Exam Code: CCD-410
Exam Name: Cloudera Certified Developer for Apache Hadoop (CCDH)
Certification Provider: Cloudera
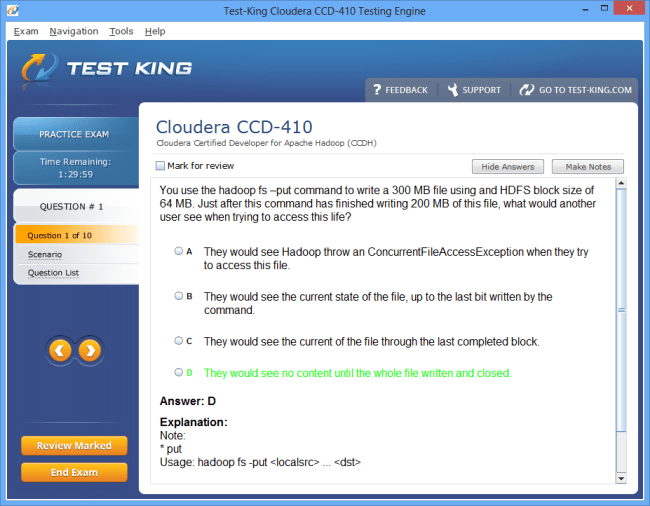
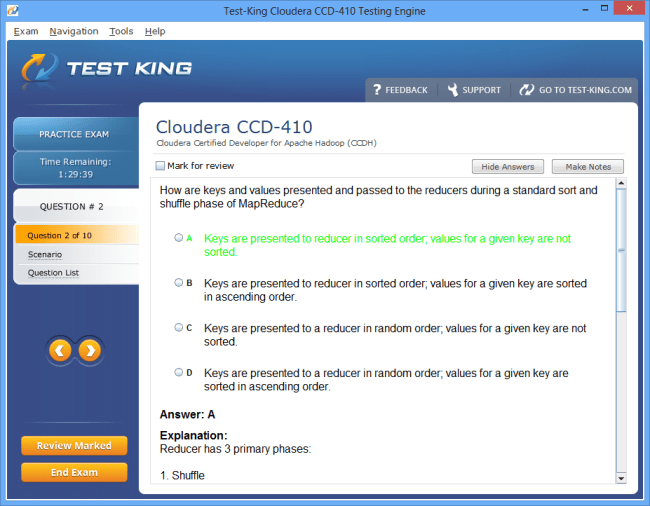
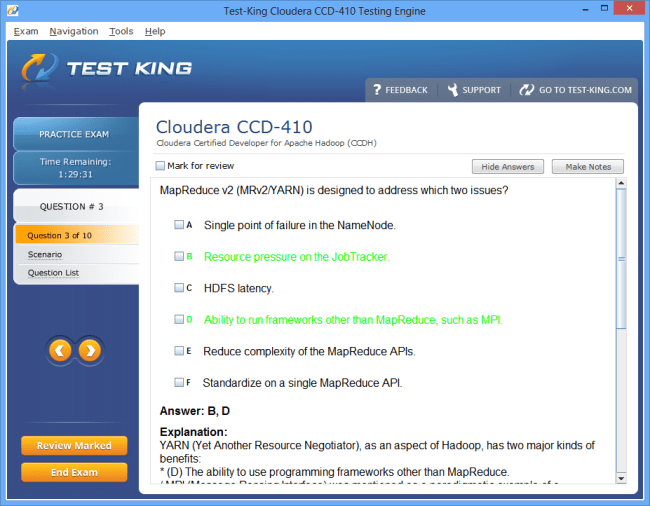
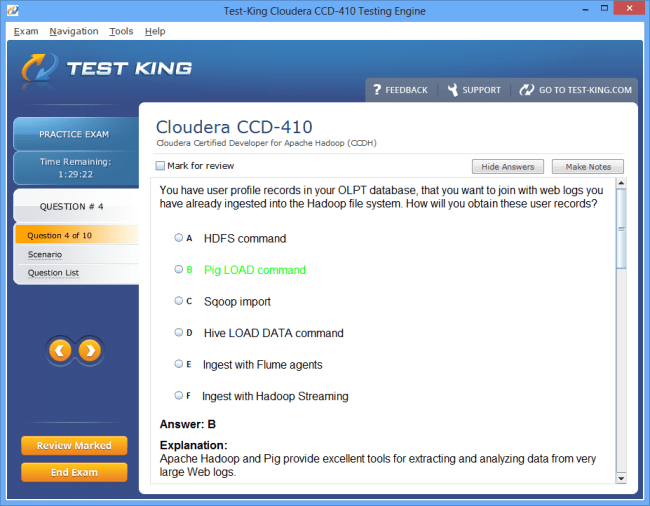
CCD-410 Exam Product Screenshots
Product Reviews
Outstanding study material
"Selecting an outstanding material with rich content is important for the CCD-410 exam. I selected test-king because of its excellent service and support. It covered all the exam oriented topics like Mapreduce and all. The Q&A materials are explained in detail. This orientations reduced my preparation time and helped me concentrate on own work. It is the best product that I have ever seen. So a hearty thanks, especially for the test-king professional and their team.
Jim Bechtold,
Barcelona, Spain."
Helped me significantly
"The test-king product was an important step to achieve in Cloudera Certified Developer for Apache Hadoop exam. The high value of the solution and its explanation for the Q&A material has also enabled me to launch myself with subject knowledge. Their capabilities in demonstration on Hadoop ecosystem and its answers helped me significantly. The depth and breadth in the skill sets of their professional helped me to achieve in my CCD-410 exam. Thanks a lot team.
Cathryn Riley,
Adygeysk, Russia."
Cleared my difficulties
"HDFS architecture is one among the necessary topic in the CCD-410 exam. The only material that has detailed orientation on this topic was Test-king only. The Q&A helped to grasp the concept and subject knowledge in a short time period. It cleared my doubts and difficulties on this subject. There are no words to describe your perfect material. Please pass my thanks and well wishes to the entire group. Sure I will use this for my upcoming exams too.
Ian Floyed,
Chongjin, North Korea."
Offline support to all
"The technical knowledge is the added plus point of the test-king's Q&A study material. In my CCD-410 exam it helped me to prepare without any difficulties and trouble. In such a way they explained the question and answers in the material on the HiveQL statement topic. I and my friend are happy with the resource which provide material for me. I would be happy to recommend this to anyone. Keep up your good work guys.
Cecilia Callmer,
Changwon, South Korea."
Grateful to you
"I have used test-kings Q&A study material for the CCD-410 exam. I must say there is no material available in the market like this. I have seen students prepare with some other resources and they never give good result like me. It is the only best resource for this which were a great help in preparing for this exam. I also highly recommend Professional Hadoop Solutions by Boris Lublinsky book for this exam who wants to score more.
Ken Lever,
Bengbu, China."
Reliable material
"Test-king's Q&A is the reliable material where you can start to study for CCD-410 exam. The material are specially designed by the experts with years of experience. It covered the syllabus with all the important topic for the Cloudera Certified Developer for Apache Hadoop (CCDH) exam. I really appreciate the way you handled the questions in the study material. It was a helpful material for the slow learners like me. I attended the entire 50 plus questions in the exam.
