Certification: Certified SOA Consultant
Certification Full Name: Certified SOA Consultant
Certification Provider: SOA
Exam Code: S90.02
Exam Name: SOA Technology Concepts (S90-02A)
S90.02 Exam Product Screenshots
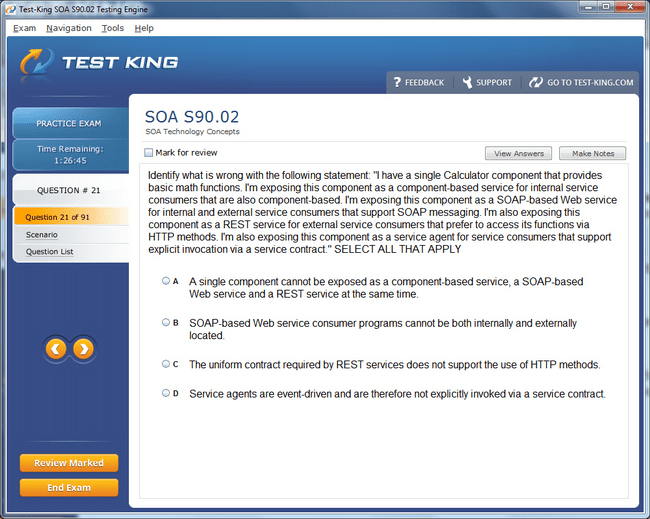
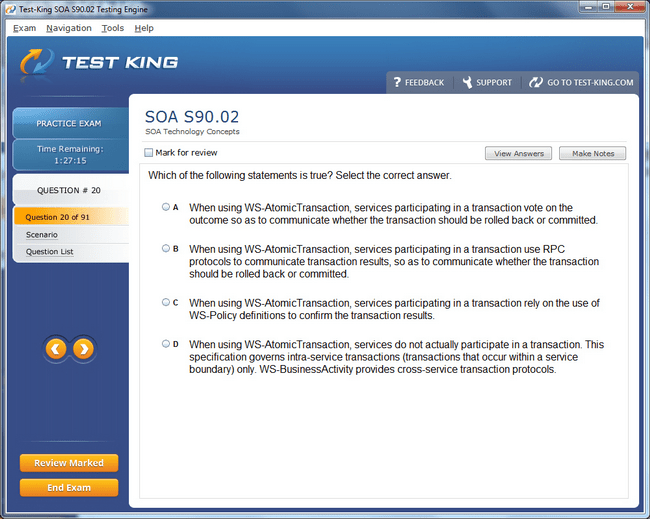
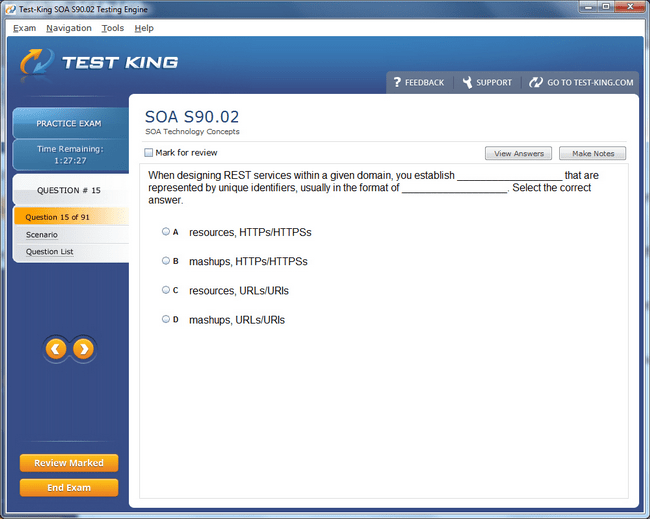
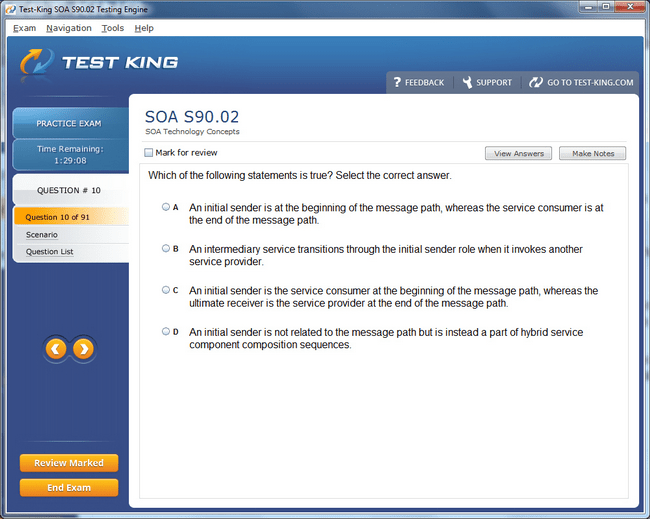
Step-by-Step Guide to Earning the Certified SOA Consultant Certification
In the evolving landscape of enterprise architecture and digital transformation, Service-Oriented Architecture has emerged as a pivotal paradigm for organizations seeking agility, interoperability, and streamlined processes. SOA represents a methodology in which software components, referred to as services, are designed to perform discrete functions while maintaining the ability to communicate and collaborate within larger systems. This approach allows organizations to respond to dynamic business requirements with agility, reusing existing assets, and orchestrating them to create new functionalities.
Understanding SOA and the Role of a Certified SOA Consultant
The role of a Certified SOA Consultant is not merely a technical one; it is a hybrid of strategic insight, analytical acumen, and practical expertise. Professionals in this capacity are tasked with designing, implementing, and optimizing SOA frameworks that align with business objectives. Their responsibilities extend from evaluating current IT landscapes, identifying redundancies, and recommending service-level enhancements to facilitating seamless integration between disparate systems. The certification serves as a formal recognition of an individual’s proficiency in these domains, validating not only technical competence but also strategic reasoning and problem-solving capabilities.
Earning the Certified SOA Consultant credential signals to employers and clients that the individual possesses a thorough understanding of service orientation principles, governance practices, and integration methodologies. This expertise is increasingly sought after in industries ranging from finance and healthcare to telecommunications and government sectors. As organizations grapple with complex enterprise architectures, the consultant’s ability to design reusable, scalable, and resilient services becomes a critical differentiator.
SOA emphasizes modularity and interoperability, allowing services to function independently while being capable of interaction through defined interfaces. For a consultant, mastering these principles requires a deep comprehension of service design patterns, orchestration techniques, and the nuances of communication protocols. The certification curriculum delves into these concepts, providing candidates with structured pathways to assimilate theoretical knowledge and practical application. A candidate’s journey often begins with understanding foundational service concepts, progressing to the governance frameworks that ensure consistency, reliability, and security across services.
The practical impact of SOA is profound. Organizations leveraging well-designed service-oriented architectures achieve improved system scalability, faster deployment of business processes, and enhanced maintainability. A consultant certified in SOA is uniquely positioned to advise on best practices for service lifecycle management, performance monitoring, and adaptation to emerging technological trends such as microservices, cloud integration, and API-led connectivity. The certification underscores the consultant’s ability to navigate this evolving ecosystem with precision and foresight.
