Certification: GPHR
Certification Full Name: Global Professional in Human Resources
Certification Provider: HRCI
Exam Code: GPHR
Exam Name: Global Professional in Human Resources
GPHR Exam Product Screenshots
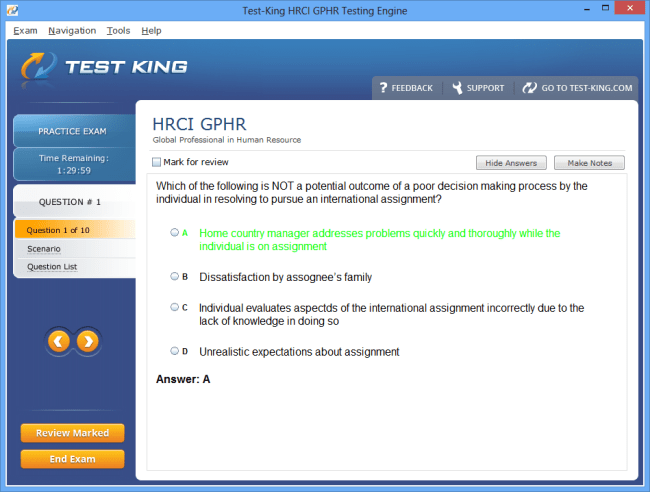
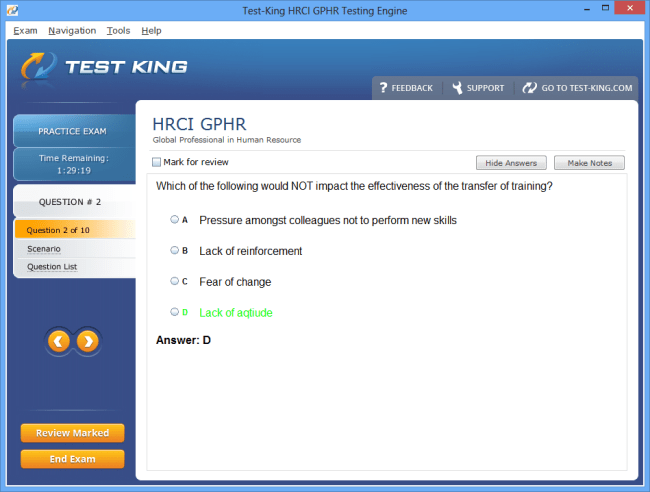
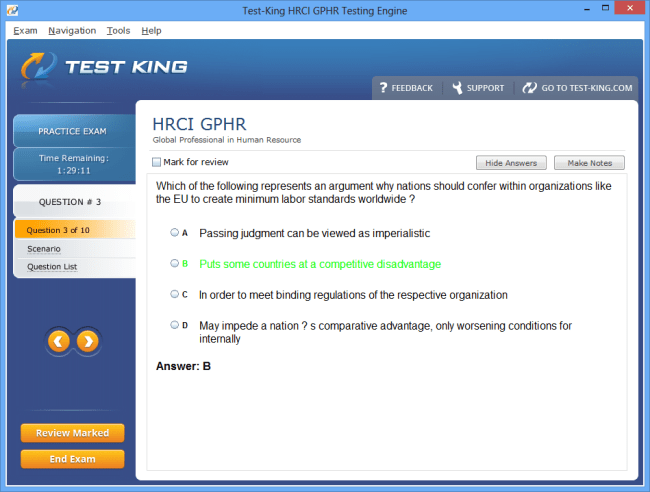
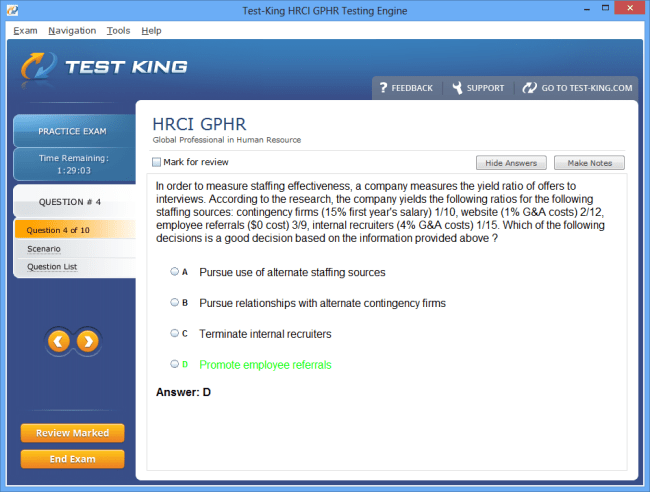
HRCI GPHR Certification Exam Overview and Syllabus
The HRCI Global Professional in Human Resources certification is an emblem of mastery for those navigating the intricate landscapes of international human resource management. It is designed for professionals who aspire to lead global organizations with insight, cultural acumen, and strategic foresight. The GPHR credential represents a global benchmark that recognizes one’s ability to align human capital strategies with multifaceted business goals that span continents, time zones, and diverse regulatory environments. This qualification goes beyond theoretical comprehension; it measures how effectively an HR practitioner can translate global dynamics into sustainable workforce frameworks that support enterprise expansion and resilience.