Oday Abbosh,
Jeddah, Saudi Arabia"
Helped out tremendously
"You guys are really rocking. Whenever I use your study material I am able to perform well in the examination very professionally. Recently I used it for the CCD-410 exam, I answered all the questions in just 80 minutes in the given time duration just because of test-king Q&A detailed study material. This worked so well for me. Thanks a bunch test-king for all your support and help. Thank you providing such a helpful material.
Mike Maxwell,
Tsukuba, Japan."
Extremely fast preparation
"The exam study material available in the test-king Q&A product really helps me in an extremely fast preparation. I just tried this for my CCD-410 exam. I just used their material for 10 days during my preparation. The answered are explained, detailed in their material which helps me to grasp the knowledge as well as conceptualized in the short time. The minimum pass mark for this exam was 70, but I have scored 85 marks which is unbelievable.
Shawn,
Charleville-Mezieres, France."
Right choice for this exam
"The test-king's Q&A study material is the right choice for the CCD-410 exam. I was worried about the time duration in this exam. Because I have to complete 50-55 questions in just 90 minutes time limit. But their study material helps to manage the given time with the help of the shortcut methods they used in the material. It tackles all my worries and I completed my exam in 85 minutes. It was really an amazing experience for me.
Mike Gatio,
Nanxiong, China."
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get the products after purchase?
All products are available for download immediately from your Member's Area. Once you have made the payment, you will be transferred to Member's Area where you can login and download the products you have purchased to your computer.
How long can I use my product? Will it be valid forever?
Test-King products have a validity of 90 days from the date of purchase. This means that any updates to the products, including but not limited to new questions, or updates and changes by our editing team, will be automatically downloaded on to computer to make sure that you get latest exam prep materials during those 90 days.
Can I renew my product if when it's expired?
Yes, when the 90 days of your product validity are over, you have the option of renewing your expired products with a 30% discount. This can be done in your Member's Area.
Please note that you will not be able to use the product after it has expired if you don't renew it.
How often are the questions updated?
We always try to provide the latest pool of questions, Updates in the questions depend on the changes in actual pool of questions by different vendors. As soon as we know about the change in the exam question pool we try our best to update the products as fast as possible.
How many computers I can download Test-King software on?
You can download the Test-King products on the maximum number of 2 (two) computers or devices. If you need to use the software on more than two machines, you can purchase this option separately. Please email support@test-king.com if you need to use more than 5 (five) computers.
What is a PDF Version?
PDF Version is a pdf document of Questions & Answers product. The document file has standart .pdf format, which can be easily read by any pdf reader application like Adobe Acrobat Reader, Foxit Reader, OpenOffice, Google Docs and many others.
Can I purchase PDF Version without the Testing Engine?
PDF Version cannot be purchased separately. It is only available as an add-on to main Question & Answer Testing Engine product.
What operating systems are supported by your Testing Engine software?
Our testing engine is supported by Windows. Andriod and IOS software is currently under development.
Top Skills Tested in the CCDH Certification (CCD-410) and How to Master Them
The Cloudera Certified Developer for Apache Hadoop, commonly referred to by its exam code CCD-410, is an esteemed credential that validates the practical proficiency and conceptual understanding required to work with the Hadoop ecosystem. In an era dominated by big data and distributed computing, possessing a thorough comprehension of Hadoop frameworks is no longer a mere advantage; it has become a professional imperative. Organizations are increasingly reliant on the ability to ingest, process, and analyze massive datasets efficiently, and the CCDH certification serves as a testament to one’s capacity to navigate these intricate landscapes. Unlike theoretical certifications, this examination is designed to probe both conceptual knowledge and practical skills, compelling aspirants to demonstrate real-world problem-solving abilities, from data ingestion to workflow orchestration and advanced analytics.
Understanding the CCD-410 Exam and Its Significance
Candidates preparing for this certification are expected to master a myriad of skills, ranging from the understanding of Hadoop Distributed File System and MapReduce to practical expertise in Hive, Pig, Spark, and Impala. The examination is not merely an assessment of rote learning; it evaluates one’s aptitude in applying theoretical knowledge in practical contexts, often requiring a dexterous balance between analytical reasoning and technical acumen. The CCD-410 exam, therefore, occupies a pivotal role in certifying developers who are capable of architecting, deploying, and optimizing large-scale data solutions in enterprise environments. The mastery of this certification can open doors to positions such as data engineer, Hadoop developer, or big data consultant, where the ability to manage complex datasets is indispensable.
In preparation for this exam, candidates need to cultivate a blend of skills that encompass not only the technical understanding of Hadoop and its components but also the finesse to troubleshoot and optimize workflows. The intricacies of the Hadoop ecosystem are vast; from understanding the nuances of the HDFS architecture to leveraging YARN for resource management, a candidate must navigate a labyrinth of concepts that interconnect to form a cohesive data processing environment. Those who succeed in mastering these skills gain not just a certificate but a cognitive framework for thinking about large-scale data problems, enabling them to design robust and scalable solutions in professional contexts.
Core Knowledge Areas and Practical Expertise
The examination evaluates several fundamental domains of the Hadoop ecosystem, beginning with the Hadoop Distributed File System, which forms the backbone of large-scale data storage. HDFS is architected to distribute massive volumes of data across a cluster of commodity hardware, ensuring both redundancy and fault tolerance. A developer must comprehend the mechanics of data replication, block management, and the trade-offs involved in balancing storage efficiency with resiliency. Beyond the theoretical understanding, practical expertise involves being able to interact with HDFS, efficiently manage directories, and troubleshoot common errors that arise during data ingestion or retrieval.
MapReduce, the original programming model of Hadoop, remains a critical component of the exam. Its paradigm emphasizes the decomposition of tasks into discrete mappable units that can be processed in parallel, followed by a reduction phase that aggregates the results. Understanding the lifecycle of a MapReduce job, from input splits to task scheduling, is vital. Candidates are expected to visualize how data flows through the system, how keys and values are shuffled and sorted, and how performance bottlenecks can be mitigated. Developing an intuitive grasp of MapReduce requires both conceptual study and hands-on practice, as exam questions often present scenarios where optimal job configuration and resource utilization must be determined.
YARN, which stands for Yet Another Resource Negotiator, is another indispensable skill area. YARN provides a generalized resource management framework, allowing multiple processing engines to operate simultaneously within a Hadoop cluster. A candidate should be able to explain how YARN schedules resources, monitors node health, and manages application lifecycles. Understanding YARN is not merely about memorizing its components but about recognizing how it interacts with MapReduce, Spark, and other processing frameworks to optimize throughput and ensure cluster stability.
The Hadoop ecosystem extends beyond these core components, encompassing tools like Hive, Pig, HBase, and Spark. Hive serves as a data warehouse infrastructure that provides an SQL-like interface to query data stored in HDFS, translating declarative queries into optimized execution plans. Pig, in contrast, offers a scripting language, Pig Latin, that allows for flexible data transformations and workflow definitions. HBase provides low-latency access to sparse datasets, complementing HDFS for specific use cases, while Spark introduces in-memory computation to accelerate large-scale data processing. Each of these tools requires not only familiarity with syntax but also a deep understanding of performance implications, data modeling strategies, and integration possibilities. In the examination, candidates may encounter scenario-based questions requiring them to select appropriate tools or design workflows that meet specified performance and scalability requirements.
