Exam Code: CCA-505
Exam Name: Cloudera Certified Administrator for Apache Hadoop (CCAH) CDH5 Upgrade
Certification Provider: Cloudera
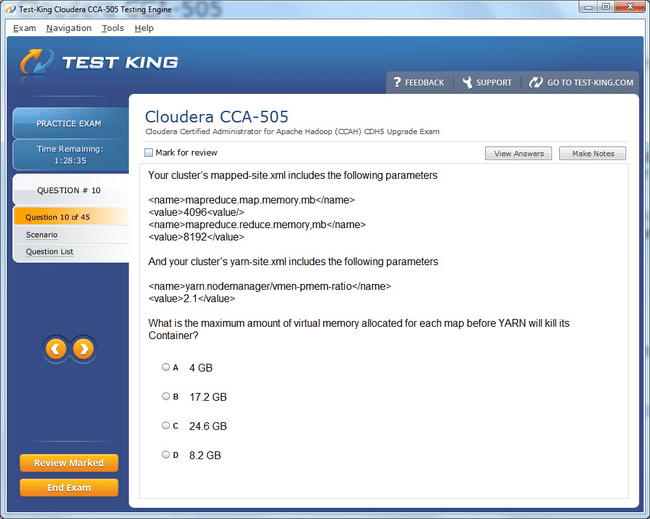
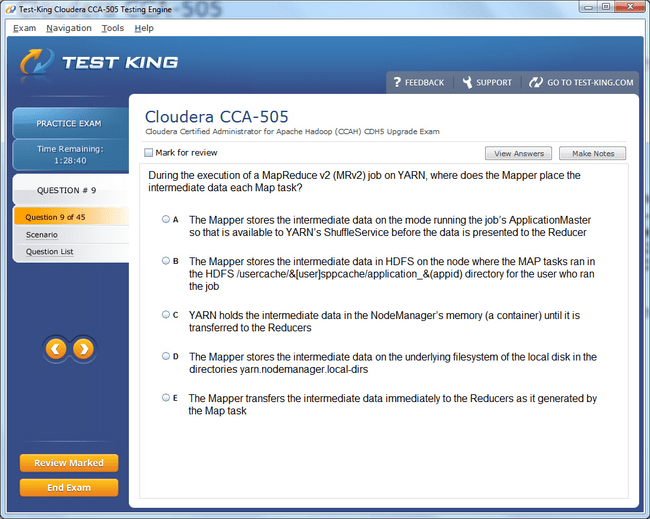
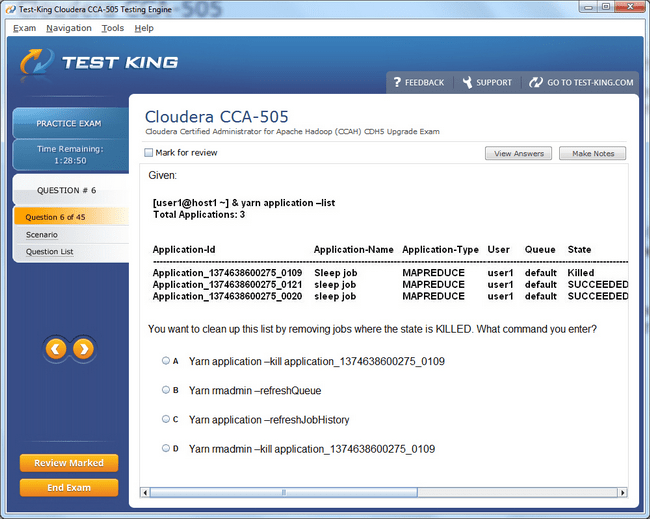
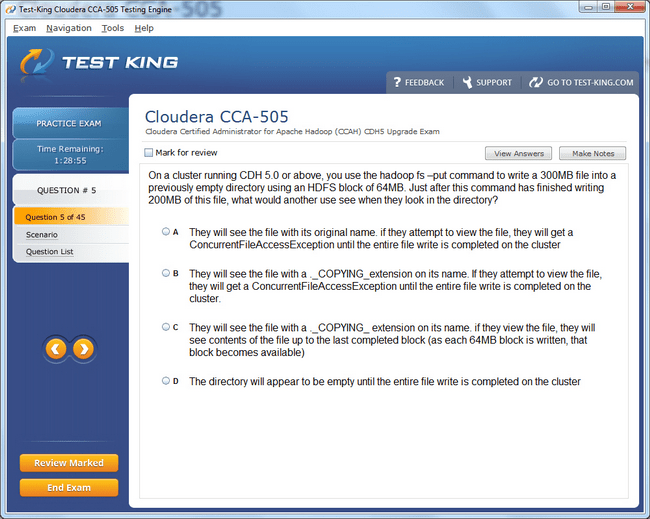
CCA-505 Exam Product Screenshots
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get the products after purchase?
All products are available for download immediately from your Member's Area. Once you have made the payment, you will be transferred to Member's Area where you can login and download the products you have purchased to your computer.
How long can I use my product? Will it be valid forever?
Test-King products have a validity of 90 days from the date of purchase. This means that any updates to the products, including but not limited to new questions, or updates and changes by our editing team, will be automatically downloaded on to computer to make sure that you get latest exam prep materials during those 90 days.
Can I renew my product if when it's expired?
Yes, when the 90 days of your product validity are over, you have the option of renewing your expired products with a 30% discount. This can be done in your Member's Area.
Please note that you will not be able to use the product after it has expired if you don't renew it.
How often are the questions updated?
We always try to provide the latest pool of questions, Updates in the questions depend on the changes in actual pool of questions by different vendors. As soon as we know about the change in the exam question pool we try our best to update the products as fast as possible.
How many computers I can download Test-King software on?
You can download the Test-King products on the maximum number of 2 (two) computers or devices. If you need to use the software on more than two machines, you can purchase this option separately. Please email support@test-king.com if you need to use more than 5 (five) computers.
What is a PDF Version?