Preparing for the Certified SOA Consultant Certification
The journey to becoming a Certified SOA Consultant begins with a comprehensive understanding of the prerequisites and professional expectations. Candidates typically require a combination of academic background and practical experience in software architecture, systems integration, or enterprise IT management. Familiarity with distributed computing, web services, and middleware technologies forms the foundation for more advanced exploration of SOA principles.
Strategic preparation involves identifying learning resources that align with both conceptual understanding and hands-on application. Authoritative guides, official certification manuals, and workshop-based learning provide structured exposure to the breadth of SOA topics. Complementing these resources with peer discussions, scenario-based exercises, and reflective study practices fosters a more profound comprehension of service-oriented design challenges. The consultant’s role often demands not only designing services but also anticipating operational bottlenecks and integration conflicts, making experiential learning an invaluable component of preparation.
A key aspect of preparation involves cultivating analytical and critical thinking skills. SOA consultants are frequently called upon to evaluate existing systems, diagnose inefficiencies, and recommend optimization strategies. Certification assessments test these abilities by presenting candidates with complex scenarios that simulate real-world consulting challenges. By engaging with case studies and problem-solving exercises, aspirants refine their aptitude for dissecting architectural issues, prioritizing service enhancements, and proposing solutions that align with overarching business goals.
Time management and structured study plans are indispensable for candidates pursuing the certification. Breaking down the vast syllabus into manageable units, scheduling periodic reviews, and reinforcing learning through practice questions enhances retention and comprehension. Integrating multidisciplinary perspectives, such as combining technical knowledge with business process understanding, strengthens the consultant’s capacity to devise solutions that are both technically robust and operationally viable.
Core Competencies and Knowledge Areas
The Certified SOA Consultant credential emphasizes a range of competencies essential for effective practice in enterprise environments. Central to these is mastery of service design principles, including service granularity, statelessness, composability, and reusability. Understanding the subtleties of service boundaries, dependencies, and orchestration mechanisms enables consultants to create architectures that are both efficient and adaptable.
Governance forms another critical pillar of SOA expertise. Governance frameworks provide the rules, policies, and standards necessary to maintain consistency, ensure compliance, and safeguard the integrity of services. Certified SOA Consultants must be adept at designing governance models that balance flexibility with control, facilitating innovation while mitigating risks. This encompasses establishing service registries, versioning policies, security protocols, and monitoring mechanisms to oversee service performance.
Integration proficiency is also paramount. Consultants must navigate a labyrinth of disparate systems, protocols, and platforms, ensuring that services communicate seamlessly and reliably. Mastery of messaging protocols, service orchestration techniques, and event-driven architectures enables professionals to construct cohesive ecosystems where each service contributes to the organization’s strategic objectives. The certification rigorously evaluates the candidate’s ability to orchestrate services across diverse technical landscapes, reflecting real-world expectations.
Performance optimization represents another domain of significance. Certified SOA Consultants are expected to identify potential bottlenecks, analyze throughput, and implement improvements that enhance responsiveness and reliability. This involves understanding load balancing, caching strategies, and fault-tolerant design principles. By integrating performance considerations into the architecture design phase, consultants ensure that services are not only functionally correct but also operationally efficient.
Additionally, a holistic understanding of emerging trends and technologies is increasingly vital. The consultant must remain conversant with innovations such as microservices architecture, API management, cloud-native integration, and containerization. These developments influence service orientation strategies and are often incorporated into certification curricula to prepare candidates for contemporary challenges. The certification ensures that consultants are not only grounded in established practices but also agile in adopting new methodologies that enhance organizational agility.
Practical Applications and Consulting Scenarios
Certified SOA Consultants operate in dynamic environments where theory must translate into actionable solutions. Real-world scenarios often involve diagnosing architectural inefficiencies, proposing service decomposition strategies, and orchestrating integration across multiple systems. Consultants leverage their knowledge of service contracts, interface standards, and middleware technologies to align IT capabilities with business imperatives.
The practical application of SOA principles spans multiple domains. In financial institutions, consultants may streamline transaction processing systems, integrating legacy platforms with modern payment gateways. Healthcare organizations benefit from SOA in enabling interoperability between electronic health record systems, laboratory information systems, and telemedicine applications. In the public sector, service-oriented strategies support the harmonization of citizen services, regulatory compliance, and secure data exchange.
A Certified SOA Consultant’s approach typically begins with assessment and discovery. Evaluating current architectures, identifying redundant or overlapping services, and mapping service dependencies allow for the formulation of actionable recommendations. Subsequent stages involve designing service enhancements, implementing governance controls, and monitoring performance. This cyclical process of evaluation, design, execution, and optimization reflects the consultant’s strategic contribution to organizational success.
Scenario-based learning during certification preparation mirrors these professional challenges. Candidates encounter case studies that simulate integration conflicts, performance bottlenecks, or governance dilemmas. Analyzing these cases cultivates the ability to synthesize information, anticipate operational impacts, and propose solutions that balance technical rigor with business pragmatism. The certification validates the consultant’s capacity to navigate such complexities with confidence and expertise.
Career Opportunities and Professional Impact
Achieving the Certified SOA Consultant credential opens pathways to diverse career opportunities. Professionals equipped with this certification are positioned for roles such as enterprise architect, integration specialist, IT strategist, and digital transformation consultant. Organizations value these professionals for their ability to bridge technical and business domains, ensuring that technology investments deliver tangible value.
The certification also enhances professional credibility. Clients and employers recognize certified individuals as possessing validated skills, analytical acumen, and practical expertise. This recognition often translates into leadership opportunities, higher remuneration, and the capacity to influence strategic decision-making within organizations. Furthermore, the consultant’s insights into service-oriented design principles contribute to organizational resilience, scalability, and competitive advantage.
Continuous professional development remains integral to sustained success. SOA is an evolving discipline, and consultants must remain attuned to emerging frameworks, integration techniques, and governance models. Networking with peers, participating in workshops, and engaging with professional communities ensure that knowledge remains current and relevant. The certification acts as both a milestone and a foundation for ongoing learning, supporting long-term career progression.
The influence of a Certified SOA Consultant extends beyond immediate technical contributions. By fostering efficient service design, enhancing system interoperability, and enabling faster deployment of business processes, these professionals drive broader organizational transformation. Their strategic recommendations shape IT investments, improve operational efficiency, and facilitate innovation. The certification, therefore, is not merely a credential but a testament to the consultant’s capacity to effect meaningful change in complex enterprise environments.
Eligibility Criteria and Professional Prerequisites
Earning the Certified SOA Consultant credential demands a blend of academic foundation, professional experience, and technical familiarity. Candidates typically possess a background in information technology, computer science, software engineering, or systems management, but the certification is also attainable by professionals from allied disciplines who have accrued practical experience in enterprise IT environments. Prior exposure to distributed computing, middleware technologies, and service-oriented design principles provides a substantial advantage, as it facilitates comprehension of the intricate dynamics involved in designing and managing services.