Data Ingestion, Transformation, and Workflow Optimization
A significant portion of the CCDH certification emphasizes the ability to manage data pipelines effectively. Data ingestion from heterogeneous sources, including relational databases, log files, streaming sources, and external APIs, is a critical skill. Candidates must demonstrate the capacity to handle varying data formats, address inconsistencies, and preprocess data for downstream analysis. Transforming raw data into structured formats often involves the use of Pig or Hive scripts, and successful candidates must show an understanding of optimization strategies, such as minimizing redundant reads, leveraging partitioning, and employing indexing techniques where applicable.
Workflow orchestration is another area of importance. In practical environments, data pipelines are rarely linear; they involve conditional logic, error handling, and dependency management. Developers are expected to design workflows that are robust, fault-tolerant, and maintainable. The ability to anticipate failure modes, implement retries, and log execution details is indicative of mastery. In addition, performance tuning, such as configuring memory allocation, optimizing join operations, and selecting appropriate file formats, is a recurring theme in the examination. Candidates who cultivate a mental model of data flows and resource utilization are better equipped to answer scenario-based questions that probe their practical decision-making skills.
Hive and Pig Proficiency
The ability to work effectively with Hive and Pig represents another pivotal skill assessed in the CCD-410 exam. Hive abstracts the complexity of MapReduce by allowing users to write declarative queries, but optimal use requires understanding the underlying execution plan, indexing options, partitioning strategies, and storage formats. Knowledge of Hive is evaluated through questions that present realistic business scenarios, where candidates must determine the most efficient query design, identify potential bottlenecks, and propose enhancements to improve runtime performance. Understanding data types, functions, and the nuances of HiveQL is essential, as the exam tests both correctness and efficiency.
Pig, with its scripting language, complements Hive by enabling developers to express complex transformations succinctly. Mastery involves knowing when to use Pig over Hive, how to chain multiple operations, and how to debug scripts when unexpected results occur. The ability to translate business logic into Pig scripts is evaluated through questions framed as data processing tasks, where optimization and clarity are equally important. A nuanced understanding of both Hive and Pig, combined with the ability to switch seamlessly between declarative and procedural paradigms, is a hallmark of a proficient Hadoop developer.
Spark and Advanced Data Processing Skills
Modern big data ecosystems often leverage Spark for its in-memory computation capabilities. The CCDH certification evaluates a candidate’s ability to harness Spark’s performance advantages while integrating it with traditional Hadoop storage layers. Understanding Resilient Distributed Datasets, DataFrames, and the execution plan is critical, as is the ability to perform transformations and actions effectively. Spark’s flexibility allows for batch and stream processing, and candidates must demonstrate an ability to choose appropriate paradigms depending on the problem context.
Impala, another analytic tool, is assessed for its capacity to provide low-latency SQL queries on HDFS. Candidates should understand when Impala queries outperform Hive queries, how to structure tables for efficient scans, and how to balance real-time responsiveness with resource consumption. Mastery of these advanced tools requires a combination of conceptual understanding, practical experience, and the foresight to anticipate performance bottlenecks.
Strategies for Success and Skill Consolidation
While technical knowledge forms the core of the examination, success is often determined by how well candidates integrate their skills into cohesive problem-solving approaches. Scenario-based questions compel aspirants to evaluate the trade-offs between various processing frameworks, optimize resource allocation, and design workflows that are both efficient and maintainable. The ability to think critically about distributed systems, anticipate potential failures, and propose effective solutions is as important as familiarity with commands or syntax.
To prepare effectively, candidates should immerse themselves in hands-on projects, simulate real-world data scenarios, and review case studies that illustrate practical applications of Hadoop components. Reviewing cluster logs, analyzing performance metrics, and experimenting with workflow optimizations develop an intuitive sense of system behavior. Those who cultivate this combination of conceptual depth and practical agility are more likely to excel in the CCD-410 exam and carry forward a skill set that is highly valued in the domain of big data engineering.
Deep Dive into Hadoop Distributed File System
A foundational component evaluated in the Cloudera Certified Developer for Apache Hadoop exam is the Hadoop Distributed File System, which serves as the bedrock for large-scale data storage and retrieval. HDFS is designed to handle massive volumes of data across a cluster of commodity hardware, providing both fault tolerance and high throughput. Understanding the architecture of HDFS is indispensable for any aspirant seeking to demonstrate expertise. Data in HDFS is divided into blocks, typically 128 or 256 megabytes in size, which are distributed and replicated across multiple nodes to ensure durability and reliability. Knowledge of how replication works, including the default replication factor and the behavior when nodes fail, is critical. Candidates must also be familiar with the NameNode and DataNode hierarchy, appreciating how the NameNode maintains metadata while DataNodes store actual data blocks. Proficiency in navigating HDFS, performing routine file operations, and troubleshooting common anomalies is necessary for practical mastery.
The practical application of HDFS involves more than just understanding storage mechanics. A candidate must be adept at designing directory structures that optimize data access patterns, balancing the need for granularity with efficiency. Proper organization affects subsequent processing workflows, impacting performance during MapReduce jobs or Hive queries. Additionally, the examination tests knowledge of file formats suitable for different use cases, such as sequence files, Parquet, or ORC, and their influence on read and write performance. A nuanced comprehension of how HDFS interacts with other ecosystem tools, including YARN and Spark, is vital for developing scalable solutions.
MapReduce Paradigm and Job Management
MapReduce remains a core competency assessed in the CCDH certification. It represents a distributed computing model designed to process vast datasets in parallel. Candidates are expected to conceptualize the lifecycle of a MapReduce job, which includes the stages of mapping, shuffling, sorting, and reducing. Each stage has specific functions: the map phase transforms input data into key-value pairs, the shuffle phase redistributes data based on keys, and the reduce phase aggregates results to produce the final output. An intimate understanding of this flow allows developers to optimize job configurations, avoid bottlenecks, and enhance cluster utilization.
Practical skills extend to recognizing performance challenges, such as skewed key distributions, inefficient joins, or excessive intermediate data. The CCD-410 exam often tests scenario-based knowledge, requiring candidates to identify optimal approaches for diverse workloads. For instance, when faced with a job processing millions of records with repeated joins, a proficient developer might propose strategies such as partitioning or leveraging combiners to minimize overhead. Developing intuition about job execution, resource allocation, and data movement within the cluster distinguishes a capable candidate from one with superficial knowledge.
YARN and Resource Management
Yet Another Resource Negotiator, known as YARN, is another critical element of the Hadoop ecosystem examined in CCDH. YARN serves as a resource management layer, orchestrating multiple applications simultaneously on a shared cluster. Candidates must comprehend how YARN allocates memory and CPU resources to containers, schedules tasks, and monitors node health. The intricacies of YARN include understanding how application masters negotiate resources, how capacity and fairness schedulers operate, and how to configure queues for efficient workload distribution.
Practical proficiency involves not only the theoretical understanding of YARN but also the ability to troubleshoot allocation failures, optimize job performance, and predict resource contention. Scenario-based questions may present complex workloads with multiple competing jobs, requiring the candidate to propose configurations that ensure high throughput without sacrificing stability. Recognizing the interplay between YARN, MapReduce, and Spark is essential, as mismanagement of resources can lead to cascading performance issues or job failures.
Hive and Pig Integration with Hadoop
Hive and Pig are evaluated for their ability to abstract the complexity of Hadoop’s underlying processing while offering flexibility in querying and transforming data. Hive provides a data warehouse interface for querying HDFS using SQL-like statements, translating queries into efficient execution plans. Understanding table structures, partitioning, bucketing, and indexing is essential for optimizing performance. For example, partitioning large datasets based on a frequently queried column can drastically reduce scan times. Candidates are expected to know when to leverage Hive for batch analytics versus when to prefer Pig for more procedural and iterative data transformations.