PDF Version is a pdf document of Questions & Answers product. The document file has standart .pdf format, which can be easily read by any pdf reader application like Adobe Acrobat Reader, Foxit Reader, OpenOffice, Google Docs and many others.
Can I purchase PDF Version without the Testing Engine?
PDF Version cannot be purchased separately. It is only available as an add-on to main Question & Answer Testing Engine product.
What operating systems are supported by your Testing Engine software?
Our testing engine is supported by Windows. Andriod and IOS software is currently under development.
CCA-505 : Step-by-Step Strategy to Pass the Cloudera CCAH CDH5 Upgrade Exam
Embarking on the journey to achieve the Cloudera Certified Administrator for Apache Hadoop certification can seem like navigating an intricate labyrinth of distributed systems, configurations, and data orchestration. The CCA-505 exam, specifically designed to validate skills in upgrading CDH5 clusters, demands not only practical experience but also a meticulous understanding of Hadoop’s architecture, ecosystem, and operational nuances. The exam tests a candidate’s ability to deploy, manage, and troubleshoot an enterprise-level Hadoop environment while ensuring continuity during upgrades. The path to proficiency requires a blend of strategic planning, hands-on experimentation, and theoretical grounding, coupled with an appreciation for the idiosyncrasies of distributed computing.
Mastering the Cloudera Certified Administrator for Apache Hadoop
A foundational step in preparing for the CCA-505 examination involves establishing a comprehensive grasp of the CDH5 architecture. Apache Hadoop’s distributed file system, YARN resource management, MapReduce processing, and high-availability configurations form the cornerstone of this certification. Candidates must be adept at understanding the flow of data across nodes, how resource scheduling impacts cluster performance, and the subtleties of HDFS replication strategies. Familiarity with Hadoop’s daemons, including NameNode, DataNode, ResourceManager, and NodeManager, is indispensable. Knowing how these components interact under varying workloads equips administrators with the foresight to anticipate potential pitfalls during an upgrade.
Equally critical is mastering the intricacies of performing a CDH5 upgrade without disrupting the operational integrity of the cluster. The exam evaluates one’s ability to plan an upgrade, execute it in stages, and recover from contingencies. It is essential to develop a strategy that includes a thorough pre-upgrade audit, assessment of service dependencies, and verification of cluster health. Administrators should simulate upgrade scenarios in a controlled environment, meticulously recording the sequence of steps, any anomalies encountered, and the corrective measures applied. This practice fosters a procedural memory that becomes invaluable during actual exam scenarios, where troubleshooting under time constraints is necessary.
The practical component of the CCA-505 exam emphasizes hands-on command over Hadoop administration. Candidates must be comfortable navigating Cloudera Manager, configuring services, and monitoring cluster performance metrics. Knowledge of service-specific parameters, such as HDFS block sizes, YARN memory allocations, and Hive metastore configurations, can dramatically influence operational efficiency. Furthermore, understanding the interdependencies between services ensures that administrators can identify root causes of performance degradation or failure with precision. For instance, a seemingly minor misconfiguration in HDFS replication can cascade into widespread processing delays, a nuance frequently tested in the exam.
Troubleshooting forms a significant portion of the skill assessment. Administrators are expected to diagnose and rectify service failures, connectivity issues, and configuration inconsistencies. Exam scenarios often present clusters under simulated duress, requiring candidates to employ diagnostic tools, logs analysis, and strategic problem-solving. Developing a mental catalog of common error patterns and their resolutions enhances response speed and accuracy. For example, errors in HDFS can manifest as corrupted blocks or inaccessible directories, each necessitating a specific corrective approach that preserves data integrity. Similarly, YARN resource contention issues demand careful adjustments to queues and container allocations to restore equilibrium.
A holistic preparation strategy integrates both theoretical study and immersive practice. Candidates benefit from structured learning resources, including official Cloudera documentation, training modules, and community knowledge bases. However, rote memorization is insufficient; the exam rewards comprehension, adaptability, and the ability to apply concepts in dynamic scenarios. Constructing a lab environment that mirrors production-level clusters allows aspirants to experiment with upgrades, service restarts, and failure recovery. Documenting these exercises with reflections on outcomes, challenges faced, and lessons learned fortifies understanding and builds confidence.
Understanding cluster security and governance is another crucial dimension. Hadoop administrators must navigate Kerberos authentication, service-level authorization, and data encryption, ensuring compliance with organizational policies while maintaining system accessibility. The CCA-505 exam evaluates the ability to implement security measures seamlessly within an operational cluster. Candidates should practice configuring principal identities, managing keytabs, and applying permission schemes across HDFS and Hive. A nuanced grasp of audit logging and access control mechanisms not only aids in passing the exam but also equips administrators for real-world enterprise environments.
Monitoring and performance tuning are equally pivotal. Administrators must be capable of analyzing cluster metrics, identifying bottlenecks, and optimizing resource utilization. Tools such as Cloudera Manager provide a centralized view of health indicators, but success lies in interpreting the data effectively. Understanding how YARN scheduling, HDFS replication, and MapReduce job parallelism interact allows administrators to make informed decisions. Performance tuning exercises, such as adjusting memory allocations or modifying service parameters to enhance throughput, are invaluable for reinforcing the principles tested in the examination.
Another dimension often underestimated is time management during preparation and the exam itself. Developing a study plan that balances learning new concepts, revisiting challenging topics, and engaging in practical exercises prevents last-minute cramming and fosters deep retention. During the exam, systematically approaching each scenario, documenting steps, and verifying outcomes mitigates errors and reduces stress. Familiarity with the exam interface, types of questions, and common pitfalls ensures that candidates can navigate the assessment efficiently while demonstrating mastery of content.
Lastly, adopting a reflective mindset is critical. After practice exercises or simulated upgrades, administrators should analyze mistakes, identify gaps in understanding, and refine their approach. This iterative cycle of practice, reflection, and correction mirrors the operational realities of Hadoop administration, where continuous learning is indispensable. Engaging with peer communities, forums, and discussion groups also broadens perspectives, introduces rare insights, and exposes aspirants to diverse problem-solving methodologies that are often absent from textbooks.