Strategic Global Human Resources and the Architecture of Global HR Mastery
The HRCI Global Professional in Human Resources examination requires candidates to demonstrate profound comprehension across six domains, with the Strategic Global Human Resources category bearing the heaviest emphasis. This field of study encompasses an intricate interplay between corporate vision and global human resource strategies. It requires the practitioner to synthesize business intelligence, policy awareness, and talent optimization into a cohesive operational plan that functions across different jurisdictions. The domain holds immense significance because, in today’s interconnected economies, organizations must function seamlessly in multiple environments while maintaining compliance and competitiveness.
Strategic Global Human Resources represents the epicenter of global HR capability. It necessitates understanding how internal business ambitions correspond with external realities such as economic volatility, political transformations, labor market fluctuations, and technological progressions. The professional who masters this area develops the ability to anticipate change, design adaptable strategies, and foster a resilient global workforce. The global professional must view the human resource system not as a collection of isolated processes, but as a holistic ecosystem that fuels international expansion, sustains organizational identity, and upholds ethical governance standards.
To operate effectively at this level, one must first learn to interpret and apply environmental scanning tools like PESTLE analysis. This analytical method allows human resource strategists to evaluate political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental dimensions that shape global operations. For instance, expanding into a region with volatile political systems requires deep awareness of regulatory implications and local labor laws, while entry into emerging markets may demand recalibration of workforce planning and compensation strategies. These variables are not static; they evolve with market shifts, currency fluctuations, and governmental reforms, all of which must be accounted for in HR strategy formulation.
Workforce planning stands as a cardinal element in this field. The HR professional must evaluate current and future labor needs while considering cost factors, availability of specialized skills, language proficiencies, and regional labor regulations. Effective workforce planning ensures that talent acquisition aligns with corporate goals while maintaining equilibrium between global efficiency and local adaptability. When organizations undergo transformation, such as mergers or acquisitions, workforce planning becomes an indispensable mechanism for maintaining stability and retaining institutional knowledge.
Another critical function within this domain is the ability to design and execute global workforce restructuring. This involves not only operational considerations but also moral, legal, and reputational dimensions. In global environments, restructuring may involve navigating local employment laws, union obligations, international compliance frameworks, and even employee sentiment. Missteps can damage corporate image or lead to financial and legal repercussions. Thus, global HR strategists must weigh all outcomes before implementing significant workforce adjustments. They must analyze factors such as cost implications, training capabilities, cultural cohesion, and the emotional impact on employees to ensure transitions occur smoothly and ethically.
One of the defining skills in global HR practice is the creation of an effective HR delivery model. Multinational enterprises often deploy regional or global centers of excellence, business partnering models, or decentralized frameworks to manage their human capital systems. The objective is to optimize cost, maintain high service quality, and ensure consistency across geographic boundaries. When constructing such models, HR professionals must account for linguistic diversity, time zone variations, and the technological infrastructure available in each region. The concept of “follow the sun” operations, for instance, illustrates how a globally distributed HR team can provide continuous service coverage without interruption.
The design of global organizational structures also demands a nuanced approach. Professionals in this discipline must understand how to balance centralized governance with local autonomy. While a unified global structure ensures alignment with corporate strategy, local adaptations allow flexibility in response to regional cultural norms, labor expectations, and economic realities. Designing global organizations involves intricate decisions regarding reporting hierarchies, communication systems, and technology platforms that facilitate cross-border collaboration. It also includes understanding local management expectations, compliance requirements, and the subtleties of leadership across cultures.
A modern HR leader must also comprehend the role and implications of outsourcing, offshoring, and shared services. These operational models enable organizations to achieve cost efficiencies and focus on strategic priorities. However, they are accompanied by inherent risks related to quality control, data privacy, and dependency on third-party vendors. Therefore, the HR strategist must evaluate the advantages and constraints of each approach, ensuring that outsourcing decisions complement overall business objectives and preserve institutional values.
Metrics form the backbone of strategic HR evaluation. Without precise measurement, even the most elegantly designed strategies may lack accountability. Common HR metrics include cost per hire, time to fill, turnover rate, engagement indices, and employee net promoter scores. These indicators provide empirical evidence of how effectively HR initiatives contribute to organizational success. Beyond numerical values, these metrics tell a story about how human capital investments influence business growth, innovation, and global competitiveness. Measuring return on investment in areas like international training, leadership development, and expatriate assignments is vital to justify resource allocation and refine strategic decisions.