Eligibility for the certification often encompasses both educational and experiential components. While formal degrees establish foundational knowledge, real-world experience in implementing or managing IT solutions forms the bedrock of consulting competence. Professionals with exposure to integration projects, business process optimization initiatives, or service architecture frameworks are particularly well-positioned to navigate the rigorous requirements of the certification. Understanding the interplay between business objectives and technological capabilities is central to a candidate’s readiness, as the consultant’s role extends beyond coding or configuration to strategic architectural decision-making.
The professional prerequisites underscore the expectation that candidates are capable of engaging with complex enterprise landscapes. This includes familiarity with legacy systems, contemporary service platforms, and integration middleware. A Certified SOA Consultant must appreciate both technical and operational constraints, understanding how to design services that are resilient, interoperable, and aligned with organizational goals. The eligibility criteria ensure that candidates possess not only theoretical understanding but also practical exposure, allowing them to translate knowledge into actionable solutions in diverse business contexts.
Knowledge Foundations and Skill Requirements
Successful candidates demonstrate proficiency in several key domains essential for service-oriented consulting. Core knowledge encompasses service design principles, including service granularity, composability, statelessness, and reusability. Consultants must understand how to decompose monolithic systems into discrete services while maintaining coherence and efficiency across the architecture. This requires analytical acumen and the ability to anticipate interdependencies, performance implications, and governance requirements.
Governance knowledge is equally critical. Candidates are expected to comprehend the frameworks that regulate service creation, deployment, versioning, and security. Effective governance ensures consistency, reliability, and compliance across service landscapes. A Certified SOA Consultant is adept at establishing registries, defining policies for service evolution, and implementing monitoring mechanisms to maintain operational integrity. Understanding governance is not merely procedural; it involves recognizing patterns, anticipating conflicts, and devising solutions that balance agility with control.
Integration proficiency represents another cornerstone of eligibility. Candidates must navigate heterogeneous systems, bridging gaps between disparate technologies, platforms, and protocols. Expertise in orchestration, messaging standards, and event-driven architectures is essential, as services rarely function in isolation. The consultant’s ability to synchronize multiple services into cohesive workflows determines the effectiveness of the overall architecture. Familiarity with performance tuning, scalability considerations, and fault tolerance further strengthens a candidate’s preparedness.
Soft skills complement technical acumen. Analytical thinking, problem-solving, and effective communication are indispensable attributes for a consultant. The ability to convey complex concepts to stakeholders, negotiate technical trade-offs, and facilitate collaborative decision-making enhances the practical value of certification. Eligibility, therefore, extends beyond tangible knowledge to encompass professional demeanor, strategic insight, and adaptive reasoning.
Assessment of Professional Experience
Practical experience plays a pivotal role in shaping a candidate’s eligibility for the Certified SOA Consultant credential. Organizations seeking SOA expertise value demonstrable involvement in designing, implementing, or managing service-oriented projects. Experience may include evaluating existing enterprise systems, identifying redundancies, proposing architectural improvements, or leading integration initiatives. Candidates who have contributed to end-to-end lifecycle management of services often possess the nuanced understanding necessary to excel in certification assessments.
Professional exposure equips candidates with the capacity to tackle complex architectural dilemmas. Through hands-on engagement, they develop a comprehension of constraints imposed by legacy systems, cross-platform interoperability challenges, and organizational requirements. This knowledge allows them to approach certification scenarios with pragmatism, balancing technical precision with operational feasibility. The certification recognizes this expertise, affirming the candidate’s readiness to operate in environments where decisions have tangible business implications.
In addition to direct technical experience, candidates benefit from exposure to governance, project management, and stakeholder engagement. Certified SOA Consultants frequently mediate between business units and IT teams, translating strategic goals into technical specifications. Experience in these roles enriches their perspective, fostering a holistic understanding of organizational dynamics and enhancing their capacity to propose solutions that are sustainable, scalable, and aligned with enterprise objectives.
Recommended Preparation Pathways
Preparation for certification begins with evaluating personal competencies against eligibility expectations. Candidates should conduct a self-assessment of technical skills, practical experience, and familiarity with SOA concepts. Identifying gaps allows for targeted preparation, whether through formal training, workshops, online modules, or project-based learning. Exposure to real-world case studies enhances understanding by contextualizing theoretical concepts within practical scenarios.
Structured learning resources facilitate comprehensive coverage of certification topics. Authoritative manuals, practice exercises, and scenario simulations provide opportunities to engage with both conceptual and applied knowledge. Peer collaboration and mentoring further enrich preparation, allowing candidates to exchange perspectives, clarify ambiguities, and develop nuanced problem-solving approaches. The objective is to cultivate confidence and competence across all domains evaluated by the certification.
Time management and disciplined study routines are integral to effective preparation. Candidates benefit from segmenting complex topics into manageable units, integrating periodic reviews, and applying iterative practice strategies. Simulating consulting scenarios, evaluating architectural trade-offs, and analyzing service dependencies reinforce comprehension and foster readiness. Preparation is not limited to rote memorization; it emphasizes analytical reasoning, decision-making, and adaptability, reflecting the realities faced by Certified SOA Consultants in professional contexts.
Aligning Prior Experience with Certification Requirements
Candidates from diverse professional backgrounds can align their experience with certification expectations through reflective analysis of past projects. Those who have managed IT infrastructure, conducted system integrations, or optimized business processes may map these experiences to the competencies evaluated in the certification. Documenting specific instances of architectural planning, service orchestration, or governance implementation demonstrates preparedness and reinforces confidence during assessment.
For candidates transitioning from adjacent domains, targeted skill development ensures alignment with SOA-specific requirements. Engaging in project simulations, developing proof-of-concept services, or participating in workshops focused on service-oriented principles bridges gaps between existing expertise and certification expectations. This approach underscores the consultant’s commitment to mastery and positions them favorably for successful credentialing.
The certification framework implicitly emphasizes adaptability. Professionals who can translate their prior experience into structured solutions, appreciate both technical and organizational nuances, and demonstrate analytical rigor are well-positioned to meet eligibility expectations. By consciously aligning past work with the demands of service-oriented consulting, candidates create a foundation of readiness that facilitates both assessment and future professional engagement.
Preparing for Assessment and Evaluation
Assessment for the Certified SOA Consultant credential evaluates a candidate’s proficiency across technical, analytical, and strategic dimensions. Candidates are expected to demonstrate understanding of service design principles, governance models, integration strategies, and performance optimization techniques. Evaluation often includes scenario-based exercises that mirror professional challenges, requiring candidates to analyze situations, propose architectural solutions, and justify their decisions.
To excel, candidates integrate technical knowledge with critical thinking. Understanding the rationale behind service decomposition, orchestration, and governance policies enables them to propose coherent and effective solutions. Practical familiarity with tools, protocols, and integration frameworks enhances the ability to navigate complex scenarios efficiently. Assessment evaluates not merely factual knowledge but the capacity to apply concepts in a manner consistent with organizational objectives and industry best practices.
Preparation also involves cultivating professional judgment. Candidates anticipate potential bottlenecks, consider trade-offs, and evaluate the operational implications of their recommendations. By internalizing these evaluative skills, candidates enhance their capacity to respond to unstructured challenges and demonstrate the strategic insight expected of a Certified SOA Consultant. Integrating reflective practice, iterative learning, and scenario simulation into preparation strengthens readiness and supports performance during assessment.