In sum, succeeding in the CCA-505 exam hinges on a blend of practical dexterity, conceptual understanding, and strategic preparation. Mastery over cluster architecture, upgrade procedures, troubleshooting techniques, security implementations, and performance optimization forms the bedrock of competence. Simulated environments, deliberate practice, and reflective learning consolidate knowledge and enhance confidence. Aspiring administrators who embrace this comprehensive approach cultivate not only the skills required for certification but also the acumen for managing complex Hadoop ecosystems in enterprise scenarios, ensuring both exam success and professional growth.
Developing Expertise in Cluster Management and Upgrade Operations
Successfully navigating the Cloudera CCAH CDH5 Upgrade Exam requires a meticulous approach to cluster management, a deep understanding of Hadoop’s ecosystem, and the ability to anticipate and resolve potential complications before they manifest. The exam evaluates candidates on their capability to manage, upgrade, and troubleshoot enterprise-grade clusters with precision, ensuring data integrity, performance continuity, and service reliability. Achieving mastery in these domains demands a combination of structured preparation, experiential practice, and nuanced comprehension of Hadoop’s operational intricacies.
Understanding the architecture of CDH5 is essential for managing cluster operations effectively. Hadoop’s distributed environment relies on a delicate interplay between multiple daemons, each fulfilling specific roles. The NameNode orchestrates metadata, ensuring that data locations and replication details are accurately maintained, while DataNodes manage the physical storage of data blocks. The ResourceManager and NodeManager facilitate resource allocation, task scheduling, and workload distribution across nodes. Proficiency in recognizing the impact of resource contention, network latency, and storage bottlenecks is critical for maintaining cluster stability during upgrades or high-load scenarios. Candidates should immerse themselves in practical exercises that illustrate how changes to one component can ripple through the entire ecosystem.
Upgrading CDH5 clusters demands a comprehensive strategy that balances caution with efficiency. Prior to initiating an upgrade, administrators must perform a thorough audit of the cluster’s current state, examining service versions, configuration files, dependencies, and the health of all nodes. Identifying potential points of failure in advance allows administrators to design contingency plans that minimize downtime and preserve data integrity. Practicing upgrades in a controlled, non-production environment provides invaluable insights into the sequencing of service restarts, the verification of service interdependencies, and the mitigation of unforeseen errors. Familiarity with Cloudera Manager’s upgrade wizards, logging mechanisms, and rollback procedures is indispensable for this stage.
A profound understanding of service configuration enhances the ability to manage clusters effectively. HDFS parameters, such as block size, replication factor, and name directory locations, can significantly influence storage efficiency and fault tolerance. YARN settings, including memory allocation for containers, queue prioritization, and scheduling policies, impact the cluster’s ability to handle simultaneous jobs. Hive metastore configurations, Pig scripts, and other ecosystem services add layers of complexity that require careful attention. Candidates should engage in methodical exercises that involve modifying configurations, monitoring the resultant performance effects, and documenting their observations. This experiential approach ensures not only familiarity with configuration nuances but also the ability to apply knowledge under exam conditions.
Troubleshooting constitutes a substantial portion of the skills assessed in the CCA-505 exam. Administrators are frequently presented with scenarios in which services are partially functional, metrics indicate anomalous behavior, or logs reveal cryptic errors. The ability to interpret these signals, isolate root causes, and implement corrective actions is critical. For instance, a misconfigured HDFS replication factor may manifest as slow job execution or frequent block errors. Addressing such issues involves more than simply adjusting settings; it requires understanding the interdependencies between services, analyzing logs methodically, and predicting the cascading effects of interventions. By cultivating a systematic problem-solving methodology, candidates can navigate complex scenarios with confidence.
Cluster security and compliance represent another dimension of competence required for the CCAH exam. Administrators must be adept at implementing Kerberos authentication, managing principal identities, applying service-level authorizations, and configuring encryption for data in transit and at rest. The practical application of these concepts often involves generating keytabs, configuring secure service connections, and auditing permissions across multiple services. Understanding the subtleties of user roles, access control lists, and privilege escalation prevents inadvertent service interruptions while maintaining adherence to organizational security standards. Regular hands-on practice in a lab environment helps candidates internalize these procedures, ensuring fluency in both routine and exceptional circumstances.
Monitoring, metrics analysis, and performance tuning are fundamental skills for sustaining an operationally resilient cluster. Administrators must evaluate CPU utilization, memory consumption, network throughput, and disk I/O metrics to identify inefficiencies or potential points of failure. Service-specific indicators, such as HDFS block health, YARN job latency, or Hive query execution times, provide further insight into cluster performance. By systematically adjusting configuration parameters and observing the resulting impact, candidates develop an intuitive understanding of optimal cluster settings. This iterative process of observation, modification, and evaluation cultivates an analytical mindset that proves invaluable during the exam’s practical challenges.
Effective preparation for the CCA-505 exam necessitates the integration of structured study and immersive practice. Official Cloudera documentation, online training modules, and community forums serve as indispensable references. However, comprehension alone is insufficient; success relies on translating theoretical knowledge into applied skills. Establishing a lab environment that replicates production-level clusters enables candidates to experiment with upgrades, configuration modifications, and failure recovery exercises. Recording detailed notes on each exercise, including challenges encountered and strategies employed, reinforces understanding and builds procedural confidence. This methodical approach ensures that candidates can perform tasks reliably under the scrutiny of the exam environment.
Time management, both during preparation and on the exam itself, is a crucial determinant of success. Developing a realistic study plan that allocates time for learning concepts, revisiting complex topics, and engaging in hands-on exercises prevents the inefficiencies of last-minute cramming. During the examination, systematic approaches to scenario-based questions, stepwise documentation of interventions, and deliberate verification of outcomes mitigate errors and reduce cognitive overload. Familiarity with the exam’s interface, expected question formats, and common pitfalls enhances efficiency and reduces anxiety, allowing candidates to demonstrate competence with clarity and precision.
