The GD0-110 certification emphasizes the importance of adhering to legal and ethical standards throughout the investigative process. Candidates must be familiar with the legal frameworks governing digital evidence in their respective jurisdictions, including privacy regulations, chain-of-custody procedures, and admissibility standards for court proceedings. Ethical considerations, such as maintaining confidentiality, ensuring impartiality, and avoiding conflicts of interest, are equally critical. The exam evaluates not only technical proficiency but also the candidate’s ability to conduct investigations responsibly, ensuring that forensic findings can withstand scrutiny in legal or regulatory contexts. This combination of technical skill and ethical judgment distinguishes certified professionals in the field.
Exam Format and Assessment Approach
The GD0-110 exam employs a combination of multiple-choice questions, scenario-based problems, and practical simulations to assess candidates comprehensively. Multiple-choice items test theoretical knowledge, while scenario-based questions evaluate the candidate’s ability to apply concepts to real-world situations. Practical simulations are designed to replicate investigative challenges, requiring candidates to analyze digital evidence and present findings accurately. The exam is timed, demanding both efficiency and precision in responses. Success requires not only familiarity with forensic concepts but also the ability to think critically under pressure and synthesize complex information into coherent conclusions.
Preparing for the GD0-110 Exam
Effective preparation for the GD0-110 exam involves a structured study plan that integrates theoretical study with hands-on practice. Candidates should explore official Guidance Software materials, including study guides, practice labs, and online resources. Engaging with community forums, attending workshops, and participating in simulated forensic exercises can further enhance readiness. A methodical approach to learning, emphasizing understanding over memorization, is essential, as the exam tests the application of knowledge in diverse investigative scenarios. Consistent practice in using forensic tools, reconstructing case scenarios, and analyzing varied datasets builds the competence and confidence required to excel in the examination.
The Value of GD0-110 Certification
Achieving the GD0-110 certification confers professional recognition and validates an individual’s expertise in digital forensics. Certified professionals gain credibility in the eyes of employers, law enforcement agencies, and clients, demonstrating their ability to conduct thorough and reliable investigations. The certification can lead to career advancement, higher remuneration, and opportunities to participate in complex or high-profile forensic projects. For candidates outside North America, this credential provides a globally recognized benchmark, enhancing international mobility and access to professional networks. Beyond career benefits, the certification represents a commitment to the principles of accuracy, integrity, and ethical conduct in forensic practice.
Common Challenges in the Exam
Candidates often encounter challenges related to the breadth and complexity of the GD0-110 exam. The diversity of operating systems, file structures, and forensic tools requires comprehensive preparation. Time management can be a critical factor, as practical simulations demand careful analysis within constrained periods. Understanding the nuances of legal and ethical frameworks in different jurisdictions may also pose difficulties. Additionally, candidates must navigate scenarios involving corrupted, encrypted, or incomplete datasets, which require advanced problem-solving and analytical skills. Awareness of these challenges and proactive preparation can mitigate obstacles and enhance the likelihood of success.
Enhancing Success with Study Strategies
To maximize success on the GD0-110 exam, candidates should adopt a multifaceted study strategy. Combining textbook knowledge with interactive labs allows for reinforcement of practical skills. Simulated case studies and mock exams offer exposure to the types of scenarios likely to appear in the examination. Peer study groups and professional networks provide opportunities for knowledge exchange and discussion of complex forensic issues. Time management during preparation, coupled with regular review of core concepts, ensures retention and application of critical knowledge. Candidates who integrate these strategies can approach the exam with confidence and competence, fully prepared to demonstrate their expertise.
Approach the GD0-110 Exam
Approaching the GD0-110 exam requires a comprehensive understanding of both the technical content and the methodology behind digital forensic investigations. Candidates are advised to begin with a thorough assessment of their current knowledge and practical experience. This allows them to identify gaps and focus their study efforts efficiently. The exam evaluates not only theoretical knowledge but also the application of concepts in realistic investigative scenarios. Therefore, a balanced preparation strategy that combines conceptual study with hands-on practice is essential. Candidates must cultivate the ability to analyze complex digital artifacts and interpret findings with precision, while adhering to established investigative procedures.
Fundamental Knowledge Areas for Candidates
Success in the GD0-110 examination relies heavily on mastery of several fundamental knowledge areas. Candidates must be well-versed in the architecture and functioning of computer systems, understanding how operating systems manage files, memory, and processes. They should have insight into the structure and characteristics of various file systems, including FAT, NTFS, HFS+, and ext, and be able to differentiate between volatile and non-volatile data. Understanding storage media types, their behavior, and potential points of data loss or corruption is crucial. Additionally, familiarity with network structures, protocols, and common security configurations enables candidates to analyze network traffic and identify potential digital evidence efficiently.
Digital Evidence Acquisition Techniques
A core objective of the GD0-110 certification is ensuring that candidates can acquire digital evidence in a forensically sound manner. This involves the application of procedures that prevent contamination or alteration of data. Techniques such as disk imaging, memory capture, and cloning of storage media are essential. Candidates must demonstrate knowledge of hardware and software tools used for acquisition, understanding their limitations and best-use scenarios. The exam also tests the ability to handle unusual or compromised systems, requiring inventive problem-solving to preserve data integrity. Proper documentation during evidence acquisition is emphasized, as it underpins the chain of custody and validates the credibility of subsequent forensic analysis.