Professional Growth and Strategic Relevance
Eligibility for the Certified SOA Consultant credential aligns with broader professional growth trajectories. Individuals who meet certification requirements often find themselves positioned for strategic roles within organizations, contributing to architectural planning, digital transformation initiatives, and operational optimization. The certification affirms the consultant’s ability to navigate complex enterprise landscapes, fostering trust among stakeholders and enhancing career mobility.
The credential also reflects the evolving expectations of the consulting profession. Modern enterprises value consultants who can integrate technological expertise with business acumen, designing services that support scalability, resilience, and adaptability. Eligibility criteria ensure that candidates possess not only technical mastery but also the analytical perspective, strategic foresight, and communicative proficiency necessary to operate effectively in these multifaceted roles.
Through preparation aligned with eligibility standards, candidates cultivate a nuanced understanding of service-oriented architecture, governance frameworks, integration strategies, and performance optimization. This comprehensive competence allows Certified SOA Consultants to influence decision-making, enhance system interoperability, and contribute to sustainable organizational transformation. The certification validates both current expertise and the capacity for continued professional evolution, reinforcing the consultant’s relevance in dynamic technological landscapes.
Creating an Effective Preparation Framework
Embarking on the journey toward becoming a Certified SOA Consultant necessitates a meticulously structured preparation framework. The credential evaluates a blend of technical mastery, analytical reasoning, and strategic understanding, requiring candidates to adopt a disciplined and deliberate approach to learning. The first step in planning an effective study strategy involves assessing personal competencies, identifying strengths and gaps, and aligning existing knowledge with the certification’s expectations. Understanding one’s baseline proficiency ensures that preparation efforts target areas that demand improvement while reinforcing core concepts already mastered.
A comprehensive preparation framework incorporates multiple learning modalities. Traditional study guides and manuals provide foundational knowledge, while interactive workshops, online courses, and simulation exercises enrich experiential understanding. Candidates are encouraged to integrate theoretical study with practical application, cultivating the ability to translate conceptual principles into actionable solutions. Such an approach mirrors the real-world responsibilities of a Certified SOA Consultant, where analytical precision and operational pragmatism converge.
Time management is a pivotal component of any preparation plan. The breadth of the certification syllabus requires candidates to allocate study periods strategically, balancing intensity with retention. Establishing a timeline that sequences topics logically, incorporating both review and application phases, enhances comprehension and reduces cognitive fatigue. By defining clear milestones and tracking progress, candidates foster accountability and maintain momentum throughout their preparation journey.
Selecting Learning Resources and Tools
The selection of appropriate learning resources plays a critical role in shaping the preparation strategy. Official certification manuals, vendor-specific documentation, and authoritative publications provide structured insights into service-oriented architecture, governance, and integration methodologies. Complementing these materials with case studies, scenario analyses, and peer discussions allows candidates to internalize principles and evaluate their application across diverse contexts.
Interactive tools, such as simulation exercises and practice assessments, further augment understanding. These resources offer opportunities to engage with realistic consulting scenarios, reinforcing decision-making skills, problem-solving techniques, and architectural reasoning. By confronting situations that mimic professional challenges, candidates cultivate confidence, analytical acuity, and operational foresight, all of which are essential attributes for a Certified SOA Consultant.
Collaborative learning also enhances preparation. Engaging with peers, mentors, or professional communities fosters knowledge exchange, clarifies ambiguities, and exposes candidates to alternative approaches and perspectives. Discussion of complex topics, evaluation of architectural trade-offs, and collaborative problem-solving exercises provide multidimensional insights that enrich comprehension beyond what solitary study can achieve.
Structuring Study Plans for Optimal Retention
A strategic study plan involves segmenting the syllabus into coherent modules that reflect both conceptual and practical dimensions of the certification. Prioritizing areas based on complexity, familiarity, and relevance ensures efficient allocation of cognitive resources. Candidates benefit from integrating review cycles that reinforce retention while continuously applying learned principles to simulated consulting tasks.
Techniques such as active recall, spaced repetition, and scenario-based exercises enhance memory consolidation and facilitate long-term understanding. Active recall involves retrieving knowledge without reference to study materials, promoting deeper comprehension. Spaced repetition spaces review intervals to optimize retention, while scenario-based exercises contextualize abstract principles within realistic consulting challenges. Together, these techniques cultivate both theoretical proficiency and practical readiness for certification assessment.
Regular self-assessment is indispensable for monitoring progress. Practice quizzes, architectural exercises, and reflective journaling enable candidates to identify areas of weakness, evaluate comprehension, and adjust study strategies dynamically. This iterative process of learning, application, and evaluation mirrors the problem-solving and analytical reasoning expected of a Certified SOA Consultant in professional contexts.
Integrating Practical Experience with Study
Effective preparation for certification necessitates a synthesis of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Candidates are encouraged to apply service-oriented principles within professional projects, experimental setups, or simulated environments. Implementing service decomposition, orchestrating workflows, and evaluating governance policies fosters a deeper understanding of core concepts, enabling candidates to internalize nuances that are often overlooked in purely theoretical study.
Real-world application provides a dual benefit. First, it reinforces retention by contextualizing abstract principles within tangible scenarios. Second, it enhances analytical reasoning, as candidates confront operational constraints, performance considerations, and integration complexities. For a Certified SOA Consultant, the ability to navigate these challenges with precision and foresight is critical, and experiential preparation ensures that theoretical knowledge translates into actionable competency.
Documenting practical exercises is a recommended practice. Maintaining records of design decisions, architectural trade-offs, and performance evaluations enables reflective learning, facilitating insights that refine both technical and strategic understanding. Such documentation serves as a personal reference, reinforcing memory retention and providing a resource for revision as the certification assessment approaches.
Cultivating Analytical and Strategic Thinking
The preparation journey emphasizes the development of analytical and strategic thinking. A Certified SOA Consultant must evaluate existing systems, identify inefficiencies, and propose solutions that align with business objectives. Study strategies that foster these abilities include scenario analysis, problem decomposition, and exploration of alternative architectural approaches. Candidates are encouraged to interrogate the rationale behind design decisions, assess potential outcomes, and anticipate operational challenges.
Analytical exercises involve breaking down complex systems into constituent components, evaluating service interactions, and identifying points of vulnerability or inefficiency. Strategic exercises extend this analysis by considering organizational objectives, regulatory requirements, and long-term sustainability. By integrating analytical rigor with strategic foresight, candidates prepare for the multidimensional challenges encountered both in certification assessment and in professional practice.
Decision-making simulations further enhance cognitive agility. By presenting candidates with dilemmas that require balancing technical feasibility, business value, and operational risk, these exercises cultivate the judgment necessary for effective consulting. Engaging repeatedly with such scenarios reinforces adaptive reasoning, enabling candidates to approach novel challenges with confidence and clarity.
Time Management and Consistency
Sustained success in certification preparation requires disciplined time management and consistency. Candidates are advised to allocate daily or weekly study periods, establishing routines that balance focused effort with restorative intervals. Consistency in engagement fosters progressive mastery, allowing complex concepts to be internalized gradually rather than superficially.