Reflective learning reinforces mastery and fosters adaptive expertise. After completing practical exercises, candidates should analyze their performance, identify gaps in comprehension, and refine their methodologies. Engaging with peer discussions, forums, and knowledge-sharing platforms exposes candidates to rare scenarios, unconventional troubleshooting techniques, and innovative strategies that may not be readily available in standard learning materials. Cultivating this mindset of continuous improvement mirrors the professional demands of Hadoop administration, where clusters are dynamic, workloads are variable, and unexpected challenges arise frequently.
In addition to hands-on practice, cultivating a conceptual map of cluster operations enhances cognitive agility. Understanding the interplay between data storage, resource allocation, job execution, and network latency enables administrators to anticipate potential disruptions and apply corrective measures preemptively. Developing mental models of cluster behavior under diverse workloads, including peak traffic conditions, service failures, and incremental upgrades, enhances decision-making and problem-solving efficiency. These cognitive frameworks, coupled with experiential practice, ensure that candidates are equipped to respond to both predictable and unforeseen challenges during the CCA-505 exam.
Finally, integrating security, performance optimization, and upgrade management into a cohesive operational strategy underscores the holistic nature of Hadoop administration. Administrators must balance the demands of maintaining service availability, safeguarding data, and executing complex upgrades while adhering to organizational policies and best practices. This multidimensional approach not only prepares candidates for the examination but also equips them with the expertise necessary to manage enterprise-level clusters with sophistication and resilience. Through deliberate practice, reflective analysis, and methodical preparation, aspirants cultivate both the technical and cognitive skills essential for success in the CCAH CDH5 Upgrade Exam.
Enhancing Operational Skills and Troubleshooting Techniques
Achieving mastery over the Cloudera CCAH CDH5 Upgrade Exam requires a nuanced understanding of Hadoop’s operational ecosystem and a proficiency in troubleshooting complex cluster scenarios. The examination evaluates not only theoretical comprehension but also the candidate’s capacity to manage distributed environments with precision, ensuring minimal disruption during maintenance, upgrades, or unexpected failures. Excelling in this domain demands deliberate preparation, extensive hands-on experience, and the cultivation of analytical skills capable of discerning subtle anomalies in cluster behavior.
A profound comprehension of cluster topology is fundamental. Hadoop clusters are composed of multiple nodes, each hosting critical services whose interdependencies define the cluster’s operational stability. The NameNode, functioning as the central metadata authority, must be meticulously monitored, while DataNodes handle the granular storage of data blocks. ResourceManager coordinates the allocation of computational resources, and NodeManagers execute tasks assigned to their respective containers. Understanding the intricacies of this interplay allows administrators to anticipate potential bottlenecks and implement proactive measures, ensuring that performance remains consistent even during upgrade operations.
The execution of CDH5 upgrades is a multidimensional process that involves careful pre-upgrade planning, configuration assessment, and validation of service interdependencies. Administrators are required to verify cluster health, check for outdated or incompatible configurations, and ensure that sufficient resources are available to support upgrade operations. Practicing upgrades in a simulated environment equips candidates with the knowledge to sequence service restarts correctly, handle version-specific adjustments, and troubleshoot anomalies without impacting cluster stability. Familiarity with Cloudera Manager’s diagnostic tools, logs, and rollback mechanisms is essential for building confidence in upgrade management.
Operational expertise extends beyond routine maintenance into service configuration management. Parameters such as HDFS block size, replication factor, and storage directories directly influence data reliability and processing efficiency. YARN configurations, including memory allocations, container sizes, and scheduling policies, affect workload distribution and task execution. Hive and Impala service configurations determine query performance and data accessibility. By experimenting with these parameters in controlled scenarios, administrators develop an intuitive understanding of how each adjustment impacts cluster behavior. This practical knowledge is crucial for performing well in scenarios that require immediate troubleshooting and optimization.
Troubleshooting is a critical competency assessed in the exam. Administrators are frequently confronted with clusters exhibiting partial failures, resource contention, or erratic performance. Success depends on the ability to analyze logs methodically, recognize patterns indicative of underlying issues, and implement targeted corrective actions. For instance, a discrepancy in HDFS block replication might manifest as failed MapReduce jobs or intermittent data access errors. Resolving such issues requires a combination of root cause analysis, corrective configuration changes, and verification of results. Cultivating a systematic approach to troubleshooting reduces response time, enhances reliability, and instills confidence in dynamic exam scenarios.
Cluster security management is an integral element of operational proficiency. Administrators must implement Kerberos authentication, configure secure service connections, manage principal identities, and enforce permissions across HDFS and related services. Data encryption both in transit and at rest ensures compliance with organizational policies and mitigates risk. Effective security management also involves auditing access, detecting anomalies, and applying remedial measures when necessary. Hands-on exercises that simulate security breaches or misconfigurations enhance the candidate’s readiness to address these challenges during the examination.
Performance monitoring and optimization are additional pillars of cluster administration. Administrators must track CPU utilization, memory consumption, disk I/O, and network throughput to detect inefficiencies. Service-specific metrics such as HDFS block health, YARN container utilization, and query execution latency provide insight into operational performance. By adjusting configurations, reallocating resources, and optimizing scheduling policies, administrators can enhance throughput and ensure that clusters operate efficiently under variable workloads. Regular practice in interpreting metrics and applying corrective measures fosters an analytical mindset that is indispensable for the CCA-505 exam.
Time management during preparation and examination scenarios is crucial. Developing a structured study plan that balances theoretical learning, configuration exercises, and troubleshooting drills ensures comprehensive readiness. During the exam, methodical documentation of steps, verification of intermediate results, and sequential problem-solving enhance efficiency and accuracy. Familiarity with the types of practical tasks and the pacing required for complex scenarios allows candidates to demonstrate skill while maintaining composure under time constraints.