Analyzing Digital Artifacts
Digital artifact analysis forms a significant portion of the GD0-110 examination. Candidates are required to examine files, logs, emails, and metadata to extract meaningful information relevant to investigations. Techniques such as timeline reconstruction, file signature analysis, and identification of deleted or hidden files are fundamental. Analysis extends to mobile devices, cloud environments, and network logs, reflecting the breadth of contemporary digital investigations. The ability to synthesize disparate data points into coherent conclusions is critical. Candidates must also evaluate the reliability and authenticity of evidence, ensuring that conclusions drawn are accurate, defensible, and contextually relevant.
Advanced Forensic Tools and Methodologies
The GD0-110 exam expects candidates to demonstrate proficiency with advanced forensic tools and methodologies. This includes software suites designed for disk and memory analysis, email examination, and recovery of encrypted data. Candidates should be adept at using automated tools while retaining the ability to perform manual analysis when necessary. Understanding the underlying principles behind these tools is essential, as it allows candidates to adapt techniques to unique investigative circumstances. The exam emphasizes the practical application of these tools in controlled simulations, testing the candidate’s ability to manage data systematically and extract actionable insights efficiently.
Maintaining Ethical and Legal Standards
Adherence to ethical and legal standards is a central objective of the GD0-110 certification. Candidates must understand the legal frameworks governing digital evidence, including privacy laws, regulatory compliance, and procedures for admissibility in court. Ethical responsibilities, such as impartiality, integrity, and confidentiality, are equally vital. The exam evaluates the candidate’s ability to navigate situations where legal and ethical considerations intersect with technical challenges. Professionals must demonstrate decision-making that respects the rights of involved parties while ensuring that investigative procedures meet accepted standards. Mastery of these principles ensures that forensic findings are credible and defensible in any legal or regulatory setting.
Real-World Scenarios and Simulations
The GD0-110 exam incorporates real-world scenarios and simulations to assess candidates’ applied knowledge. These scenarios replicate investigative challenges, including data breaches, fraudulent activity, and system compromises. Candidates must analyze digital evidence, reconstruct events, and provide conclusions based on their findings. The simulations test problem-solving skills, attention to detail, and the ability to work under time constraints. Candidates are evaluated on their capacity to prioritize investigative steps, select appropriate tools, and maintain meticulous documentation. This practical component underscores the importance of translating theoretical knowledge into actionable investigative outcomes.
Time Management and Exam Strategy
Effective time management is crucial for candidates attempting the GD0-110 exam. The exam’s structure, which includes multiple-choice questions, practical exercises, and scenario analysis, requires careful allocation of time. Candidates must develop a strategy that balances speed with accuracy, ensuring that each question or simulation is addressed thoroughly. Familiarity with the exam format and practicing under timed conditions can enhance performance. Strategic reading, prioritization of tasks, and effective problem-solving are essential skills that enable candidates to navigate complex scenarios efficiently and confidently, ultimately contributing to a successful outcome.
Leveraging Study Materials and Resources
To prepare for the GD0-110 exam, candidates should utilize a combination of official study guides, online tutorials, and hands-on laboratories. Official materials from Guidance Software provide comprehensive coverage of exam objectives and recommended tools. Supplementary resources, such as forums, professional networks, and practice exercises, enhance understanding by offering practical insights and alternative approaches. Regular engagement with these resources fosters a deep comprehension of forensic methodologies, encourages critical thinking, and reinforces familiarity with investigative tools. Candidates who integrate diverse study resources develop the analytical skills and technical proficiency necessary to excel in both theoretical and practical components of the exam.
Developing Analytical and Critical Thinking Skills
Analytical and critical thinking skills are indispensable for GD0-110 candidates. The exam emphasizes the ability to assess complex datasets, identify patterns, and draw accurate conclusions. Candidates must interpret evidence in the context of investigative objectives, discerning relevant information from extraneous data. Problem-solving skills are tested through practical simulations and scenario questions, which require innovative approaches to unexpected challenges. By cultivating these cognitive abilities, candidates enhance their capacity to make informed decisions, evaluate alternative hypotheses, and construct coherent investigative narratives. The development of these skills ensures that candidates can approach real-world digital forensic cases with confidence and precision.
The Role of Documentation in Forensic Investigations
Proper documentation is a critical component of successful digital investigations. Candidates preparing for the GD0-110 exam are expected to maintain meticulous records of investigative procedures, evidence acquisition, and analytical processes. Documentation serves multiple purposes: it ensures traceability, supports the chain of custody, and provides transparency for judicial or organizational review. Candidates must learn to record observations clearly and systematically, detailing every step of the investigation and justifying decisions made during analysis. Mastery of documentation practices not only reinforces procedural integrity but also strengthens the credibility of forensic findings in professional and legal contexts.