Prioritization is essential. Topics that underpin multiple domains of service-oriented architecture, governance, and integration should receive initial attention, forming a foundation upon which more specialized subjects can be layered. Scheduling review sessions for previously covered material prevents cognitive decay and reinforces the interconnections between concepts, enabling a more holistic understanding.
Integration of reflective practice enhances the efficiency of study routines. After engaging with exercises, simulations, or readings, candidates benefit from pausing to evaluate insights gained, challenges encountered, and potential applications. This reflective lens fosters meta-cognitive awareness, allowing learners to optimize study strategies, deepen comprehension, and internalize lessons in a manner consistent with professional consulting practices.
Leveraging Technology for Study Enhancement
Digital tools and platforms offer substantial advantages in certification preparation. Online learning modules, video tutorials, and interactive simulations provide flexible and immersive experiences, accommodating diverse learning preferences. Candidates can access scenario-based exercises, track performance metrics, and engage in collaborative discussions, all of which reinforce understanding and facilitate skill development.
Virtual labs enable experiential learning without reliance on organizational resources. Implementing service-oriented solutions, orchestrating workflows, and experimenting with governance mechanisms in controlled environments allows candidates to explore the operational implications of design decisions. This hands-on approach bridges the gap between theory and practice, enhancing readiness for both certification assessment and professional application.
Data-driven study tools also offer insights into learning patterns. By tracking completion rates, accuracy, and engagement metrics, candidates can identify strengths and weaknesses, calibrate study intensity, and adjust priorities dynamically. Integrating such feedback into preparation routines optimizes efficiency, ensuring that effort is directed toward areas of highest impact.
Maintaining Motivation and Focus
Long-term preparation demands sustained motivation and focus. Candidates are encouraged to establish clear objectives, visualize professional benefits, and cultivate intrinsic interest in service-oriented architecture. Recognizing the relevance of certification to career advancement, consulting expertise, and organizational impact reinforces commitment to disciplined study.
Mindfulness techniques, periodic reflection, and small achievements foster persistence. Celebrating milestones, however incremental, reinforces progress, mitigates burnout, and sustains enthusiasm. Engaging with professional communities, attending workshops, and sharing insights with peers provides social reinforcement, further enhancing motivation and promoting continuous engagement with study material.
The psychological dimension of preparation is critical. Candidates who maintain clarity of purpose, balanced routines, and positive engagement with challenges are more likely to absorb knowledge effectively, apply it strategically, and perform confidently during assessment. Motivation, therefore, functions not merely as a supplement but as an integral element of the preparation framework, supporting the development of both competence and professional identity as a Certified SOA Consultant.
Mastering Core Principles of Service-Oriented Architecture
The foundation of becoming a Certified SOA Consultant rests upon a profound comprehension of service-oriented architecture principles. SOA embodies a paradigm that emphasizes modularity, interoperability, and reusability of services within an enterprise ecosystem. Each service, while functioning autonomously, contributes to a larger orchestration, enabling organizations to adapt dynamically to evolving business requirements. Understanding service granularity, composability, statelessness, and discoverability is crucial for designing solutions that are both scalable and resilient.
Service granularity pertains to defining the scope and boundary of a service. A consultant must assess whether a service should encapsulate a broad range of functionalities or remain narrowly focused, balancing the trade-offs between reusability and manageability. Excessive granularity can lead to orchestration complexity, while overly coarse services may hinder flexibility and responsiveness. Mastery of this principle allows the Certified SOA Consultant to design architectures that optimize both efficiency and adaptability.
Composability refers to the ability of individual services to be orchestrated into more complex workflows. This requires an understanding of dependencies, data flow, and process interconnections. Consultants must ensure that composed services maintain coherence while allowing individual components to evolve independently. Composability underpins the agility that organizations seek, enabling rapid deployment of new functionalities without extensive redevelopment.
Statelessness, another core principle, ensures that services do not retain client-specific information between interactions. By minimizing state dependency, services achieve higher scalability, resilience, and easier integration. Certified SOA Consultants leverage this principle to reduce complexity, enhance fault tolerance, and simplify system maintenance. Discoverability complements these concepts by enabling services to be located and invoked efficiently, ensuring that architectural components interact seamlessly across the enterprise.
Governance and Standards in Service-Oriented Architecture
Governance forms an integral aspect of SOA mastery. Effective governance frameworks provide rules, policies, and standards that ensure consistency, compliance, and security across services. Certified SOA Consultants must possess the ability to define and enforce governance mechanisms that balance control with operational flexibility. Governance encompasses versioning policies, service registries, security protocols, and monitoring mechanisms that collectively safeguard the integrity and reliability of services.
The application of governance extends beyond rule enforcement; it involves strategic oversight and anticipatory management. Consultants evaluate potential conflicts, enforce standards across distributed teams, and ensure that service evolution aligns with organizational objectives. Effective governance reduces the risk of service redundancy, performance degradation, and operational failures, enhancing overall system reliability. Understanding both prescriptive and adaptive governance models allows consultants to tailor frameworks that suit diverse organizational cultures and technological landscapes.
Standards are interwoven with governance. Adherence to communication protocols, data formats, and interface definitions ensures interoperability between heterogeneous systems. Certified SOA Consultants leverage standardized approaches to reduce integration complexity, promote cross-platform compatibility, and facilitate seamless communication. Familiarity with industry standards such as SOAP, REST, and messaging formats enables consultants to navigate complex environments with precision and predictability.
Designing and Implementing Services
Designing effective services is at the heart of a Certified SOA Consultant’s responsibilities. The process begins with analyzing business requirements, identifying functional areas, and decomposing them into services that reflect operational priorities. Each service must encapsulate a coherent set of functionalities, support reuse, and maintain minimal coupling with other components. Consultants evaluate dependencies, potential performance bottlenecks, and integration challenges to ensure optimal service design.
Service implementation involves translating design into operational artifacts that adhere to established standards and governance policies. Certified SOA Consultants must consider messaging patterns, data transformation requirements, and transactional consistency. Implementation also includes ensuring scalability, fault tolerance, and responsiveness, factors that directly influence system robustness and user experience. Consultants frequently employ design patterns, orchestration frameworks, and middleware solutions to achieve these objectives efficiently.
Lifecycle management is equally critical. Services evolve over time, responding to changing business needs, technological advancements, and operational feedback. Certified SOA Consultants oversee version control, monitor performance metrics, and implement updates without disrupting dependent processes. Effective lifecycle management ensures continuity, adaptability, and alignment with strategic goals, reinforcing the value of service-oriented architectures in dynamic enterprise environments.
Integration Strategies and Interoperability
Integration represents one of the most challenging and impactful areas of SOA practice. Enterprises typically operate heterogeneous systems, including legacy platforms, modern applications, and third-party services. Certified SOA Consultants must navigate these environments to ensure seamless interoperability, consistent data flow, and coordinated process execution. Integration strategies involve selecting appropriate messaging protocols, orchestrating workflows, and implementing data transformation mechanisms.