Reflective learning reinforces operational mastery. After conducting upgrades, troubleshooting exercises, or configuration changes, administrators should analyze the outcomes, identify mistakes, and refine their approach. Engaging with professional communities, forums, and discussion groups introduces rare insights, innovative solutions, and uncommon scenarios that may not be evident from standard documentation. This iterative cycle of practice, reflection, and adaptation develops the cognitive flexibility necessary to tackle unpredictable challenges, both in the exam environment and in real-world cluster management.
Understanding the dependencies between various Hadoop services enhances an administrator’s ability to predict and mitigate potential issues. For example, modifications in HDFS can directly impact MapReduce or Spark jobs, while changes in YARN scheduling policies may influence Hive query execution. Recognizing these interdependencies allows administrators to sequence tasks correctly during upgrades and to implement changes without triggering cascading failures. Such comprehension is cultivated through repeated practice, observation of outcomes, and meticulous note-taking on the impact of each adjustment.
In addition, proficiency in using Cloudera Manager to monitor, diagnose, and optimize cluster operations is essential. This tool provides centralized visibility into service health, configuration discrepancies, and resource utilization. Administrators must interpret dashboards, evaluate alert thresholds, and prioritize remediation efforts based on severity and potential impact. Hands-on interaction with Cloudera Manager, coupled with simulated operational scenarios, reinforces the ability to respond quickly and effectively under exam conditions.
Data governance and auditing form another dimension of competence. Administrators are expected to track data lineage, manage access controls, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements. Understanding audit logs, implementing monitoring policies, and enforcing user permissions across services ensures that clusters remain secure and accountable. Practice in applying these governance measures prepares candidates to address exam scenarios that simulate real-world administrative responsibilities, reinforcing both technical and procedural knowledge.
The integration of all these skills—configuration mastery, troubleshooting acumen, performance optimization, security management, and governance—creates a holistic operational competence. Candidates who approach preparation strategically, combining theoretical understanding with immersive hands-on practice, develop the versatility needed to respond to diverse challenges. Through repeated engagement with practical exercises, analysis of errors, and refinement of methodologies, administrators cultivate both confidence and proficiency, positioning themselves to excel in the Cloudera CCAH CDH5 Upgrade Exam.
Emphasizing hands-on experimentation reinforces conceptual understanding. Administrators should replicate production scenarios in lab environments, performing upgrades, service restarts, configuration adjustments, and simulated failure recovery exercises. Documenting these exercises, noting observed behaviors, and reflecting on corrective strategies solidifies knowledge and strengthens procedural memory. Such immersive practice, combined with analytical reflection, builds a robust foundation for responding effectively to the dynamic and practical challenges posed in the examination.
Advanced Techniques for Cluster Optimization and Maintenance
Excelling in the Cloudera CCAH CDH5 Upgrade Exam requires an intricate blend of operational expertise, strategic foresight, and practical experience. The evaluation emphasizes the candidate’s capability to manage, maintain, and optimize Hadoop clusters while performing upgrades and troubleshooting issues in a live environment. Achieving mastery in this realm necessitates a disciplined preparation strategy that intertwines theoretical comprehension with hands-on experimentation, ensuring that administrators can maintain system integrity, efficiency, and resilience throughout complex operational tasks.
A fundamental aspect of cluster management involves understanding the delicate architecture of CDH5. Hadoop’s distributed design relies on a cohesive interaction between daemons such as the NameNode, which manages metadata, and DataNodes, responsible for storing the actual data blocks. ResourceManager orchestrates task scheduling, while NodeManagers allocate computational resources to individual jobs. Proficiency in analyzing this network of interactions allows administrators to identify potential bottlenecks, anticipate failure points, and implement measures that optimize throughput and reliability. Practicing with varying workloads enhances the ability to manage these dynamics effectively.
Performing a CDH5 upgrade demands meticulous planning and an intimate knowledge of cluster behavior. Administrators must first conduct a comprehensive audit of the cluster, evaluating current service versions, configurations, and node health. This process also involves identifying dependencies between services and assessing the readiness of the system for an upgrade. Simulation of the upgrade in a lab environment enables candidates to experience real-world scenarios, observe the consequences of sequencing errors, and develop corrective strategies. Understanding rollback procedures, managing upgrade logs, and anticipating configuration conflicts are pivotal to executing seamless upgrades.
Service configuration management constitutes another critical competency. HDFS parameters, including replication factor, block size, and storage directory allocation, play a crucial role in data durability and processing performance. YARN configuration, covering memory limits, container sizes, and scheduling policies, influences task allocation and cluster efficiency. Services such as Hive, Impala, and Pig have their own specific parameters affecting query execution, data accessibility, and job performance. Through systematic experimentation with these configurations, administrators gain a nuanced understanding of the interplay between service parameters and cluster behavior, enabling them to troubleshoot efficiently and optimize operations.
Troubleshooting is an essential skill evaluated in the exam. Administrators often encounter clusters exhibiting performance degradation, partial service failures, or inconsistent job executions. Success in such scenarios requires the ability to interpret diagnostic logs, recognize patterns indicative of systemic issues, and implement targeted corrective measures. For instance, misalignment in HDFS replication may lead to frequent job failures, while misconfigured YARN queues could cause resource contention across multiple jobs. Cultivating a methodical approach to identifying root causes and applying corrective actions is vital for ensuring reliable cluster operations under pressure.
Security and compliance are integral components of cluster administration. Implementing Kerberos authentication, managing service principals, and configuring access permissions are essential for maintaining secure environments. Administrators must also ensure encryption of data both at rest and in transit, adhere to organizational policies, and monitor audit logs for anomalous activity. Engaging in practical exercises that simulate permission misconfigurations, service breaches, or unauthorized access helps candidates internalize security protocols and prepares them to handle similar scenarios during the examination.