Adapting to Technological Changes
Digital forensics is an evolving field, and candidates must demonstrate adaptability to emerging technologies. The GD0-110 exam tests the ability to apply established principles to new operating systems, storage devices, and communication platforms. Candidates must understand trends in cybercrime, the evolution of digital storage, and the implications of cloud computing and mobile technology on evidence acquisition. Adaptability ensures that forensic techniques remain relevant and effective in diverse investigative contexts. Candidates who can integrate contemporary technological insights with foundational forensic knowledge are better positioned to conduct thorough and accurate investigations in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
Building Professional Confidence
Achieving competence in the areas assessed by the GD0-110 exam instills professional confidence in candidates. Mastery of technical skills, ethical considerations, and investigative strategies enables individuals to approach complex cases with assurance. Confidence is further reinforced through repeated exposure to practical simulations and case studies, which mimic the pressures and challenges of real-world forensic work. Certified professionals gain recognition among peers, clients, and employers, reflecting their ability to conduct thorough, accurate, and ethical investigations. This confidence underpins professional growth, enhances credibility, and fosters a proactive approach to problem-solving in digital forensics.
Core Competencies Evaluated in the GD0-110 Exam
The GD0-110 certification exam is meticulously designed to measure a candidate’s mastery of essential competencies in digital forensics outside North America. Candidates are evaluated on their ability to acquire, preserve, and analyze electronic evidence with precision, ensuring that investigative conclusions are both accurate and legally defensible. Core competencies include an understanding of operating systems, storage devices, file systems, and the handling of volatile and non-volatile data. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in using forensic tools to recover, reconstruct, and interpret data from diverse sources, including desktops, servers, mobile devices, and cloud environments. Beyond technical skill, the exam also assesses the candidate’s ability to apply ethical judgment and maintain procedural integrity in complex investigative scenarios.
Understanding Operating Systems and File Systems
A profound understanding of operating systems and file systems forms the foundation of the GD0-110 examination. Candidates must comprehend how different operating systems manage memory, processes, and data storage, including the peculiarities of Windows, macOS, and Linux environments. File systems, such as FAT, NTFS, HFS+, and ext, present unique challenges in forensic analysis, requiring candidates to discern differences in metadata handling, file allocation, and journaling techniques. Knowledge of file system structures enables investigators to reconstruct deleted or corrupted data, interpret file timestamps, and understand the storage patterns of malicious or hidden files. Mastery of these areas ensures that candidates can analyze systems systematically, preserving evidence integrity while extracting meaningful insights.
Techniques for Evidence Acquisition
The acquisition of digital evidence is a critical skill assessed in the GD0-110 exam. Candidates must be proficient in forensically sound methods for copying data, capturing memory, and imaging storage devices without altering the original evidence. This requires an understanding of hardware and software tools, their appropriate application, and limitations. Techniques include bit-by-bit imaging, selective file copying, and live system analysis, all conducted with meticulous documentation to preserve the chain of custody. Candidates are also expected to handle challenging scenarios, such as damaged or encrypted drives, ensuring that evidence is preserved in its most authentic form. The ability to adapt acquisition strategies to diverse situations underscores a candidate’s competence and versatility.
Analysis of Digital Artifacts
Analyzing digital artifacts is central to the GD0-110 examination, requiring candidates to interpret files, logs, metadata, emails, and other electronic records with accuracy and context. This involves constructing timelines, identifying anomalies, and discerning patterns that reveal user activity, system compromise, or unauthorized access. Candidates must also examine network traffic, browser histories, and cloud storage data, integrating these findings into coherent investigative narratives. The exam emphasizes practical application, where candidates demonstrate the ability to extract actionable intelligence while maintaining the integrity of the evidence. Analytical skills are crucial, as investigators must distinguish relevant information from extraneous data to support accurate conclusions.
Utilization of Forensic Tools
The GD0-110 exam tests candidates on their proficiency with advanced forensic tools and software applications. These tools facilitate tasks such as disk and memory analysis, file recovery, email examination, and detection of hidden or encrypted data. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to use automated features effectively while retaining the capacity for manual analysis when necessary. Understanding the principles behind these tools allows investigators to adapt their application to unique cases and unusual data structures. Practical exercises in the exam challenge candidates to select appropriate tools, execute analysis efficiently, and document findings comprehensively. Proficiency in tool utilization is indispensable, ensuring that investigations are thorough, precise, and defensible.
Legal and Ethical Responsibilities
Legal and ethical responsibilities are integral to the GD0-110 certification. Candidates are expected to navigate the complexities of privacy regulations, chain-of-custody procedures, and the admissibility of evidence in various jurisdictions. Ethical considerations, such as maintaining impartiality, safeguarding confidentiality, and avoiding conflicts of interest, are equally emphasized. The exam evaluates the candidate’s capacity to make decisions that uphold professional standards while applying forensic techniques. Professionals must balance technical requirements with legal and ethical obligations, ensuring that investigations are conducted responsibly and findings are credible. Mastery of these principles reinforces trust in forensic processes and enhances the credibility of investigative outcomes.
Simulated Investigative Scenarios
The GD0-110 examination includes simulated investigative scenarios that mirror real-world challenges. Candidates are required to analyze data breaches, fraudulent activities, or compromised systems, reconstructing events and providing evidence-based conclusions. These simulations test the ability to prioritize investigative steps, select suitable tools, and interpret complex datasets accurately. Candidates must demonstrate meticulous attention to detail, problem-solving capabilities, and efficient time management. Exposure to diverse scenarios fosters adaptive thinking, enabling candidates to apply theoretical knowledge effectively in practical contexts. Simulations cultivate professional competence, preparing candidates to address challenges encountered in actual forensic investigations.