Event-driven architectures, publish-subscribe models, and service orchestration patterns are common strategies employed to facilitate interoperability. Consultants assess the trade-offs of synchronous versus asynchronous communication, balancing latency, reliability, and operational efficiency. Integration also entails managing transactional integrity, error handling, and exception propagation across distributed systems. Mastery of these concepts allows the Certified SOA Consultant to create cohesive ecosystems that support operational agility and minimize disruptions.
Middleware technologies play a pivotal role in integration. Message brokers, ESB frameworks, and API gateways serve as conduits for service communication, enabling abstraction, routing, and transformation. Consultants must evaluate middleware solutions in the context of scalability, reliability, and alignment with organizational objectives. Selecting the right tools, configuring them appropriately, and monitoring their performance ensures that integration is not only functional but optimized for long-term sustainability.
Performance Optimization and Scalability
Certified SOA Consultants must prioritize performance and scalability in all design and implementation decisions. Service-oriented architectures, while flexible, can introduce latency, overhead, or resource contention if not carefully managed. Consultants analyze throughput, identify bottlenecks, and implement strategies that enhance responsiveness, efficiency, and reliability.
Caching strategies, load balancing, and asynchronous processing are common techniques to improve service performance. By anticipating peak loads and designing services for elasticity, consultants ensure that systems remain resilient under variable demand. Monitoring and performance analytics provide actionable insights, enabling proactive adjustments and continuous improvement. Certified SOA Consultants integrate these considerations into both design and operational management, reinforcing the strategic value of service-oriented architectures.
Scalability extends beyond technical considerations. Consultants assess organizational growth projections, evolving business requirements, and potential technological shifts to design services that can accommodate change. By anticipating future needs, Certified SOA Consultants create architectures that remain robust, adaptable, and cost-effective, reducing the risk of disruptive redesigns or operational inefficiencies.
Applying SOA in Real-World Scenarios
The practical impact of SOA principles is best understood through real-world applications. Certified SOA Consultants apply their expertise across industries such as finance, healthcare, telecommunications, and government, addressing unique challenges and operational objectives. In financial institutions, services streamline transaction processing, integrate disparate banking platforms, and enhance regulatory compliance. Healthcare organizations benefit from interoperability between electronic health records, laboratory systems, and telemedicine platforms, improving patient care and operational efficiency.
Consultants approach these scenarios by first assessing existing architectures, identifying inefficiencies, and mapping service dependencies. They then design services that optimize workflows, reduce redundancy, and facilitate integration. Orchestration of multiple services ensures coherent process execution, while governance frameworks maintain compliance and operational integrity. Performance monitoring and iterative refinement complete the cycle, enabling continuous improvement and long-term sustainability.
Scenario-based application also informs certification preparation. Candidates engage with exercises that simulate architectural challenges, integration conflicts, and governance dilemmas. Analyzing these situations cultivates problem-solving abilities, analytical reasoning, and strategic judgment. The experience gained mirrors professional consulting, preparing candidates to translate theoretical knowledge into actionable solutions upon achieving certification.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
The domain of service-oriented architecture is continually evolving. Emerging trends such as microservices, cloud-native integration, containerization, and API-led connectivity influence design and implementation practices. Certified SOA Consultants remain conversant with these innovations, assessing their relevance and applicability to enterprise architectures.
Microservices, for instance, extend the modularity principle by decomposing applications into independently deployable units. Consultants evaluate the trade-offs between microservices and traditional SOA, considering scalability, operational overhead, and integration complexity. Cloud-native architectures introduce elasticity and on-demand provisioning, requiring consultants to align service design with distributed cloud environments. API management, container orchestration, and event-driven integration further expand the toolkit available to Certified SOA Consultants, enhancing agility and resilience in complex systems.
By integrating emerging trends into practice, consultants ensure that organizations remain competitive, adaptable, and technologically advanced. Continuous learning, experimentation, and reflective application are essential components of maintaining expertise in a rapidly evolving field. The certification validates the consultant’s ability to engage with these trends intelligently, applying them to practical scenarios in alignment with organizational objectives.
Structuring an Effective Exam Preparation Strategy
Achieving the Certified SOA Consultant credential requires not only technical knowledge but also mastery of strategic thinking, analytical reasoning, and practical application. Preparing for the examination demands a carefully orchestrated approach that balances theoretical comprehension with experiential practice. Candidates begin by identifying the areas of the syllabus that hold the greatest complexity, ensuring sufficient time is devoted to service design principles, governance frameworks, integration methodologies, and performance optimization techniques. This prioritization allows learners to build a strong foundation while progressively addressing more nuanced topics.
Creating a structured study plan is essential for balancing cognitive load and maintaining focus. The plan should integrate a mix of reading, hands-on exercises, and scenario-based practice. Dedicated periods for reflection and review consolidate knowledge, while simulation exercises mimic the cognitive demands of real-world consulting scenarios. By blending multiple modalities of learning, candidates internalize principles more effectively and cultivate the judgment necessary to navigate intricate service-oriented architecture challenges.
Time management plays a pivotal role in preparation. With the breadth of topics covered by the certification, candidates must allocate study periods strategically, balancing intensity with sustainability. Establishing a timeline that sequences topics logically, incorporates frequent review, and progressively increases the complexity of practice exercises enhances retention and reduces cognitive fatigue. Consistent engagement over weeks or months fosters both mastery and confidence, essential attributes for successful exam performance.
Engaging with Practice Exercises and Simulations
Practical exercises and simulation activities constitute a central element of preparation. Candidates benefit from engaging with realistic scenarios that emulate the challenges encountered by Certified SOA Consultants in professional contexts. These exercises often involve evaluating existing architectures, diagnosing inefficiencies, orchestrating service workflows, and proposing governance or integration solutions. By repeatedly interacting with such scenarios, candidates develop the analytical acuity, strategic insight, and problem-solving agility expected in both the exam and real-world consulting.
Scenario-based exercises enhance comprehension by contextualizing abstract principles within tangible applications. Candidates learn to balance technical feasibility, business objectives, and operational constraints, ensuring that recommended solutions are pragmatic and sustainable. This process also cultivates adaptability, enabling candidates to respond effectively to novel or complex challenges. Engaging with a diversity of scenarios strengthens cognitive flexibility, a critical skill for Certified SOA Consultants who must navigate multifaceted enterprise environments.
Simulation exercises extend beyond theoretical evaluation, encompassing operational and performance considerations. Candidates are encouraged to analyze service dependencies, evaluate orchestration patterns, and assess transactional integrity. Implementing these simulations in controlled environments enables candidates to experiment with decision-making, observe outcomes, and refine approaches. The iterative cycle of practice, evaluation, and adjustment mirrors professional consulting, reinforcing the application-oriented mindset necessary for success.
Techniques for Enhancing Knowledge Retention
Effective exam preparation requires strategies that promote long-term retention and deep understanding. Techniques such as active recall, spaced repetition, and cognitive mapping are particularly valuable. Active recall involves retrieving knowledge without reference materials, encouraging neural reinforcement and deeper comprehension. Spaced repetition spaces study intervals strategically, optimizing memory consolidation and minimizing forgetting. Cognitive mapping enables candidates to visualize relationships between concepts, aiding integration of service design, governance, and integration principles.