Performance monitoring and tuning form another pillar of effective cluster management. Administrators are expected to analyze CPU utilization, memory allocation, disk I/O, and network throughput to detect inefficiencies. Service-specific metrics such as HDFS block health, YARN container utilization, and query execution time provide deeper insight into cluster performance. Adjusting configurations, redistributing workloads, and fine-tuning scheduling policies are critical to maintaining optimal throughput. Repeated practice in performance analysis cultivates an analytical mindset, enabling administrators to identify bottlenecks quickly and implement sustainable optimizations.
Effective preparation integrates structured learning with immersive hands-on practice. Candidates benefit from studying Cloudera’s official documentation, exploring online training resources, and engaging with community discussions. Yet comprehension alone is insufficient; translating knowledge into practical skill is essential. Establishing lab environments that mirror production-level clusters allows administrators to simulate upgrades, modify configurations, and conduct failure recovery drills. Documenting each exercise, analyzing outcomes, and noting lessons learned strengthens both procedural memory and conceptual understanding, which are indispensable during the exam.
Time management is crucial both in preparation and during the examination. Developing a structured study schedule that balances conceptual learning, configuration exercises, and troubleshooting simulations ensures comprehensive readiness. During the exam, a methodical approach—careful documentation, sequential problem-solving, and verification of intermediate results—enhances accuracy and efficiency. Familiarity with the format and pacing of the examination allows candidates to allocate their time judiciously, ensuring they can navigate complex scenarios without unnecessary delays or stress.
Reflective learning is a vital component of skill consolidation. After completing practical exercises, administrators should review their performance, identify gaps in understanding, and refine strategies accordingly. Engaging with professional forums and discussion groups exposes candidates to unconventional solutions, rare troubleshooting techniques, and atypical scenarios that may not be documented in official materials. This iterative cycle of practice, reflection, and adaptation builds resilience and cognitive agility, equipping administrators to handle unpredictable challenges effectively both in the exam and in operational contexts.
Understanding service interdependencies further enhances operational competence. Adjustments in HDFS can influence MapReduce and Spark jobs, while YARN scheduling changes can affect Hive queries. Recognizing these interconnections ensures that administrators implement changes without inducing cascading failures. Repeated experimentation, coupled with careful observation of outcomes, fosters a deep comprehension of service dynamics, which is crucial for executing upgrades and troubleshooting efficiently.
Cloudera Manager serves as an indispensable tool in monitoring, diagnosing, and optimizing clusters. Administrators must interpret dashboards, track metrics, and prioritize remediation actions based on severity and impact. Practical familiarity with Cloudera Manager, combined with simulated operational exercises, reinforces the ability to respond effectively under time constraints. Candidates who develop proficiency with this tool gain a tactical advantage in the exam, as they can quickly identify issues, implement solutions, and validate outcomes with confidence.
Data governance and auditing are also critical elements of cluster administration. Administrators must manage access controls, track data lineage, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Applying governance policies, monitoring audit logs, and enforcing permissions across services maintains cluster security and accountability. Practicing these tasks in a lab environment allows candidates to experience the operational implications of governance policies and prepares them for examination scenarios that simulate enterprise-level responsibilities.
The integration of configuration management, troubleshooting acumen, performance optimization, security enforcement, and governance forms the foundation of comprehensive operational expertise. Candidates who combine theoretical understanding with immersive, reflective practice cultivate the versatility and judgment required to manage dynamic, distributed environments. Through repeated exercises, analysis of errors, and refinement of methodologies, administrators build both confidence and proficiency, positioning themselves to excel in the Cloudera CCAH CDH5 Upgrade Exam.
Advanced Troubleshooting and Performance Management in Hadoop Clusters
Navigating the Cloudera CCAH CDH5 Upgrade Exam requires a sophisticated grasp of Hadoop cluster operations, an acute ability to troubleshoot anomalies, and a refined understanding of performance optimization techniques. The examination evaluates the candidate’s capability to manage enterprise-grade clusters effectively, execute upgrades with precision, and ensure system resiliency in complex environments. Achieving success demands a methodical approach that combines theoretical knowledge, practical application, and the cultivation of analytical acumen capable of identifying subtle inefficiencies within distributed systems.
A deep understanding of the Hadoop cluster architecture is imperative for managing upgrades and operational tasks efficiently. The NameNode, as the metadata authority, governs the mapping of file blocks to DataNodes, ensuring consistency and accessibility. DataNodes handle the physical storage of blocks, while the ResourceManager oversees job scheduling, and NodeManagers allocate computational resources to containers. Mastery of these components and their interrelations enables administrators to anticipate potential bottlenecks and mitigate performance degradation, particularly during high-demand workloads or incremental upgrades. Experiential practice with varied cluster topologies is instrumental in reinforcing this comprehension.
Executing a CDH5 upgrade necessitates thorough pre-upgrade evaluation. Administrators must perform a detailed audit of the cluster’s configuration, verify service compatibility, and assess node health to ensure a seamless transition. Laboratory simulations of upgrades provide a controlled environment for practicing service sequencing, detecting misconfigurations, and executing rollback procedures when anomalies arise. Understanding the intricacies of version compatibility, dependency management, and service interrelationships enhances the administrator’s ability to manage upgrades without compromising data integrity or operational continuity.
Service configuration management is another pillar of expertise. Hadoop’s ecosystem relies on meticulous parameterization, including HDFS block size, replication factor, and storage directories, which directly impact data durability and cluster performance. YARN settings, encompassing memory allocation, container sizing, and scheduling policies, influence task execution and job throughput. Additional services, such as Hive, Impala, and Pig, introduce further configuration nuances affecting query performance and data accessibility. Systematic experimentation and careful observation of changes enable administrators to develop intuitive insights into the consequences of parameter modifications, which is critical for both exam scenarios and real-world administration.
Troubleshooting complex cluster issues is a core competency examined in the CCAH certification. Administrators encounter situations such as partial service failures, latency spikes, or unexpected job terminations. Effective resolution requires a structured approach to log analysis, root cause identification, and targeted corrective action. For instance, an HDFS replication imbalance may manifest as job failures or inconsistent query results, necessitating careful adjustment of replication parameters and verification of block health. Similarly, misconfigurations in YARN queues may induce resource contention, requiring dynamic reassignment of resources to restore equilibrium. Repeated engagement with such scenarios develops problem-solving acuity and procedural efficiency.