Preparing Effectively for the Exam
Effective preparation for the GD0-110 exam involves a structured approach that balances theoretical study with practical experience. Candidates should engage with official study guides, online resources, and practice exercises offered by Guidance Software. Supplementary learning, such as participating in forums, attending workshops, and performing simulated forensic analyses, reinforces comprehension and technical skill. Regular practice with forensic tools, including memory and disk analysis, file recovery, and network monitoring, develops proficiency and confidence. Critical thinking exercises, scenario evaluation, and hands-on labs allow candidates to apply knowledge dynamically, ensuring readiness for the multifaceted challenges presented in the examination.
Developing Problem-Solving Skills
Problem-solving is a vital skill evaluated by the GD0-110 exam. Candidates encounter complex investigative scenarios that require innovative thinking and analytical rigor. They must interpret incomplete, corrupted, or encrypted data while maintaining procedural integrity and evidence authenticity. The ability to identify patterns, recognize anomalies, and formulate evidence-based conclusions is critical. Candidates must also anticipate potential challenges in investigations, adapt methodologies as needed, and justify their decisions. Cultivating these problem-solving capabilities enhances performance in both the exam and professional practice, ensuring that candidates can approach forensic investigations with intelligence and discernment.
Importance of Documentation
Accurate documentation is essential in digital forensic investigations and is a focal point of the GD0-110 exam. Candidates are expected to maintain comprehensive records of investigative procedures, tool usage, and analytical findings. Documentation supports the chain of custody, provides transparency, and validates conclusions for review by legal authorities or professional peers. Candidates must articulate observations clearly, ensuring that each investigative step is recorded systematically. Mastery of documentation practices demonstrates professional diligence and reinforces the credibility of findings. Effective documentation not only aids in examination scenarios but also equips candidates with skills vital for real-world forensic responsibilities.
Adapting to Emerging Technologies
Digital forensics is a dynamic field, and the GD0-110 exam evaluates the candidate’s capacity to adapt to emerging technologies. Candidates must apply foundational principles to new operating systems, storage media, mobile devices, and cloud infrastructures. Understanding contemporary trends in cybercrime, network security, and data storage practices is critical for effective investigation. Adaptability allows candidates to respond to technological shifts without compromising investigative accuracy or evidence integrity. Professionals who can integrate evolving technology knowledge with established forensic methodologies are better equipped to manage diverse and complex investigative scenarios.
Building Professional Competence
Achieving competence in the areas tested by the GD0-110 exam instills professional confidence and credibility. Mastery of forensic tools, investigative techniques, ethical considerations, and analytical reasoning ensures that candidates are prepared to handle complex cases. Confidence is further reinforced through practical exercises, case study analysis, and repeated exposure to simulated investigative scenarios. Certified professionals gain recognition from peers, employers, and clients, reflecting their capacity to conduct accurate, ethical, and reliable investigations. This professional competence serves as a foundation for career growth, international recognition, and the ability to navigate high-stakes forensic challenges with assurance.
Preparing Candidates for Comprehensive Digital Forensics
The GD0-110 certification exam is meticulously crafted to prepare candidates for the intricate and evolving field of digital forensics outside North America. Candidates are expected to demonstrate mastery of both theoretical knowledge and practical investigative skills. The exam evaluates the ability to collect, preserve, and analyze electronic evidence while maintaining adherence to legal and ethical standards. It also tests problem-solving capabilities, analytical reasoning, and adaptability to diverse investigative scenarios. Candidates are assessed on their capacity to navigate complex digital environments, extract relevant data, and interpret findings accurately, establishing credibility as proficient forensic professionals on an international scale.
Mastery of Operating Systems and File Systems
Proficiency in operating systems and file systems is a cornerstone of the GD0-110 examination. Candidates must comprehend the inner workings of Windows, macOS, and Linux environments, including memory management, process control, and file system architecture. Knowledge of FAT, NTFS, HFS+, and ext file systems is crucial, as candidates are often required to reconstruct deleted or corrupted data and interpret file metadata. The ability to understand file allocation, journaling, and timestamp variations allows investigators to reconstruct accurate timelines and uncover hidden activity. Mastery of these systems enables candidates to apply forensic principles methodically, ensuring the reliability and validity of their analysis.
Techniques for Evidence Preservation
Evidence preservation is fundamental to digital forensics and a primary focus of the GD0-110 exam. Candidates must be proficient in acquiring data without altering or compromising its integrity. Techniques include bit-by-bit disk imaging, memory capture, and cloning of storage media. Candidates are expected to handle hardware and software tools effectively, understand their operational limitations, and apply best practices in challenging scenarios, such as damaged or encrypted systems. Documentation is emphasized at every stage, preserving the chain of custody and providing traceable records of all investigative actions. These skills ensure that collected evidence is admissible, verifiable, and defensible in professional and legal contexts.