Integrating reflective practice into study routines further enhances retention. After engaging with exercises or simulations, candidates benefit from reviewing decisions made, analyzing outcomes, and considering alternative approaches. Reflective analysis not only reinforces learning but also sharpens evaluative judgment, preparing candidates to navigate complex scenarios under examination conditions. Documentation of these reflections creates a repository of insights, serving as a personalized reference for review and reinforcement.
Contextual learning also contributes to mastery. Candidates are encouraged to relate theoretical principles to professional experiences, drawing parallels between past projects and exam scenarios. By linking abstract concepts to tangible applications, learners enhance comprehension and develop the ability to apply knowledge flexibly. This synthesis of theory and practice is a hallmark of Certified SOA Consultant proficiency, enabling candidates to demonstrate competence across both structured and unstructured assessment formats.
Approaching Scenario-Based Questions
Scenario-based questions constitute a significant portion of the certification evaluation, requiring candidates to analyze complex situations, identify critical issues, and propose effective solutions. The ability to deconstruct problems systematically, evaluate dependencies, and consider operational constraints is central to success. Candidates are encouraged to approach these questions methodically, first identifying the core problem, then mapping relevant service-oriented principles, and finally formulating recommendations that balance feasibility, efficiency, and strategic alignment.
Critical thinking and analytical reasoning are indispensable for navigating these questions. Candidates must assess service design quality, governance effectiveness, integration robustness, and performance implications. Each recommendation should be justified with reference to principles of service-oriented architecture, ensuring that solutions are coherent, practical, and aligned with organizational objectives. Developing proficiency in this approach requires repeated exposure to diverse scenarios, fostering the ability to synthesize information, anticipate consequences, and respond with precision.
Time management during scenario-based evaluation is equally vital. Candidates must allocate sufficient time to understand context, analyze components, and construct well-reasoned responses. Practicing under timed conditions simulates examination pressure, training candidates to make judicious decisions without sacrificing analytical depth. Iterative engagement with scenario exercises cultivates both speed and accuracy, reinforcing readiness for the demands of the Certified SOA Consultant examination.
Balancing Conceptual Knowledge with Practical Application
The certification evaluates candidates not merely on memorization but on their ability to apply concepts strategically. Effective preparation involves integrating theoretical study with hands-on practice, ensuring that candidates can translate principles into operational solutions. This balance is achieved through the design of simulated architectures, orchestration of services, and evaluation of governance frameworks within controlled exercises.
Practical application enhances comprehension by revealing nuances that may not be apparent in textual study. Candidates learn to anticipate integration challenges, assess service performance, and implement governance policies effectively. Engaging with these elements holistically fosters an understanding of interdependencies and operational trade-offs, reflecting the realities faced by Certified SOA Consultants in professional environments. This integrative approach ensures that candidates are prepared to respond adeptly to both examination scenarios and real-world consulting demands.
Utilizing Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Feedback is a critical component of preparation, enabling candidates to identify strengths, uncover weaknesses, and refine strategies. Practice exercises, simulations, and peer reviews provide actionable insights into performance, highlighting areas requiring additional focus. Candidates who systematically incorporate feedback into study routines enhance comprehension, correct misconceptions, and develop more effective problem-solving approaches.
Continuous improvement also involves iterative practice. By revisiting scenarios, re-evaluating design decisions, and analyzing alternative solutions, candidates cultivate adaptability and resilience. This iterative engagement mirrors the consulting process itself, where repeated assessment, refinement, and optimization are essential for success. Certified SOA Consultants benefit from developing this mindset, as it reinforces both technical proficiency and strategic judgment.
Reflection on performance further strengthens learning outcomes. Candidates maintain records of errors, successful strategies, and conceptual breakthroughs, creating a personalized knowledge repository. Reviewing this documentation prior to examination reinforces memory, consolidates insights, and enhances confidence. The combination of reflective practice, iterative simulation, and feedback utilization equips candidates with the cognitive tools necessary for high-stakes assessment and professional excellence.
Managing Stress and Exam Readiness
Preparation for certification includes attention to psychological and physiological readiness. High-stakes assessment can induce stress, potentially impairing performance. Candidates are encouraged to adopt techniques for stress management, including structured study routines, mindfulness practices, and regular physical activity. Maintaining a balanced approach ensures cognitive clarity, reduces anxiety, and supports sustained focus during examination conditions.
Simulated examinations under timed conditions are particularly effective for building readiness. Candidates learn to navigate time constraints, prioritize questions, and manage cognitive load efficiently. Exposure to the pacing and pressure of examination environments reduces uncertainty and enhances confidence. By integrating these strategies with robust preparation in both theoretical knowledge and practical application, candidates cultivate the resilience and mental acuity necessary for success.
Integrating Long-Term Knowledge Retention
Preparation for the Certified SOA Consultant credential extends beyond immediate examination readiness. Candidates are encouraged to develop a mindset of long-term retention and continuous learning. Consolidating knowledge through repetition, application, and reflection ensures that expertise remains accessible and applicable in professional practice.
Scenario-based simulations and hands-on exercises play a vital role in this process, as they reinforce the application of principles in realistic contexts. Continuous engagement with emerging technologies, evolving service patterns, and governance innovations further supports the consultant’s ongoing professional development. By combining exam-focused preparation with enduring cognitive reinforcement, candidates establish a foundation for sustained success, both in certification achievement and in practical consulting endeavors.
Maximizing Career Opportunities with Certification
Achieving the Certified SOA Consultant credential represents a significant milestone in professional development, opening avenues to advanced roles in enterprise architecture, integration strategy, and digital transformation initiatives. Organizations increasingly recognize the strategic value of service-oriented expertise, seeking professionals capable of designing modular, scalable, and interoperable solutions. This credential signals to employers, peers, and clients that the individual possesses not only technical proficiency but also strategic insight, analytical reasoning, and the ability to apply complex concepts in operational environments.
Certified SOA Consultants find opportunities in diverse sectors such as finance, healthcare, government, telecommunications, and information technology. Within these domains, the demand for professionals who can bridge technical and business objectives continues to grow. Roles often encompass enterprise architecture, integration management, IT strategy, solution design, and consulting, all requiring the knowledge and skills validated by certification. The credential differentiates candidates in competitive markets, positioning them for leadership responsibilities and higher-level engagements where their expertise influences organizational outcomes.
Career trajectories for Certified SOA Consultants are not linear but multidimensional, reflecting the breadth of the discipline. Professionals may evolve into strategic architects, leading teams in the design and deployment of service-oriented infrastructures. Others may specialize in governance, integration, or performance optimization, applying deep expertise to ensure system reliability and operational efficiency. The versatility of the certification allows professionals to navigate multiple pathways, aligning roles with personal strengths, interests, and evolving market demands.
Enhancing Professional Credibility and Recognition
Professional credibility is a key benefit of certification. Organizations and clients value consultants whose capabilities have been formally validated, particularly in complex, high-stakes environments. The Certified SOA Consultant credential provides assurance that the individual has mastered essential principles of service-oriented architecture, governance frameworks, integration methodologies, and performance management. This recognition fosters trust, enabling consultants to influence decision-making, advocate for architectural improvements, and lead transformational initiatives with authority.