Pig, with its scripting language Pig Latin, allows developers to define complex workflows succinctly. Practical expertise involves chaining multiple operations, debugging scripts, and optimizing data transformations. The exam may present questions as data processing scenarios where candidates must select the most efficient tool or design a workflow that meets specific performance criteria. An aspirant who can reason about the underlying execution plan while maintaining clarity and efficiency in scripts demonstrates the deep understanding necessary to succeed.
HBase and Real-Time Data Management
HBase introduces the dimension of real-time access to sparse datasets within the Hadoop ecosystem. Unlike HDFS, which excels at batch processing, HBase provides low-latency reads and writes, making it suitable for applications that demand immediate data retrieval. Candidates are expected to understand column-family-based data storage, schema design considerations, and the role of regions and region servers in distributing and managing data. Knowledge of versioning, consistency models, and data compaction mechanisms is vital. Scenario-based questions may require the candidate to select the most appropriate table design or access strategy to meet latency and throughput objectives, reflecting real-world considerations in enterprise deployments.
Spark and Its Integration with Hadoop
Although Hadoop was initially synonymous with MapReduce, modern big data environments increasingly rely on Spark for in-memory data processing. Spark provides a flexible framework for batch and streaming computations, offering APIs for Resilient Distributed Datasets, DataFrames, and structured queries. Candidates must understand Spark’s execution model, including the role of the driver, executors, and DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) scheduler. Mastery involves the ability to perform transformations, actions, and optimizations while considering resource allocation within a YARN-managed cluster.
The examination evaluates a candidate’s ability to integrate Spark with traditional Hadoop storage layers. Practical skills include configuring jobs to leverage in-memory computation efficiently, partitioning datasets to balance workloads, and caching frequently accessed data to reduce latency. Scenario-based questions often require candidates to weigh trade-offs between Spark and MapReduce solutions, justifying their approach based on dataset characteristics, execution time, and cluster resources. Those who can anticipate bottlenecks and design workflows for scalability exhibit a level of expertise aligned with professional expectations.
Ecosystem Synergy and Workflow Design
A recurring theme in the CCD-410 exam is the candidate’s ability to synthesize knowledge across multiple ecosystem components. It is insufficient to understand HDFS, MapReduce, YARN, Hive, Pig, HBase, and Spark in isolation. Instead, candidates must demonstrate an ability to design integrated workflows that optimize resource usage, minimize latency, and ensure data integrity. Scenario-based assessments may involve ingesting heterogeneous datasets, transforming and enriching data with Pig, storing intermediate results in HBase, querying aggregated results via Hive, and performing analytics with Spark. Effective workflow design requires foresight, analytical reasoning, and practical intuition about how each component behaves under varying conditions.
Resource optimization is another critical skill. Candidates should be able to identify potential bottlenecks in data flows, propose strategies for partitioning, caching, or indexing, and adjust configurations for both performance and reliability. An intuitive understanding of cluster behavior, including node health, task scheduling, and memory consumption, is essential for designing resilient workflows. The ability to foresee the consequences of design choices on downstream processing is often the difference between a proficient developer and one who struggles with real-world implementations.
Troubleshooting and Performance Optimization
Finally, practical mastery encompasses troubleshooting and performance optimization. Candidates must be capable of identifying and resolving common issues, such as failed MapReduce jobs, data skew, or inefficient Hive queries. Performance tuning requires a nuanced understanding of cluster resources, data locality, execution plans, and framework-specific configurations. For instance, recognizing that a particular join operation in Hive is causing excessive shuffling can prompt the use of partitioning, bucketing, or map-side joins to alleviate the bottleneck. Similarly, understanding Spark’s caching mechanisms and DAG execution can lead to substantial performance improvements in iterative algorithms.
Practical exercises and hands-on experience are invaluable in developing this level of understanding. Candidates who actively engage with cluster monitoring, resource profiling, and real-world data scenarios gain an intuitive sense of system behavior that is difficult to acquire through theoretical study alone. The ability to apply diagnostic reasoning, adjust configurations, and optimize execution distinguishes highly competent Hadoop developers and is precisely what the CCD-410 examination seeks to evaluate.
Mastering Data Ingestion Techniques
A pivotal aspect of the Cloudera Certified Developer for Apache Hadoop exam revolves around the ability to efficiently ingest data from diverse sources into the Hadoop ecosystem. Data ingestion is the initial step in any big data pipeline and often determines the success or failure of subsequent processing and analysis. Developers are expected to demonstrate competence in handling heterogeneous data types originating from relational databases, log files, message queues, streaming platforms, and external APIs. Each source presents unique challenges that require thoughtful preprocessing and integration strategies.
Candidates must be familiar with batch ingestion techniques, which typically involve transferring large volumes of structured or semi-structured data into Hadoop Distributed File System using tools or scripts designed to ensure reliability and scalability. Equally important is the understanding of streaming ingestion for real-time data. Streaming data sources often demand low-latency processing, error handling, and mechanisms to handle data bursts or schema evolution. Practical mastery requires the ability to configure ingestion pipelines, validate data integrity, and monitor performance to avoid bottlenecks that could cascade into downstream tasks. Scenario-based questions in the examination frequently simulate situations where ingestion speed, fault tolerance, and resource allocation must be balanced to achieve optimal throughput.
Understanding the subtleties of data formats and compression techniques is essential during ingestion. Developers should know how to work with delimited text files, JSON, Avro, Parquet, and ORC formats, recognizing the impact of each on storage efficiency and processing speed. Choosing the appropriate file format can drastically reduce I/O operations and enhance query performance when interacting with Hive or Spark. Moreover, knowledge of compression codecs such as Snappy, Gzip, or LZO can improve storage utilization without significantly impacting processing efficiency, and questions in the exam often require candidates to justify their choices based on scenario constraints.
Data Transformation and Cleansing Proficiency
Once data is ingested, transforming and cleansing it is a critical skill area for candidates pursuing the CCDH certification. Transformation involves converting raw data into structured, analyzable formats suitable for downstream processing. This may include normalization, denormalization, aggregation, or enrichment operations. Developers must be adept at recognizing anomalies in datasets, handling missing values, and standardizing inconsistent formats, which are common in enterprise-grade data lakes.
Data cleansing extends beyond correcting errors; it involves implementing systematic approaches to ensure data reliability and accuracy. Practical experience includes filtering irrelevant records, deduplicating entries, and managing outliers in numerical datasets. In real-world Hadoop workflows, these tasks are often accomplished using Pig scripts, Hive queries, or Spark transformations. The examination assesses a candidate’s ability to apply appropriate transformations based on the context of the problem while considering performance implications. For instance, performing a join operation on massive datasets without partitioning or bucketing may lead to excessive shuffling and degraded performance, a nuance that candidates are expected to understand.
An intricate part of transformation is schema evolution, particularly when dealing with streaming or incremental data sources. Candidates must anticipate changes in incoming data structures, implement robust handling mechanisms, and maintain compatibility with existing workflows. Scenario-based questions often test this knowledge, requiring aspirants to devise solutions that accommodate schema drift while preserving historical data integrity. Developers who can balance these competing requirements demonstrate the kind of foresight and technical dexterity that distinguishes proficient Hadoop developers.