Analyzing Digital Artifacts and Metadata
Analyzing digital artifacts and metadata constitutes a significant portion of the GD0-110 examination. Candidates are required to extract information from files, logs, emails, and network data to reconstruct user activity and system events. Techniques such as timeline analysis, file signature verification, and metadata interpretation allow investigators to identify anomalies, hidden activity, and potential compromises. Analysis extends to mobile devices, cloud services, and remote storage environments, requiring adaptability and precision. Candidates must integrate disparate data points into coherent investigative narratives while maintaining rigorous attention to detail, ensuring that conclusions are accurate and contextually grounded.
Utilizing Forensic Tools Effectively
Proficiency in forensic tools is a key objective of the GD0-110 exam. Candidates must demonstrate competency with software designed for disk analysis, memory examination, email recovery, and encrypted data extraction. They should be adept at using automated functions while retaining the ability to conduct manual analysis when necessary. Understanding the underlying principles of these tools is critical for adapting techniques to unique cases or unconventional data structures. The exam assesses the candidate’s ability to execute investigations efficiently, apply tools judiciously, and document outcomes clearly. Competence in tool utilization reinforces investigative accuracy and facilitates reliable evidence interpretation.
Legal and Ethical Responsibilities in Forensics
Adherence to legal and ethical responsibilities is a central aspect of the GD0-110 certification. Candidates must navigate privacy regulations, chain-of-custody procedures, and the standards governing evidence admissibility in court or organizational reviews. Ethical considerations include impartiality, integrity, and confidentiality, ensuring that investigations uphold professional and legal norms. The exam evaluates the candidate’s ability to apply forensic techniques within these frameworks, making responsible decisions that protect the rights of all stakeholders. Mastery of legal and ethical principles ensures that findings are credible, defensible, and maintain the trust of clients, employers, and judicial authorities.
Practical Simulations and Investigative Scenarios
The GD0-110 exam incorporates practical simulations and investigative scenarios to test applied knowledge. Candidates face challenges such as data breaches, system compromises, and fraudulent activities. They must reconstruct events, analyze complex datasets, and provide evidence-based conclusions. Simulations require prioritization, tool selection, and meticulous documentation. These exercises evaluate problem-solving skills, adaptability, and efficiency under time constraints. Exposure to realistic scenarios fosters critical thinking and reinforces the candidate’s ability to apply theoretical knowledge in practice. Success in simulations demonstrates readiness to handle professional forensic investigations with precision and competence.
Developing Analytical and Critical Thinking Abilities
Analytical and critical thinking are essential skills for GD0-110 candidates. The exam challenges candidates to assess complex datasets, identify patterns, and formulate accurate conclusions. Candidates must discern relevant evidence from irrelevant information and evaluate the reliability of their findings. Problem-solving is tested through simulations and scenario questions, requiring candidates to devise innovative approaches to challenges. Developing these abilities ensures that candidates can interpret forensic data methodically, anticipate investigative obstacles, and construct coherent narratives. Analytical competence is critical for professional credibility and success in the field of digital forensics.
Study Strategies and Resource Utilization
Preparing effectively for the GD0-110 exam involves a structured and comprehensive study approach. Candidates should engage with official study guides, practice labs, and tutorials provided by Guidance Software. Supplementary resources such as peer discussions, forums, and professional networks enhance understanding and expose candidates to diverse perspectives. Practical exercises, mock investigations, and scenario analysis reinforce technical skills and conceptual knowledge. A methodical approach, emphasizing understanding over memorization, enables candidates to internalize forensic principles and apply them dynamically. Consistent practice and exposure to varied investigative contexts cultivate the expertise necessary for exam success.
Time Management and Exam Performance
Time management is crucial for candidates undertaking the GD0-110 exam. The exam encompasses multiple-choice questions, scenario-based challenges, and practical simulations, all requiring careful allocation of time. Candidates must balance speed with accuracy, ensuring thorough analysis and effective problem-solving. Familiarity with the exam format, practicing under timed conditions, and prioritizing tasks contribute to enhanced performance. Strategic time management allows candidates to approach each question methodically, reduces the likelihood of errors, and ensures that practical tasks are completed efficiently. Mastery of time management strategies is integral to achieving a successful outcome.
Adapting to Technological Evolution
Digital forensics is a field in constant flux, requiring candidates to adapt to new technologies, operating systems, and data storage methods. The GD0-110 exam evaluates the ability to apply forensic principles to evolving digital environments, including cloud computing, mobile platforms, and networked systems. Candidates must understand contemporary trends in cybercrime, emerging threats, and the implications of technological advancements on evidence acquisition. Adaptability ensures that investigative techniques remain effective and relevant, allowing professionals to handle novel challenges without compromising accuracy or evidence integrity. Continuous learning and technological agility are essential for sustained competence in digital forensics.
Building Professional Expertise and Confidence
Achieving mastery in the areas assessed by the GD0-110 exam instills professional expertise and confidence. Candidates develop the technical skills, analytical reasoning, and ethical judgment necessary to conduct rigorous forensic investigations. Exposure to practical simulations, scenario analysis, and hands-on exercises reinforces professional capability and decision-making acumen. Certified professionals gain recognition from peers, employers, and clients, reflecting their ability to conduct thorough, accurate, and ethical investigations. This expertise enhances career mobility, access to international opportunities, and readiness to engage with complex investigative challenges. Confidence in applying forensic principles underpins professional growth and credibility in the field.