Recognition extends beyond immediate employment contexts. Certified professionals often gain visibility within professional communities, industry forums, and peer networks. Participation in conferences, workshops, and discussion groups allows consultants to share insights, exchange best practices, and contribute to the evolving knowledge base of the discipline. This visibility enhances professional reputation, opening doors to collaborative opportunities, consulting engagements, and thought leadership roles.
The credential also serves as a benchmark for continuous development. By achieving certification, consultants demonstrate a commitment to mastery, signaling to organizations that they value lifelong learning and adaptive expertise. This reputation reinforces professional standing, making certified individuals more attractive candidates for advanced roles, consulting contracts, and leadership positions in strategic initiatives.
Leveraging Certification for Strategic Career Advancement
Strategic career advancement as a Certified SOA Consultant involves aligning professional skills with organizational needs and market trends. Consultants leverage their expertise to design architectures that support scalability, resilience, and adaptability, demonstrating tangible value to business operations. This alignment between technical capability and organizational impact positions professionals for roles with increasing responsibility, including architectural leadership, program management, and digital transformation oversight.
Consultants also capitalize on certification by targeting opportunities that intersect multiple domains. For example, integrating knowledge of governance frameworks with emerging technologies such as microservices, cloud-native platforms, and API-led connectivity enhances employability and influence. By demonstrating the ability to navigate both established SOA principles and innovative approaches, Certified SOA Consultants differentiate themselves as versatile, forward-thinking professionals.
Mentorship and knowledge sharing constitute additional avenues for career progression. Certified consultants often guide junior professionals, providing insight into architectural best practices, governance policies, and integration strategies. This mentorship reinforces expertise, establishes thought leadership, and strengthens professional networks. By contributing to organizational capability development, consultants create pathways to leadership roles while fostering a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
Continuous Learning and Professional Development
Certification is both a milestone and a foundation for ongoing professional growth. The field of service-oriented architecture evolves rapidly, influenced by emerging technologies, changing business models, and innovations in integration practices. Certified SOA Consultants maintain relevance by engaging in continuous learning, exploring new methodologies, and applying contemporary approaches to real-world scenarios. This commitment ensures that their expertise remains current, strategic, and actionable.
Engagement in professional communities, workshops, and industry forums provides exposure to diverse perspectives, innovative solutions, and evolving best practices. By interacting with peers and experts, consultants gain insight into emerging trends, regulatory changes, and technological advances, enabling proactive adaptation. Participation in knowledge exchange not only enhances technical competence but also fosters strategic acumen, allowing consultants to anticipate organizational needs and propose informed solutions.
Developing specialized skills complements broad knowledge. Consultants may pursue mastery in areas such as cloud integration, performance optimization, event-driven architectures, or enterprise orchestration. Deepening expertise in these domains reinforces professional differentiation, enhances credibility, and creates opportunities for consulting, leadership, and advisory roles. The combination of broad foundational knowledge, as validated by certification, and specialized expertise enables consultants to deliver comprehensive, high-value solutions.
Networking and Strategic Visibility
Building a professional network is a critical element of leveraging certification for career growth. Certified SOA Consultants gain access to communities of practice, peer forums, and industry networks where knowledge sharing and collaboration occur. Active participation in these networks enhances visibility, provides access to opportunities, and fosters relationships with professionals across diverse sectors. Networking facilitates collaboration, mentorship, and the exchange of insights, all of which contribute to sustained career advancement.
Strategic visibility also involves demonstrating expertise through thought leadership. Publishing articles, presenting at conferences, and participating in webinars positions consultants as authorities in service-oriented architecture and enterprise integration. This visibility reinforces credibility, expands professional influence, and attracts opportunities for consulting engagements, project leadership, and advisory roles. By combining certification with active engagement in knowledge dissemination, consultants amplify the impact of their expertise across organizations and industries.
Applying Certification to Organizational Impact
The ultimate value of certification manifests in the consultant’s ability to drive organizational outcomes. Certified SOA Consultants contribute to the design and implementation of architectures that enhance system interoperability, operational efficiency, and business agility. By applying governance principles, optimizing service performance, and orchestrating integrations effectively, consultants enable organizations to respond rapidly to evolving demands, reduce operational risk, and maximize return on technological investment.
In practical terms, certified professionals identify redundancies, streamline processes, and design modular services that can be reused across multiple initiatives. They ensure that governance policies are implemented effectively, that integration is seamless, and that performance objectives are met or exceeded. This operational impact reinforces the strategic relevance of the consultant, demonstrating the tangible value of certification to both technical teams and executive leadership.
Certified consultants also contribute to long-term organizational resilience. By designing architectures that are adaptable, scalable, and maintainable, they create systems capable of evolving with business needs and technological innovation. This foresight mitigates risk, reduces future costs, and strengthens competitive positioning, positioning the consultant as a strategic partner in organizational growth and transformation.
Conclusion
The Certified SOA Consultant credential serves as a gateway to professional distinction, strategic influence, and long-term career development. Beyond validating technical expertise, the certification signals analytical acumen, strategic insight, and the ability to translate complex service-oriented principles into practical, high-value solutions. Professionals leverage this credential to access advanced roles, enhance credibility, and contribute meaningfully to organizational transformation.
By integrating continuous learning, reflective practice, and engagement with emerging technologies, Certified SOA Consultants maintain relevance and adaptability in dynamic enterprise landscapes. Networking, mentorship, and thought leadership further amplify professional impact, creating pathways to leadership, consulting, and advisory roles. Ultimately, the certification empowers consultants to influence architecture, optimize operations, and drive sustainable organizational growth, establishing a foundation for enduring professional success.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get the products after purchase?
All products are available for download immediately from your Member's Area. Once you have made the payment, you will be transferred to Member's Area where you can login and download the products you have purchased to your computer.
How long can I use my product? Will it be valid forever?
Test-King products have a validity of 90 days from the date of purchase. This means that any updates to the products, including but not limited to new questions, or updates and changes by our editing team, will be automatically downloaded on to computer to make sure that you get latest exam prep materials during those 90 days.
Can I renew my product if when it's expired?
Yes, when the 90 days of your product validity are over, you have the option of renewing your expired products with a 30% discount. This can be done in your Member's Area.
Please note that you will not be able to use the product after it has expired if you don't renew it.
How often are the questions updated?
We always try to provide the latest pool of questions, Updates in the questions depend on the changes in actual pool of questions by different vendors. As soon as we know about the change in the exam question pool we try our best to update the products as fast as possible.
How many computers I can download Test-King software on?
You can download the Test-King products on the maximum number of 2 (two) computers or devices. If you need to use the software on more than two machines, you can purchase this option separately. Please email support@test-king.com if you need to use more than 5 (five) computers.
What is a PDF Version?
PDF Version is a pdf document of Questions & Answers product. The document file has standart .pdf format, which can be easily read by any pdf reader application like Adobe Acrobat Reader, Foxit Reader, OpenOffice, Google Docs and many others.
Can I purchase PDF Version without the Testing Engine?
PDF Version cannot be purchased separately. It is only available as an add-on to main Question & Answer Testing Engine product.
What operating systems are supported by your Testing Engine software?
Our testing engine is supported by Windows. Andriod and IOS software is currently under development.