Security and governance management are integral components of cluster administration. Implementing Kerberos authentication, managing principal identities, enforcing access controls, and configuring data encryption ensures both operational security and regulatory compliance. Administrators must monitor audit logs, detect anomalous behavior, and remediate unauthorized access promptly. Hands-on exercises simulating misconfigurations or security breaches cultivate fluency in security protocols and prepare candidates to navigate the examination’s security-focused tasks effectively.
Performance monitoring and tuning represent a critical dimension of operational excellence. Administrators must interpret metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, disk I/O, and network throughput to identify potential bottlenecks. Service-specific indicators, including HDFS block health, YARN container efficiency, and query execution latency, provide granular insights into cluster performance. Strategic adjustments to configurations, container allocations, and scheduling policies enable optimization of throughput and workload balance. Repeated practice in monitoring and tuning cultivates analytical rigor and enhances the administrator’s ability to maintain performance under variable workloads.
Preparation for the CCAH exam involves both structured study and immersive hands-on practice. Candidates benefit from exploring Cloudera documentation, training modules, and community discussions, yet translating theoretical understanding into applied skill is paramount. Creating laboratory environments that replicate production clusters allows for simulation of upgrades, service restarts, configuration modifications, and recovery from failures. Meticulous documentation of these exercises, coupled with reflection on outcomes, reinforces learning and builds procedural confidence, ensuring readiness for practical examination scenarios.
Time management is essential for both preparation and examination execution. Developing a balanced study schedule that integrates conceptual learning, configuration exercises, and troubleshooting practice prevents last-minute cramming and promotes retention. During the exam, methodical approaches—sequenced problem-solving, careful documentation of steps, and verification of results—enhance efficiency and accuracy. Familiarity with the exam format and pacing allows candidates to tackle complex scenarios confidently, mitigating stress and avoiding oversight.
Reflective practice consolidates operational expertise. After performing upgrades, troubleshooting exercises, or configuration experiments, administrators should evaluate results, identify areas for improvement, and refine strategies accordingly. Engaging with professional forums and discussion groups exposes candidates to unconventional solutions, rare technical challenges, and uncommon approaches to problem-solving. This iterative cycle of practice, analysis, and adaptation develops cognitive flexibility, ensuring preparedness for unpredictable challenges both in the examination and in professional Hadoop administration.
Recognizing service interdependencies enhances operational foresight. Changes in HDFS can influence MapReduce, Spark, or Hive operations, while YARN scheduling modifications may affect container allocation and job execution. Awareness of these interconnections ensures administrators implement adjustments without inducing cascading failures, a skill particularly valuable during upgrade operations. Repeated practice in simulated environments cultivates the ability to predict outcomes and maintain cluster stability under diverse conditions.
Proficiency in Cloudera Manager is indispensable for effective cluster monitoring and management. Administrators must interpret dashboards, evaluate service metrics, identify discrepancies, and prioritize remediation based on impact. Familiarity with the tool’s alerting mechanisms, logs, and configuration management capabilities enhances the speed and accuracy of problem resolution. Practical exposure through lab exercises equips candidates to respond efficiently during the exam, enabling them to navigate complex scenarios with confidence and precision.
Data governance and auditing are critical to maintaining compliance and operational integrity. Administrators must implement access controls, track data lineage, and monitor audit logs to prevent unauthorized activity and ensure accountability. Laboratory practice in applying governance policies and simulating audit scenarios reinforces procedural knowledge and prepares candidates for practical examination challenges. Integrating governance into daily operations fosters both security awareness and operational competence, essential for managing enterprise-level clusters.
The synthesis of configuration mastery, troubleshooting ability, performance optimization, security enforcement, and governance management forms the foundation of comprehensive Hadoop administration expertise. Candidates who integrate theory with immersive, reflective practice cultivate the adaptability, precision, and analytical acumen required to manage dynamic distributed systems successfully. Through repeated engagement with practical exercises, evaluation of errors, and refinement of techniques, administrators develop the competence and confidence necessary to excel in the Cloudera CCAH CDH5 Upgrade Exam and in professional operational contexts.
Mastering Cluster Upgrades, Optimization, and Troubleshooting
The culmination of preparation for the Cloudera CCAH CDH5 Upgrade Exam revolves around consolidating operational expertise, mastering complex troubleshooting, and refining optimization techniques within Hadoop clusters. The exam evaluates administrators’ ability to perform seamless upgrades, sustain cluster performance, and resolve intricate issues that arise in distributed computing environments. Success requires a multifaceted approach, blending theoretical understanding, hands-on experimentation, and a reflective mindset capable of learning from iterative exercises and real-world scenarios.
A comprehensive understanding of the Hadoop cluster architecture is the cornerstone of operational excellence. The NameNode functions as the authoritative metadata manager, overseeing file block mapping across DataNodes, which provide distributed storage. ResourceManager orchestrates task scheduling across NodeManagers, which allocate computational resources to jobs and containers. Mastery of these components and their interactions allows administrators to anticipate bottlenecks, identify performance anomalies, and maintain stability during high-demand workloads or upgrade procedures. Hands-on engagement with clusters of varying sizes and topologies reinforces comprehension of operational dynamics and enhances practical readiness.
Executing CDH5 upgrades successfully necessitates careful pre-upgrade assessment. Administrators must audit cluster health, verify service compatibility, and evaluate node readiness. Laboratory simulations of upgrade scenarios provide the opportunity to practice sequencing service restarts, managing configuration conflicts, and employing rollback mechanisms when deviations occur. Familiarity with the nuances of version compatibility and interdependent services ensures that upgrades proceed smoothly, minimizing downtime and preserving data integrity. Repeated practice under controlled conditions builds procedural fluency, reducing the risk of errors during the actual exam.