Enhancing Competence in Digital Forensics
The GD0-110 certification exam is designed to enhance professional competence in digital forensics for candidates outside North America. It evaluates both theoretical knowledge and practical proficiency, ensuring candidates can handle complex investigative scenarios. Candidates are tested on their ability to acquire, preserve, and analyze digital evidence, as well as their understanding of ethical and legal obligations. Mastery of these competencies allows candidates to approach investigations methodically, interpret data accurately, and present findings in a clear and defensible manner. This rigorous evaluation cultivates professionals capable of operating with confidence and precision in diverse digital environments.
Deep Understanding of Operating Systems
Proficiency in operating systems is essential for success in the GD0-110 exam. Candidates must comprehend how different systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, manage memory, file storage, and processes. Knowledge of operating system architecture aids in understanding system logs, registry structures, and process activity, which are critical for forensic investigations. Candidates must also be familiar with virtual environments and multi-boot configurations, as these can influence evidence acquisition and analysis. Understanding these nuances ensures that investigators can reconstruct events accurately and identify anomalies that may indicate unauthorized or malicious activity.
File System Analysis and Metadata Interpretation
File systems form the backbone of digital investigations, and the GD0-110 exam evaluates candidates’ ability to analyze them effectively. Familiarity with FAT, NTFS, HFS+, and ext file systems allows candidates to navigate storage structures, recover deleted files, and interpret metadata. Metadata analysis is crucial for establishing timelines, user activity, and file modifications. Candidates must also understand journaling, allocation tables, and slack space, which often contain valuable forensic information. This knowledge enables investigators to uncover hidden or obfuscated data, providing critical insights into system activity and potential breaches.
Evidence Acquisition Strategies
The GD0-110 exam emphasizes forensically sound evidence acquisition techniques. Candidates are expected to perform disk imaging, memory capture, and cloning of storage media without altering original data. Mastery of both hardware and software tools for evidence collection is essential. Candidates must also handle complex scenarios, such as damaged, encrypted, or volatile systems, ensuring data integrity throughout the investigative process. Documentation of each acquisition step is critical, preserving the chain of custody and ensuring that evidence remains admissible and credible in legal or professional contexts. Effective acquisition strategies underpin the reliability of subsequent analysis and reporting.
Analytical Skills in Forensic Investigations
Analytical skills are at the core of the GD0-110 examination. Candidates are required to examine files, logs, emails, and network data to identify relevant information and reconstruct events accurately. This involves evaluating patterns, correlating disparate data points, and discerning anomalies that indicate unauthorized activity or system compromise. Candidates must also interpret evidence in the context of investigative objectives, ensuring conclusions are supported by objective data. Analytical rigor enables investigators to provide clear and actionable insights, reinforcing the credibility of their findings and the integrity of the investigative process.
Mastery of Forensic Tools
Competence with forensic tools is essential for GD0-110 candidates. The exam assesses the ability to use software suites for disk and memory analysis, email recovery, and encrypted data examination. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency with automated features while retaining the capacity for manual intervention when necessary. Understanding the principles behind these tools allows investigators to adapt techniques to unusual or complex scenarios. The ability to apply tools efficiently, document findings meticulously, and interpret results accurately is critical for achieving exam success and ensuring professional competence in forensic investigations.
Legal Frameworks and Ethical Conduct
Legal and ethical considerations are integral to the GD0-110 certification. Candidates must navigate privacy regulations, chain-of-custody requirements, and evidence admissibility standards in diverse jurisdictions. Ethical conduct involves impartiality, integrity, and confidentiality, ensuring that investigative procedures are defensible and professional. The exam evaluates the ability to make informed decisions within these frameworks while conducting rigorous analyses. Mastery of legal and ethical principles protects the rights of involved parties and maintains the credibility of investigative findings. Candidates are expected to integrate these considerations seamlessly into every stage of forensic work.
Scenario-Based Problem Solving
The GD0-110 exam incorporates scenario-based problem-solving exercises to test applied knowledge. Candidates encounter realistic challenges, including compromised systems, data breaches, and fraudulent activity. They must analyze evidence, reconstruct events, and provide substantiated conclusions. These exercises require prioritization, efficient tool utilization, and meticulous documentation. Problem-solving in simulated scenarios evaluates adaptability, critical thinking, and decision-making under pressure. Exposure to diverse investigative situations reinforces practical competence and prepares candidates to handle real-world forensic challenges effectively.
Developing Critical Thinking and Judgment
Critical thinking and sound judgment are emphasized throughout the GD0-110 examination. Candidates must interpret complex datasets, identify relevant evidence, and assess its reliability. Analytical judgment allows investigators to differentiate between pertinent and extraneous information, evaluate potential biases, and construct coherent investigative narratives. Problem-solving exercises challenge candidates to devise innovative solutions to unusual investigative obstacles. The cultivation of critical thinking skills ensures that professionals can approach investigations with clarity, precision, and confidence, producing findings that are both accurate and defensible.