Workflow Orchestration and Dependency Management
The ability to design and manage complex workflows is another critical skill assessed in the exam. In professional environments, data pipelines rarely follow a linear trajectory; they often involve multiple interdependent tasks, conditional logic, and iterative operations. Candidates are expected to create workflows that are fault-tolerant, maintainable, and optimized for performance.
A fundamental concept in workflow orchestration is task dependency management. Developers must ensure that upstream tasks complete successfully before downstream tasks commence, employing mechanisms to handle failures and retries gracefully. In addition, logging and monitoring capabilities are essential for diagnosing issues and maintaining operational visibility. The examination may present real-world scenarios where a workflow encounters partial failures, requiring the candidate to propose strategies for recovery without data loss or duplication. The ability to foresee potential pitfalls and implement preemptive checks is an indicator of mastery.
Optimizing workflow performance is closely tied to resource management and data locality. Tasks that process large volumes of data should ideally execute on nodes where the data resides, minimizing network transfer and reducing execution time. Candidates must understand how to configure job priorities, manage concurrent executions, and exploit parallelism without overwhelming cluster resources. Scenario-based questions often present workflows with competing tasks, requiring aspirants to make informed decisions about task scheduling, resource allocation, and intermediate data storage.
Leveraging Pig and Hive for Transformations
Pig and Hive serve as essential tools for implementing transformations and orchestrating complex workflows. Pig scripts allow developers to define data processing pipelines in a procedural manner, chaining operations such as filtering, grouping, joining, and aggregating. Mastery involves knowing how to optimize these scripts, reduce redundant data reads, and debug issues that arise during execution. Candidates are frequently tested on their ability to translate high-level business requirements into efficient Pig workflows, demonstrating both analytical reasoning and practical skill.
Hive complements Pig by providing a declarative interface for querying and transforming data stored in Hadoop Distributed File System. Its SQL-like language allows developers to perform aggregations, joins, and analytical operations with relative ease. However, efficiency in Hive is contingent on understanding table design, partitioning strategies, bucketing, and indexing. Scenario-based questions in the exam often present large datasets and require candidates to select the optimal query strategy that balances execution time and resource usage. Effective use of Hive involves anticipating query patterns, minimizing data scans, and leveraging metadata to accelerate access.
Advanced ETL Strategies and Optimization
Extract, Transform, Load operations form the backbone of enterprise data processing, and proficiency in designing robust ETL pipelines is a hallmark of a capable Hadoop developer. Advanced strategies involve automating repetitive tasks, implementing incremental loads, and ensuring that data transformations are idempotent and auditable. Candidates are expected to demonstrate the ability to manage batch ETL pipelines as well as near-real-time streaming operations.
Performance optimization is an integral aspect of ETL pipeline design. Developers must understand how to partition datasets for parallel processing, choose appropriate file formats to reduce I/O, and leverage caching where applicable. Knowledge of how different tools within the Hadoop ecosystem interact, such as Spark transformations feeding into Hive tables or Pig workflows reading from HBase, is essential. The examination may present scenarios where inefficient design has led to resource contention or prolonged job execution, requiring the candidate to propose and justify corrective actions.
Effective ETL design also incorporates monitoring and alerting mechanisms. Candidates should be familiar with tracking job execution, validating output correctness, and implementing notifications for failures or anomalies. This operational awareness ensures that pipelines remain resilient and reliable, reflecting the expectations of professional environments. The ability to anticipate potential failure points and design preemptive safeguards is a skill that the exam seeks to assess.
Real-World Workflow Scenarios
The CCDH certification emphasizes applying knowledge in realistic scenarios. Candidates may be presented with datasets spanning multiple sources, requiring ingestion, cleansing, transformation, and analysis. For instance, a scenario could involve ingesting log files from web servers, normalizing the data, enriching it with user information from relational databases, and performing aggregations to generate business insights. Successfully completing such tasks demands a holistic understanding of Hadoop components, ETL processes, workflow orchestration, and performance considerations.
Another common scenario might involve handling streaming data from IoT devices, requiring the implementation of near-real-time transformations, filtering anomalous readings, and storing processed data in a format optimized for analytics. Developers must demonstrate both conceptual understanding and practical capability, integrating Pig, Hive, Spark, and HDFS seamlessly. The examination evaluates how candidates reason through these problems, select appropriate tools, and optimize execution to meet performance and reliability requirements.
Best Practices for Skill Consolidation
Mastery of data ingestion, transformation, and workflow optimization requires consistent practice and exposure to complex datasets. Candidates are encouraged to engage in hands-on exercises that simulate enterprise-scale pipelines, experiment with different ingestion methods, and refine their understanding of transformation strategies. Familiarity with troubleshooting, optimizing performance, and implementing robust workflows contributes significantly to exam readiness.
Developers who cultivate an intuitive understanding of how data flows through a Hadoop ecosystem, anticipate failure points, and apply optimization techniques are well-positioned to excel. The combination of technical knowledge, practical experience, and analytical reasoning equips candidates to navigate the intricate landscape of big data processing and demonstrate proficiency in the CCD-410 examination.
Hive Fundamentals and Query Optimization
One of the central competencies tested in the Cloudera Certified Developer for Apache Hadoop examination revolves around the mastery of Hive. Hive serves as a data warehousing infrastructure that simplifies querying and managing structured data in the Hadoop Distributed File System. Its SQL-like interface abstracts the complexities of MapReduce, enabling developers to focus on analytical tasks rather than low-level programming. Understanding Hive requires more than familiarity with its syntax; it necessitates an appreciation of its internal execution model, storage formats, and optimization strategies.
A candidate must comprehend the lifecycle of a Hive query, from parsing and semantic analysis to optimization and execution. Hive generates an execution plan that translates queries into MapReduce, Tez, or Spark jobs depending on the cluster configuration. Awareness of how these jobs are scheduled and executed allows developers to anticipate performance bottlenecks. For instance, poorly designed queries that do not leverage partitioning or bucketing can result in full table scans, causing unnecessary disk I/O and network overhead. Effective Hive users are able to restructure queries to minimize data movement, apply predicate pushdown, and exploit indexing where appropriate to enhance efficiency.
Partitioning is a fundamental optimization technique that allows large tables to be divided into smaller, more manageable segments based on frequently queried columns. By organizing data into partitions, Hive reduces the volume of data scanned during query execution, which in turn decreases response time. Bucketing complements partitioning by distributing data into fixed-size buckets based on the hash of a column, enabling efficient joins and aggregations. Candidates are often evaluated on their ability to design partitioned and bucketed tables that balance query performance with storage considerations. Knowledge of file formats such as ORC and Parquet, which provide compression and columnar storage, is also critical for achieving optimal performance.
Advanced Hive optimization involves understanding the cost-based optimizer and leveraging it to generate more efficient execution plans. Developers should be able to interpret explain plans, identify expensive operations, and implement strategies to reduce computational overhead. Scenario-based questions may present datasets with millions of records, requiring candidates to propose query restructuring, indexing, or pre-aggregation to achieve acceptable runtimes. Mastery of these techniques demonstrates not only technical proficiency but also analytical reasoning and foresight.
Pig Latin Scripting and Workflow Management
Pig provides a complementary approach to Hive by offering a procedural scripting language known as Pig Latin. Unlike Hive’s declarative queries, Pig enables developers to define complex data flows through sequences of transformation operators. The CCDH exam evaluates a candidate’s ability to craft efficient Pig scripts for tasks such as filtering, grouping, joining, and aggregating datasets. Understanding the semantics of Pig operators and the underlying execution mechanics is essential for writing scripts that are both correct and performant.