Service configuration is another critical dimension of expertise. HDFS parameters, including replication factor, block size, and storage directories, influence data durability and performance efficiency. YARN configurations, encompassing container sizing, memory allocations, and scheduling policies, determine task execution effectiveness and job throughput. Hive, Impala, and other ecosystem services introduce additional configuration intricacies that impact query speed and resource allocation. Systematic experimentation with these parameters fosters an intuitive understanding of their effects on cluster behavior, enhancing the administrator’s ability to troubleshoot and optimize performance during practical assessments.
Troubleshooting complex issues is a core skill assessed in the exam. Administrators often face partial service failures, latency spikes, or unexpected job terminations. Effective troubleshooting demands methodical log analysis, pattern recognition, and targeted corrective actions. For example, an imbalance in HDFS replication can result in job failures or data accessibility issues, requiring precise adjustments and validation. Misconfigured YARN queues can cause resource contention, which necessitates strategic reassignment of resources and careful observation of performance changes. Repeated exposure to such scenarios in practice environments develops analytical acumen, procedural confidence, and the ability to respond swiftly under exam conditions.
Security management and compliance constitute another essential facet of cluster administration. Administrators must implement Kerberos authentication, configure secure service connections, manage principal identities, and enforce permissions across HDFS and other services. Encryption of data in transit and at rest, coupled with rigorous audit log monitoring, ensures both security and adherence to organizational policies. Simulating security misconfigurations or unauthorized access in lab exercises builds fluency in remediation procedures and prepares candidates to address practical exam challenges with confidence and precision.
Performance monitoring and optimization are critical for maintaining cluster efficiency. Administrators should analyze metrics such as CPU and memory utilization, disk throughput, and network performance to detect inefficiencies. Service-specific indicators, including HDFS block health, YARN container allocation, and query execution times, provide granular insights into operational performance. Adjusting configuration parameters, rebalancing workloads, and fine-tuning scheduling policies enhances throughput and maintains operational equilibrium. Repeated practice in interpreting performance data and implementing optimizations cultivates a systematic approach to cluster management that is invaluable for both the exam and professional practice.
Effective preparation integrates structured study with immersive hands-on exercises. Candidates benefit from reviewing Cloudera documentation, online tutorials, and community resources; however, true mastery comes from translating theoretical understanding into applied skills. Setting up laboratory environments that mirror production clusters allows administrators to simulate upgrades, perform service restarts, modify configurations, and recover from failure scenarios. Recording observations, analyzing outcomes, and reflecting on lessons learned consolidates knowledge, reinforces procedural memory, and enhances readiness for practical exam tasks.
Time management plays a pivotal role in both preparation and execution. Developing a balanced study plan that accommodates conceptual learning, configuration practice, and troubleshooting exercises prevents last-minute cramming and ensures comprehensive coverage. During the exam, sequential problem-solving, careful documentation of interventions, and verification of intermediate results enhance efficiency and accuracy. Familiarity with the exam interface, question types, and expected outcomes enables candidates to navigate complex scenarios with confidence while mitigating stress and cognitive overload.
Reflective learning strengthens proficiency and adaptive expertise. After practical exercises, administrators should review successes and failures, identify knowledge gaps, and refine operational strategies. Engaging with professional forums, user groups, and community discussions exposes candidates to unconventional solutions, rare problem-solving techniques, and scenarios not covered in official documentation. This iterative practice of experimentation, reflection, and adaptation fosters cognitive flexibility, preparing administrators to handle unpredictable challenges during the examination and in real-world operational environments.
Service interdependencies are crucial for anticipating potential complications. Adjustments in HDFS may affect MapReduce, Spark, or Hive operations, while YARN scheduling modifications influence container allocation and job execution. Recognizing these interconnections allows administrators to implement configuration changes without triggering cascading failures. Laboratory simulations and iterative testing reinforce understanding of these dependencies and enable administrators to make informed, proactive decisions during upgrades or troubleshooting.
Proficiency in using Cloudera Manager is vital for centralized monitoring, diagnosis, and optimization. Administrators must interpret service dashboards, identify discrepancies, and prioritize remediation based on impact. Practical familiarity with alert thresholds, log analysis, and configuration adjustments enhances speed and accuracy in responding to operational challenges. Consistent practice with Cloudera Manager equips candidates to handle practical exam scenarios efficiently, demonstrating both skill and confidence in their administrative abilities.
Data governance and auditing underpin operational integrity and compliance. Administrators should implement access controls, monitor audit logs, and track data lineage to prevent unauthorized activities and ensure accountability. Laboratory exercises involving governance and compliance policies reinforce procedural knowledge, allowing candidates to address practical exam scenarios effectively. Integrating governance into routine operations fosters security awareness and operational discipline, essential for both examination performance and real-world cluster management.
The integration of configuration mastery, troubleshooting proficiency, performance optimization, security enforcement, and governance awareness constitutes comprehensive operational expertise. Administrators who combine theoretical understanding with practical, reflective practice cultivate the versatility, judgment, and analytical skills required to manage dynamic, distributed Hadoop environments successfully. Repeated engagement with hands-on exercises, critical analysis of outcomes, and refinement of methodologies ensures that candidates are not only well-prepared for the CCAH CDH5 Upgrade Exam but also equipped to excel in professional operational contexts.
Conclusion
In passing the Cloudera CCAH CDH5 Upgrade Exam requires a harmonious blend of conceptual knowledge, applied skills, and strategic problem-solving. Mastery over cluster architecture, upgrade procedures, service configuration, troubleshooting, performance optimization, security protocols, and governance forms the foundation of success. Immersive practice in simulated environments, coupled with reflective learning and analysis, reinforces operational proficiency and builds confidence. Administrators who embrace this comprehensive, iterative approach cultivate both the technical expertise and the analytical acumen necessary to excel in the examination while establishing the capabilities required for managing complex enterprise-level Hadoop clusters effectively.