Effective Study Practices
Preparation for the GD0-110 exam requires disciplined study and hands-on practice. Candidates should engage with official Guidance Software study guides, practice exercises, and virtual labs. Supplementary resources, including professional forums, workshops, and peer discussions, provide additional insight and reinforce technical knowledge. Practical exercises, mock investigations, and scenario analysis foster familiarity with real-world challenges and reinforce analytical skills. Consistent practice and structured review ensure retention of critical concepts and techniques. Candidates who integrate diverse study approaches are well-equipped to perform effectively in the exam and professional investigations.
Time Management During the Exam
Time management is crucial for candidates undertaking the GD0-110 exam. The evaluation includes multiple-choice questions, scenario-based analyses, and practical simulations that demand careful allocation of time. Candidates must balance thoroughness with efficiency, ensuring that all tasks are completed accurately within time constraints. Practicing under timed conditions enhances familiarity with the exam format and reduces stress. Strategic prioritization, rapid problem assessment, and disciplined execution contribute to successful performance. Effective time management allows candidates to navigate complex scenarios confidently, optimizing their chances of achieving certification.
Adapting to Technological Evolution
The dynamic nature of digital forensics necessitates adaptability to new technologies, systems, and storage methods. Candidates are expected to apply foundational forensic principles to emerging platforms, including cloud computing, mobile devices, and advanced network architectures. Understanding evolving cyber threats, storage innovations, and software developments is essential for accurate and effective investigations. Adaptability ensures that investigative techniques remain relevant, enabling professionals to handle new challenges without compromising accuracy or integrity. Continuous learning and technological agility are vital for maintaining competence and credibility in digital forensic practice.
Building Professional Confidence and Recognition
Achieving proficiency in the areas tested by the GD0-110 exam instills professional confidence and enhances recognition in the field of digital forensics. Candidates develop technical expertise, analytical capabilities, and ethical awareness required to conduct complex investigations. Exposure to practical exercises, simulations, and scenario-based challenges reinforces confidence in applying knowledge under pressure. Certified professionals gain credibility with peers, employers, and clients, reflecting their ability to conduct thorough, accurate, and ethical forensic investigations. This expertise supports career advancement, international opportunities, and professional growth, solidifying the candidate’s standing in the global forensic community.
Advanced Knowledge Requirements for GD0-110 Candidates
The GD0-110 certification exam is designed to evaluate advanced knowledge and skills in digital forensics for candidates outside North America. Professionals pursuing this exam are expected to demonstrate comprehensive expertise in evidence acquisition, preservation, and analysis. Candidates must exhibit proficiency with operating systems, file systems, network configurations, and storage media, understanding how each component can impact forensic investigations. Mastery extends beyond technical ability, encompassing critical thinking, problem-solving, and ethical judgment. The exam emphasizes applied knowledge in real-world scenarios, requiring candidates to demonstrate not only what they know but also how effectively they can translate that knowledge into actionable investigative outcomes.
Operating Systems and Their Forensic Implications
A thorough understanding of operating systems is indispensable for GD0-110 candidates. Windows, macOS, and Linux environments each present unique forensic challenges. Candidates must comprehend memory management, process scheduling, registry structures, and file allocation behaviors to reconstruct accurate timelines and identify anomalies. Knowledge of virtual environments, dual-boot configurations, and system-specific logging mechanisms allows investigators to navigate complex digital landscapes. Understanding the interaction between hardware and operating system components ensures that evidence is accurately interpreted and that investigative procedures are methodical and defensible.
File Systems and Data Recovery Techniques
Candidates must demonstrate expertise in file systems, including FAT, NTFS, HFS+, and ext formats, as these are central to the GD0-110 exam. A nuanced understanding of file system structures enables investigators to recover deleted or corrupted files, interpret metadata, and analyze allocation tables. Techniques such as file carving, slack space examination, and timestamp verification are essential for reconstructing user activity. Candidates must also recognize the implications of journaling and system backups on data integrity. Proficiency in these techniques ensures that forensic analyses are comprehensive, accurate, and capable of supporting investigative conclusions in professional or legal contexts.
Evidence Acquisition and Preservation Methods
Forensically sound acquisition is a cornerstone of the GD0-110 certification. Candidates are expected to perform disk imaging, memory capture, and cloning of storage media without altering original data. Competence with both hardware and software acquisition tools is essential, as is the ability to handle challenging scenarios involving encrypted, volatile, or damaged systems. Proper documentation throughout the acquisition process preserves the chain of custody and ensures that evidence remains admissible and credible. Effective acquisition strategies form the foundation for subsequent analysis, allowing investigators to maintain the integrity and reliability of all collected data.
Analytical Techniques for Digital Artifacts
The GD0-110 exam emphasizes analytical proficiency in examining digital artifacts. Candidates must interpret files, logs, emails, and network traffic to reconstruct events and identify relevant information. Techniques include timeline reconstruction, anomaly detection, and correlation of disparate data sources. The analysis extends to mobile devices, cloud storage, and remote systems, reflecting the diversity of contemporary forensic investigations. Candidates are expected to synthesize findings into coherent investigative narratives, maintaining accuracy and objectivity. Analytical rigor ensures that conclusions drawn are defensible, actionable, and contextually relevant to the investigative objectives.