Practical expertise in Pig involves constructing modular, reusable scripts that can be easily maintained and adapted to evolving data requirements. Candidates must be adept at chaining multiple operations while minimizing redundant reads and writes. The ability to reason about how data flows through a Pig script, where intermediate results are materialized, and how operators interact with HDFS is frequently tested through scenario-based questions. For example, a dataset may require multiple transformations and joins before final aggregation, and candidates are expected to select the most efficient sequence of operations.
Debugging Pig scripts is another critical skill. Errors may arise from schema mismatches, unexpected null values, or misconfigured operators. Candidates should be capable of interpreting error messages, tracing data lineage, and applying corrective actions to resolve issues. The examination often presents practical scenarios where candidates must troubleshoot scripts while maintaining the integrity of the workflow. A developer who can efficiently identify root causes and implement fixes demonstrates the combination of technical skill and analytical acumen that the exam seeks to assess.
Integrating Hive and Pig for Complex Workflows
Mastery of Hive and Pig extends beyond individual tool proficiency to the ability to integrate them within cohesive workflows. Real-world data pipelines often require both declarative and procedural processing paradigms, depending on the nature of the task. Hive is ideal for aggregations, reporting, and analytical queries, whereas Pig excels in complex transformations, data cleansing, and iterative operations. Candidates must be able to design pipelines that leverage the strengths of each tool while maintaining efficiency and scalability.
Scenario-based assessments in the CCD-410 exam frequently present multi-step workflows where data flows from raw ingestion to final analytics. A common example might involve ingesting semi-structured log data, cleansing and transforming it using Pig, storing intermediate results in Hive tables, and performing aggregations or reporting queries. Success in such scenarios requires a comprehensive understanding of how Hive and Pig interact with HDFS, how to optimize intermediate data storage, and how to minimize redundant computations. Candidates who can reason about workflow design, anticipate bottlenecks, and apply best practices in both Hive and Pig exhibit advanced proficiency.
Schema Design and Data Modeling
Effective use of Hive and Pig also depends on thoughtful schema design and data modeling. In Hive, selecting appropriate table structures, partitioning strategies, and storage formats directly impacts query performance. Developers should be able to model data in ways that balance normalization with efficiency, considering the types of queries that will be executed most frequently. Similarly, in Pig, understanding data types, schemas, and operator compatibility is essential for writing scripts that are robust and maintainable.
Candidates are often tested on their ability to evaluate trade-offs between different schema designs. For example, denormalized tables may increase storage requirements but reduce join complexity and query time, whereas highly normalized structures may conserve space but require more complex processing. Scenario-based questions may ask developers to justify their design choices in the context of performance, scalability, and maintainability. Those who can reason through these trade-offs demonstrate a deep understanding of both Hive and Pig and their applications in large-scale data processing.
Optimizing Joins and Aggregations
Joins and aggregations are common operations that frequently determine the performance of Hive and Pig workflows. In Hive, understanding different join types—such as map-side joins, common joins, and skewed joins—is crucial for handling large datasets efficiently. Candidates must be able to select the appropriate join strategy based on data distribution and cluster resources. Similarly, aggregations in both Hive and Pig require careful consideration of intermediate data size, partitioning, and operator order to avoid excessive shuffling and reduce execution time.
Scenario-based questions may present datasets with skewed key distributions, large tables, or high-volume aggregations, challenging candidates to propose optimized strategies. Effective solutions often involve a combination of partitioning, bucketing, map-side joins, and careful selection of storage formats. Candidates who can anticipate the computational cost of different operations and optimize accordingly demonstrate practical mastery and analytical insight.
Practical Application and Scenario Analysis
The CCDH certification emphasizes applying Hive and Pig knowledge to realistic data processing scenarios. Candidates may be asked to design workflows that handle mixed datasets, perform complex transformations, and deliver analytical insights efficiently. For instance, a scenario might involve analyzing web server logs, combining them with user profile data, cleansing and transforming the records with Pig, and storing the results in Hive tables for reporting. Successful candidates must demonstrate both technical proficiency and strategic reasoning, selecting the most suitable tools, structuring queries and scripts efficiently, and optimizing workflow execution.
Other scenarios may involve iterative data processing, such as calculating moving averages, aggregating sensor data, or performing incremental updates. Candidates must apply advanced concepts, such as schema evolution, partitioned processing, and caching intermediate results, to deliver solutions that meet performance and accuracy requirements. The ability to integrate Hive and Pig seamlessly into end-to-end workflows is a key differentiator for proficient Hadoop developers.
Performance Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Effective workflow management also requires continuous monitoring and troubleshooting skills. Developers must be able to identify performance bottlenecks, analyze execution logs, and implement optimizations to improve throughput and reduce latency. In Hive, this may involve interpreting explain plans, adjusting query strategies, or refining table designs. In Pig, it may require reordering operations, optimizing data flows, or debugging script errors. Candidates are expected to demonstrate the ability to diagnose issues, propose corrective actions, and implement solutions without compromising data integrity.
Scenario-based questions in the examination often simulate real-world challenges, such as delayed job execution, partial failures, or inconsistent results. Candidates must exhibit critical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and a deep understanding of Hive and Pig mechanics to resolve such issues effectively. Hands-on experience with cluster monitoring, resource profiling, and workflow debugging is invaluable for building the intuition required to excel.
Integrating Hive and Pig with the Ecosystem
Finally, mastery of Hive and Pig includes understanding their interaction with other components of the Hadoop ecosystem. Hive queries may feed Spark jobs for advanced analytics, while Pig scripts may preprocess data for storage in HBase or other systems. Candidates must be able to design pipelines that optimize data movement, minimize redundant computations, and leverage the strengths of each tool within the ecosystem. Understanding these integrations is crucial for both exam success and practical proficiency in enterprise data environments.
Harnessing Spark for Large-Scale Data Processing
Apache Spark has emerged as a fundamental component in modern Hadoop ecosystems, offering in-memory computation and high-speed processing that surpass traditional MapReduce paradigms. The Cloudera Certified Developer for Apache Hadoop examination evaluates a candidate’s ability to utilize Spark effectively for both batch and streaming workloads. Spark introduces Resilient Distributed Datasets, DataFrames, and structured streaming, providing flexible abstractions for large-scale computations while maintaining fault tolerance and parallelism across clusters. Candidates are expected to understand Spark’s architecture, including the driver, executors, and task scheduling, and how these components interact with the Hadoop Distributed File System and YARN-managed clusters.
Practical proficiency in Spark involves crafting workflows that maximize in-memory processing while minimizing shuffles and disk I/O. Developers must be able to determine when caching datasets is advantageous, how to partition data to optimize parallelism, and how to configure execution parameters for efficient resource utilization. Scenario-based questions may present a dataset requiring iterative computations, such as machine learning model training or time-series analysis, challenging candidates to balance memory consumption, cluster load, and execution time. Mastery of Spark entails not only executing transformations and actions but also understanding the implications of execution plans on cluster performance.
DataFrames and Structured Processing
DataFrames in Spark provide a higher-level abstraction than Resilient Distributed Datasets, enabling developers to work with structured data efficiently. The CCDH exam evaluates a candidate’s ability to manipulate DataFrames using operations such as filtering, grouping, aggregating, and joining datasets. Understanding the logical and physical query plans generated by the Catalyst optimizer is crucial for optimizing performance. Candidates are expected to apply predicate pushdown, column pruning, and partitioning strategies to minimize computational overhead.
