Windows Deployment Services
Exam: Microsoft 70-646 - Windows Server 2008, Server Administrator
Windows Deployment Service, commonly referred to as WDS, can enable the remote deployment of Windows on the computer that's running on Windows Server 2008 R2. Deployment of the following operating systems can be performed remotely with WDS:
- Windows Server 2008 R2,
- Windows Server 2008,
- Windows 7 and
- Windows Vista Operating Systems.
It is a requirement of WDS that a client have PXE compliant network card. In case the same is not available the alternate method is to create a bootable image that is capable of detecting the WDS server for performing a remote installation. The process is initiated when a computer that has a PXE based network card begins and locates the WDS server. If a client is authorized and configuration has been made for multicast transmissions, the client automatically starts the setup process. Unicast transmissions that are seen as less efficient in case of multiple clients are enabled after an operating system image has been installed.
In case an Autounattended.xml answer file is not installed on the WDS server, the installation process carries on normally wherein input is required from the administrator. The main factor which separates a WDS and a normal installation is that in the former type, servers start from Windows Server R2 installation media on network whereas in the latter case it is from local DVD ROM drive.
The conditions that play an important role in installation of WDS done on a computer that is running Windows Server 2008 R2 are:
- A system with a WDS is a member of an AD DS domain. There is requirement of a DNS server which is implied by existence of the domain;
- Presence of an authorized DHCP server on the network;
- Availability of NTFS partition for storage of OS images.
WDS can be run on a computer that runs a Server Core edition of Windows Server 2008 R2. After WDS has been installed, it has to be configured before it can be activated. This can be done by using Windows Deployment Services Configuration Wizard or by using the Wdsutil.exe command-line utility.
In case the WDS server is collocated with the DHCP server, it is necessary that configuration of WDS is done so that it does not listen to port 67. If this is not done, a conflict will arise between WDS and DHCP. Configuration of WDS server in order to add option tag 60 and detection by the PXE clients is essential.
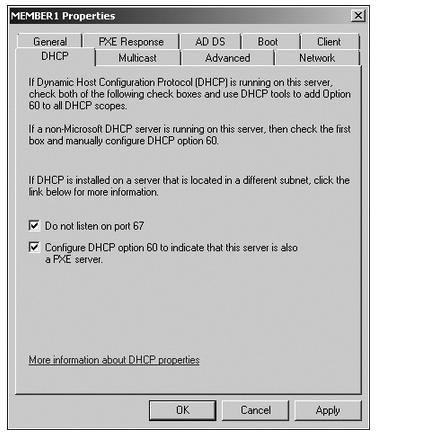
The DHCP tab of the WDS server settings dialog box
The Client tab of a WDS server's properties allows specification of an unattended installation file for particular architecture. The Autounattended.xml file may need the usual manual input during the installation process if it's not mentioned for architecture of Windows Server 2008 R2.
Some of the network environments have services like teleconferencing, video etc, require the multicast range for IP addresses. To configure the multicast range, use the Multicast Settings tab.
This way, you can manage the IP range for the WDS and UDP. Transfer settings can be configured on the tab in order to ensure that clients that are at different speeds get a different multicast session. The ability to separate the clients into different settings implies that the whole deployment transmission is not slowed down by a system that has a sluggish network card.The PXE response policy can be configured through the WDS server settings. PXE Response Delay is the very first setting to be configured. It defines the order in which the servers respond to PXE requests.
There are three options for configuring PXE response settings:
- Do Not Respond To Any Client Computer.
- Respond Only To Known Client Computers.
- Respond To All (Known And Unknown) Client Computers.
Related IT Guides
- Analyzing the IPv6 Address Structure
- Determine which edition of Windows Server is appropriate for a specific set of circumstances
- IPv4-to-IPv6 Compatibility and Transition to IPv6
- Multicast, Scheduled, and Automatic Deployment
- Plan for the installation of or upgrade to Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2
- Planning an IPv6 Network
- Planning Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 DNS
- Using IPv6 Tools
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Answer Files