Forensic Tools and Methodologies
Candidates are assessed on their mastery of forensic tools and methodologies. The GD0-110 exam evaluates the ability to use software for disk analysis, memory examination, email recovery, and encrypted data interpretation. Automated tools are valuable for efficiency, but manual analysis remains critical for complex or unusual datasets. Understanding the underlying principles of these tools enables candidates to adapt techniques to unique scenarios, ensuring accurate and thorough investigation outcomes. Effective application of forensic tools reinforces credibility and demonstrates competence in both technical skill and investigative judgment.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Legal and ethical knowledge is integral to the GD0-110 exam. Candidates must navigate privacy regulations, chain-of-custody requirements, and standards for evidence admissibility in different jurisdictions. Ethical principles, such as impartiality, integrity, and confidentiality, are essential to maintaining professional credibility. The exam evaluates the ability to apply forensic techniques responsibly, balancing technical objectives with legal obligations. Mastery of these considerations ensures that findings are credible, defensible, and trustworthy. Ethical and legal awareness distinguishes competent forensic professionals, reinforcing accountability and public confidence in investigative outcomes.
Scenario-Based Investigative Skills
Practical scenario exercises are a critical component of the GD0-110 exam. Candidates face situations such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and fraudulent activity. They must reconstruct events, analyze complex datasets, and provide evidence-based conclusions. These exercises require prioritization of investigative steps, selection of appropriate tools, and meticulous documentation. Scenario-based assessments cultivate problem-solving skills, critical thinking, and adaptability. Candidates who excel in these exercises demonstrate readiness to handle real-world challenges, effectively applying theoretical knowledge to practical investigative tasks.
Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
The GD0-110 exam emphasizes the development of critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Candidates must evaluate complex information, identify patterns, and derive accurate conclusions from incomplete or ambiguous datasets. Problem-solving requires innovation, adaptability, and precise decision-making, particularly when dealing with corrupted, encrypted, or fragmented data. Analytical skills enable candidates to construct coherent investigative narratives and anticipate potential challenges. Mastery of these cognitive processes ensures that candidates approach investigations systematically, producing findings that are reliable, actionable, and professionally defensible.
Study Strategies and Resource Integration
Effective preparation for the GD0-110 exam involves structured study strategies and the integration of multiple learning resources. Candidates should utilize official Guidance Software study guides, practice labs, and tutorials. Participation in professional forums, workshops, and peer study groups enhances understanding of complex forensic concepts. Practical exercises, mock investigations, and scenario-based drills provide exposure to real-world challenges. A consistent study schedule that balances conceptual review with hands-on practice fosters deep comprehension and confidence. Candidates who integrate diverse resources develop the analytical, technical, and procedural skills required for exam success and professional competence.
Time Management and Exam Readiness
Time management is essential for successful performance in the GD0-110 exam. The evaluation includes multiple-choice questions, scenario-based analyses, and practical simulations, all of which require careful allocation of time. Candidates must balance thoroughness with efficiency to ensure accurate completion of all tasks. Practicing under timed conditions enhances familiarity with the exam format and helps reduce stress. Strategic prioritization, effective problem assessment, and disciplined execution enable candidates to navigate complex scenarios confidently. Mastery of time management strategies maximizes exam performance and ensures that candidates can demonstrate their full competence.
Technological Adaptability in Digital Forensics
Digital forensics is an evolving field, and the GD0-110 exam assesses candidates’ adaptability to emerging technologies and systems. Candidates must apply foundational principles to new storage methods, operating systems, mobile platforms, and cloud infrastructures. Understanding contemporary cyber threats, network innovations, and storage technologies is critical for accurate investigation. Adaptability ensures that investigative techniques remain effective, relevant, and defensible. Continuous learning and technological agility equip candidates to manage diverse investigative challenges, maintain evidence integrity, and apply forensic methodologies in dynamic digital environments.
Professional Confidence and Recognition
Achieving proficiency in the areas assessed by the GD0-110 exam builds professional confidence and enhances recognition. Candidates develop expertise in technical skills, analytical reasoning, ethical judgment, and applied investigation techniques. Exposure to practical exercises, scenario simulations, and complex case studies reinforces decision-making capability and readiness to handle professional challenges. Certified professionals gain credibility among peers, employers, and clients, reflecting their ability to conduct accurate, ethical, and thorough forensic investigations. This expertise facilitates career advancement, international opportunities, and recognition in the digital forensics community.
Conclusion
The GD0-110 certification exam serves as a rigorous benchmark for professionals seeking international recognition in digital forensics. It evaluates not only technical expertise but also analytical ability, ethical judgment, and practical investigative skill. Candidates are expected to demonstrate mastery of operating systems, file systems, evidence acquisition techniques, forensic tools, and legal frameworks. Scenario-based exercises test adaptability, problem-solving, and critical thinking, preparing candidates to handle complex investigative challenges with confidence and precision. Success in this examination reflects a commitment to professional excellence, integrity, and proficiency in digital forensic practice, providing a foundation for career growth, credibility, and sustained achievement in the global forensic community.