Scenario-based questions often present complex datasets with billions of rows, requiring candidates to design queries that are both efficient and accurate. Knowledge of built-in functions, user-defined functions, and appropriate handling of null or malformed data is also assessed. Developers who can reason through query execution, anticipate potential bottlenecks, and propose optimizations demonstrate the level of skill necessary to succeed in professional big data environments and the CCD-410 exam.
Spark Streaming and Real-Time Analytics
The ability to process real-time data streams is an increasingly important skill tested in the certification. Spark Streaming allows developers to ingest, transform, and analyze data from sources such as Kafka, Flume, or network sockets with low latency. Candidates must understand micro-batch processing, window operations, and stateful transformations to implement effective streaming solutions. Practical proficiency includes configuring batch intervals, managing offsets, and ensuring exactly-once processing semantics to maintain data integrity.
Scenario-based questions may require the candidate to design a pipeline that processes continuous streams of sensor data, filters anomalies, aggregates results over time windows, and writes output to HDFS or Hive tables. Success in these scenarios demands a thorough understanding of Spark’s streaming model, fault tolerance mechanisms, and integration with other ecosystem components. Developers who can efficiently handle large-scale streams while maintaining performance and accuracy demonstrate advanced competence.
Impala for Low-Latency Queries
Impala is another critical tool evaluated for its ability to provide real-time SQL queries on data stored in HDFS and other Hadoop-compatible storage systems. Unlike Hive, which often relies on batch execution, Impala is optimized for low-latency query execution, making it suitable for interactive analytics and reporting. Candidates must understand how Impala optimizes query execution through techniques such as query planning, predicate pushdown, partition pruning, and vectorized execution.
Practical expertise involves designing schemas and queries that exploit Impala’s performance advantages. For example, partitioned and sorted tables can significantly reduce scan times for large datasets, while careful join ordering minimizes memory usage and shuffle operations. Scenario-based questions may challenge candidates to select the appropriate query strategy to meet stringent latency requirements while maintaining correctness. Mastery of Impala requires both conceptual understanding and practical skill in writing optimized queries and integrating them into larger analytical workflows.
Advanced ETL and Data Transformation Strategies
Advanced data processing within Hadoop ecosystems often involves complex ETL pipelines that combine batch and real-time workflows. Spark and Impala provide complementary capabilities, allowing developers to implement transformations, aggregations, and analytics at scale. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to design pipelines that minimize data movement, optimize resource usage, and ensure fault tolerance. Transformations may include cleansing, enrichment, aggregation, and joining of large, heterogeneous datasets.
Scenario-based questions may present a requirement to transform terabytes of raw log data into structured insights for business intelligence. Candidates must consider factors such as cluster load, partitioning strategies, caching intermediate results, and minimizing shuffle operations. The ability to anticipate computational costs and optimize workflow execution is critical for achieving performance goals and demonstrating professional proficiency.
Integration with Hive, Pig, and HBase
Effective advanced data processing requires seamless integration of Spark and Impala with other Hadoop ecosystem components. Spark can read from and write to Hive tables, enabling analytics on pre-existing structured data, while Pig scripts may preprocess datasets before they are ingested into Spark workflows. HBase provides low-latency access for real-time queries, and Spark can interact with HBase to retrieve and update records efficiently. Candidates must be able to design workflows that leverage the strengths of each tool while minimizing redundancy and maximizing throughput.
Scenario-based questions may challenge candidates to integrate multiple tools for end-to-end data processing. For example, semi-structured data may be cleansed using Pig, stored in Hive, analyzed with Spark, and queried interactively with Impala. Success in such scenarios demonstrates not only technical mastery but also the ability to reason strategically about workflow design and resource allocation. The examination evaluates how effectively candidates can manage interdependencies, optimize execution, and maintain data integrity across complex pipelines.
Performance Tuning and Optimization
Performance tuning is a recurring theme in advanced data processing evaluations. Candidates must be adept at profiling Spark jobs, identifying bottlenecks, and applying optimizations such as caching, partitioning, and resource configuration adjustments. Similarly, Impala queries require careful tuning, including selection of appropriate join strategies, predicate optimization, and leveraging columnar storage features. Scenario-based assessments often present large-scale datasets and require candidates to propose solutions that minimize execution time while ensuring accuracy and reliability.
Understanding cluster behavior, including memory allocation, CPU utilization, and disk I/O patterns, is essential for effective performance tuning. Candidates must be able to anticipate how changes in data volume, query complexity, or cluster load will affect workflow execution. Those who can diagnose performance issues, implement corrective measures, and optimize both batch and interactive workflows demonstrate the advanced skill set sought by the CCD-410 examination.
Real-World Data Processing Scenarios
The CCDH certification emphasizes practical application of Spark, Impala, and advanced data processing skills through realistic scenarios. Candidates may be asked to design pipelines that process massive logs, sensor data, financial transactions, or social media feeds, transforming raw inputs into structured outputs for analytics and decision-making. Effective solutions require a holistic understanding of the ecosystem, including HDFS storage, YARN resource management, workflow orchestration, and integration with Hive, Pig, and HBase.
Scenario-based questions may also involve streaming pipelines where data must be filtered, aggregated, and written to multiple destinations with minimal latency. Developers must demonstrate both technical proficiency and strategic reasoning, selecting appropriate tools, optimizing workflow execution, and ensuring data consistency. The ability to apply these skills effectively underpins both examination success and professional competence in large-scale data environments.
Troubleshooting and Advanced Diagnostics
Advanced data processing skills also encompass troubleshooting and diagnostics. Candidates must be able to analyze execution logs, identify performance anomalies, and implement corrective actions to optimize Spark jobs or Impala queries. Common challenges include data skew, inefficient joins, memory constraints, and cluster resource contention. Developers must be able to reason systematically about failures, propose effective solutions, and validate that optimizations achieve the desired outcomes.
Scenario-based assessments may present performance issues in complex workflows, requiring candidates to suggest improvements such as re-partitioning datasets, caching intermediate results, or adjusting job parallelism. Mastery of troubleshooting techniques, coupled with deep understanding of execution mechanics, allows candidates to maintain high-performance data pipelines and demonstrates the advanced competency expected in the CCDH certification.
Strategic Approach to Exam Preparation
Success in the Cloudera Certified Developer for Apache Hadoop examination relies not only on technical proficiency but also on a strategic approach to preparation. Candidates are expected to demonstrate a holistic understanding of the Hadoop ecosystem, encompassing HDFS, YARN, MapReduce, Hive, Pig, Spark, Impala, and HBase, and the ability to apply this knowledge in practical scenarios. To prepare effectively, aspirants must first establish a structured learning plan that prioritizes core competencies while allowing flexibility for hands-on experimentation and scenario-based practice.
Understanding the exam format is essential for devising an effective strategy. The examination is designed to test practical knowledge, analytical reasoning, and workflow optimization skills, rather than rote memorization. Candidates should familiarize themselves with the types of questions typically posed, including scenario-based assessments that require evaluating trade-offs between tools, optimizing resource allocation, and designing efficient data processing pipelines. By studying past question patterns and exploring real-world data challenges, developers can cultivate the critical thinking necessary to respond confidently under examination conditions.
Time management is another crucial aspect of preparation. Candidates should allocate sufficient time for each domain, balancing conceptual study with hands-on practice. For example, dedicating periods to understanding HDFS architecture, MapReduce mechanics, and YARN resource management can provide a solid foundation, while additional time focused on Hive query optimization, Pig scripting, and Spark transformations ensures practical proficiency. Integrating practice scenarios into study routines allows candidates to simulate examination conditions, refine workflow strategies, and identify areas requiring further reinforcement.
Hands-On Practice and Real-World Scenarios
The CCDH examination emphasizes the application of theoretical knowledge to real-world data processing scenarios. Candidates are encouraged to engage with hands-on exercises that replicate professional environments, working with large-scale datasets, diverse data formats, and complex workflows. Practical experience in ingesting, transforming, and analyzing data reinforces conceptual understanding and hones problem-solving skills.
For instance, candidates might simulate workflows that process log files, cleanse and enrich data with Pig scripts, store results in Hive tables, and perform analytics using Spark. Such exercises develop the ability to anticipate bottlenecks, optimize execution plans, and design fault-tolerant workflows. Similarly, integrating Impala for low-latency queries or utilizing HBase for real-time access to sparse datasets strengthens the candidate’s capability to select the right tool for each task. Exposure to these scenarios cultivates a mental model of system behavior, enabling aspirants to reason effectively about resource allocation, execution time, and workflow optimization.
Additionally, practicing with debugging and troubleshooting exercises is invaluable. Candidates should simulate common challenges, such as skewed data, failed jobs, inefficient joins, or memory constraints, and develop strategies to identify and resolve these issues. By engaging with realistic scenarios, developers gain intuition about system behavior and improve their ability to make informed decisions under pressure.
Exam-Taking Techniques and Mental Preparedness
Effective exam strategy extends beyond technical knowledge to include techniques for managing time, stress, and decision-making during the assessment. Candidates should approach questions methodically, analyzing scenario descriptions carefully, identifying relevant tools and operations, and evaluating potential trade-offs. The examination often presents complex workflows with multiple interdependent tasks, and aspirants must select the most efficient approach while considering performance, scalability, and reliability.
Prioritization is key when responding to scenario-based questions. Candidates should first address components they are most confident in, gradually tackling more complex or unfamiliar tasks. Maintaining composure and logical reasoning under time constraints enhances the ability to identify optimal solutions and avoid costly errors. Additionally, familiarity with common pitfalls, such as misinterpreting data flow requirements or overlooking resource limitations, helps candidates anticipate challenges and respond effectively.
Mental preparedness is equally important. Candidates benefit from building resilience through regular practice, exposure to diverse scenarios, and reflective evaluation of performance. By simulating exam conditions and analyzing errors in practice exercises, aspirants can cultivate confidence, reduce anxiety, and enhance decision-making efficiency during the actual assessment. A well-prepared candidate approaches the examination with both technical competence and strategic foresight, increasing the likelihood of success.
Leveraging Study Resources and Community Knowledge
A comprehensive preparation plan involves utilizing a variety of study resources. Official documentation, tutorials, and training materials provide foundational knowledge, while community forums, discussion groups, and collaborative projects offer insights into practical challenges and innovative solutions. Candidates who actively engage with peers and professionals gain exposure to diverse problem-solving approaches, alternative workflows, and optimization techniques that enrich their understanding of Hadoop ecosystems.
Simulation exercises and sample question repositories are particularly valuable. These resources allow candidates to practice scenario-based problem-solving, refine workflow design strategies, and evaluate their readiness against realistic challenges. By iteratively practicing and analyzing performance, aspirants can identify gaps in knowledge, strengthen weak areas, and develop the adaptability required to navigate complex examination scenarios successfully.
Career Benefits and Professional Advancement
Achieving the Cloudera Certified Developer for Apache Hadoop certification opens doors to numerous career opportunities in the rapidly expanding field of big data and distributed computing. The credential validates a developer’s ability to design, implement, and optimize large-scale data processing workflows, a skillset highly sought by enterprises managing massive datasets. Certified developers are often considered for roles such as Hadoop developer, data engineer, big data consultant, or analytics architect, where proficiency in the Hadoop ecosystem is essential.
The certification also enhances credibility within professional networks, signaling mastery of core technologies such as HDFS, MapReduce, YARN, Hive, Pig, Spark, Impala, and HBase. Employers recognize the value of candidates who can design efficient workflows, optimize performance, and troubleshoot complex data processing pipelines. In addition to technical expertise, certified developers often demonstrate strong problem-solving skills, analytical reasoning, and the ability to integrate multiple tools to meet business requirements, attributes that contribute to career growth and leadership potential.
Furthermore, the credential positions professionals to contribute to innovative projects involving real-time analytics, machine learning pipelines, and large-scale ETL processes. Organizations increasingly rely on certified developers to implement scalable solutions, improve data reliability, and derive actionable insights from vast datasets. The combination of technical proficiency, practical experience, and strategic reasoning developed through certification preparation equips candidates to excel in dynamic, data-driven environments.
Networking and Industry Recognition
Beyond immediate technical and career benefits, certification fosters networking opportunities and industry recognition. Candidates often join professional communities, attend conferences, and participate in collaborative projects that enhance visibility and facilitate knowledge sharing. Engaging with a network of certified professionals allows developers to exchange best practices, explore emerging tools, and gain insights into evolving trends in big data technologies.
The recognition associated with the certification also strengthens professional credibility. Organizations value individuals who have demonstrated the ability to navigate complex Hadoop ecosystems, optimize workflows, and apply knowledge effectively in practical scenarios. Certification serves as a benchmark for expertise, signaling commitment to professional development and proficiency in managing enterprise-scale data challenges.
Long-Term Professional Development
Mastery of the Hadoop ecosystem through CCDH certification is not an endpoint but a catalyst for ongoing professional growth. Certified developers are well-positioned to explore advanced topics such as data architecture design, performance engineering, real-time analytics, and integration with cloud-based big data platforms. The skills acquired through preparation provide a foundation for continuous learning, enabling professionals to adapt to technological advancements and emerging best practices in distributed data processing.
Continuous engagement with hands-on projects, experimentation with new tools, and participation in professional forums fosters sustained skill development. By applying knowledge in real-world scenarios, certified developers refine their expertise, enhance problem-solving capabilities, and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving industry. The certification experience cultivates a mindset of analytical reasoning, adaptability, and strategic thinking that extends beyond technical skills to encompass broader professional competence.
Conclusion
Preparing for the Cloudera Certified Developer for Apache Hadoop examination requires a combination of technical proficiency, strategic planning, hands-on experience, and scenario-based reasoning. Candidates who immerse themselves in practical exercises, understand the interplay between ecosystem components, and apply optimization strategies develop the skills necessary to excel both in the examination and in professional settings. Mastery of Spark, Impala, Hive, Pig, HBase, HDFS, YARN, and MapReduce equips developers to design efficient, scalable, and resilient workflows, ensuring success in complex data processing environments.
The certification not only validates technical knowledge but also enhances professional credibility, opens doors to advanced career opportunities, and fosters continuous growth in the big data domain. By approaching preparation with a structured strategy, engaging with realistic scenarios, and cultivating both analytical and practical skills, candidates position themselves for achievement in the CCDH certification and for long-term advancement in a competitive, data-driven industry. The combination of practical mastery, strategic foresight, and professional recognition underscores the enduring value of this credential for aspiring Hadoop developers.