In the realm of growth and expansion, HR professionals must distinguish between organic and inorganic strategies. Organic growth, such as establishing new offices or subsidiaries, often requires gradual recruitment, cultural integration, and internal leadership development. Inorganic growth, achieved through mergers or acquisitions, introduces immediate complexities such as harmonizing compensation systems, aligning leadership hierarchies, and integrating corporate cultures. The HR practitioner becomes a pivotal actor in this transformation, ensuring compliance with local laws, safeguarding employee rights, and fostering a cohesive identity amidst change.
Managing human resource processes during mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures is an arduous yet essential responsibility. HR professionals must navigate the intricacies of legal compliance, employee selection, communication planning, and resource allocation. During such transitions, transparency, empathy, and consistent messaging become crucial. The global HR leader must also consider the obligations of both buyers and sellers toward employees, including severance packages, benefit continuation, and collective bargaining implications. The capacity to guide organizations through these transformations reflects the hallmark of an accomplished HR strategist.
Operating in regions with minimal headcount presents another unique challenge. Some organizations may not have a legal entity in every location they operate, necessitating the use of alternative arrangements such as Professional Employment Organizations or partnerships with local entities. These models allow companies to employ staff without establishing full-scale operations in that jurisdiction. However, the HR leader must remain vigilant about compliance, data protection, and worker rights under such setups. Evaluating the pros and cons of outsourcing employment to a PEO demands thorough understanding of local legalities and potential reputational implications.
Strategic HR leadership also requires fluency in understanding and mitigating global risk factors that influence talent management. These include political unrest, labor shortages, economic recessions, and technological disruptions. The global HR expert should possess the foresight to design adaptive frameworks that absorb shocks while maintaining workforce stability. Scenario planning, risk assessment, and cross-border policy harmonization all form the arsenal of a capable global HR professional.
Another distinguishing aspect of global HR strategy lies in its emphasis on cultural intelligence. Organizations today operate in diverse social and linguistic milieus where cultural misunderstandings can derail productivity. Hence, HR professionals must cultivate sensitivity toward cultural values, communication styles, and behavioral norms that influence employee engagement. They must foster inclusion through tailored training programs, equitable policies, and transparent communication that respects diversity in all its dimensions.
From an operational standpoint, effective communication serves as the nervous system of global HR management. Whether it involves virtual teams, international project collaborations, or expatriate transitions, clarity in communication prevents misalignment and conflict. HR leaders must establish systems that encourage open dialogue across hierarchical and geographic boundaries. Digital communication platforms and unified HR management systems have become indispensable in bridging distances and maintaining cohesion within globally dispersed teams.
An often-overlooked yet crucial responsibility involves aligning HR strategies with the organization’s ethical and social commitments. In an age of heightened transparency, multinational corporations are scrutinized for their adherence to ethical labor practices, environmental sustainability, and equitable treatment of workers. The HR function thus extends beyond administrative boundaries into the domain of corporate stewardship. Professionals who attain the HRCI Global Professional in Human Resources credential are expected to champion ethics, compliance, and sustainability within their organizations, ensuring that global expansion aligns with social responsibility.
Furthermore, the capacity to manage data has emerged as a defining competency for modern HR professionals. Data-driven insights enable leaders to forecast attrition, identify skill gaps, and evaluate training effectiveness. When applied strategically, analytics transform human capital management from a reactive to a predictive discipline. The global HR expert must be adept at leveraging data while respecting international privacy standards such as the General Data Protection Regulation. A judicious approach to analytics ensures that decision-making remains informed, responsible, and culturally respectful.
The examination structure of the HRCI Global Professional in Human Resources certification reinforces the need for comprehensive preparation. Candidates are evaluated through multiple-choice questions designed to assess analytical reasoning, practical application, and theoretical understanding. The test includes 125 questions, with a passing score set at fifty-five percent, administered over 135 minutes with additional administrative time. The exam fee stands at four hundred and ninety-five US dollars, while the application fee amounts to one hundred dollars. Pearson VUE testing centers serve as the authorized venues for examination, ensuring standardized administration across locations.
Preparation for the HRCI Global Professional in Human Resources certification involves a multifaceted strategy. Aspirants must combine structured study with practical exposure to international HR scenarios. Engaging with sample question banks and simulated exams provides familiarity with exam patterns and enhances time management. However, genuine mastery stems from immersive professional experiences that allow candidates to internalize theoretical constructs. Real-world exposure to cross-border challenges, international employment law, and global leadership dynamics refines comprehension beyond textbook learning.
Candidates who succeed in earning this credential distinguish themselves as professionals equipped to steer organizations through the turbulence of globalization. Their ability to synchronize human capital management with transnational business strategy empowers companies to thrive in volatile markets. The certification thus serves not only as a professional milestone but as a symbol of one’s capacity to navigate complexity with intellect, empathy, and precision.
In essence, the Strategic Global Human Resources domain within the HRCI Global Professional in Human Resources examination captures the essence of modern organizational evolution. It reflects a world where people strategy determines corporate destiny, where adaptability is paramount, and where global collaboration defines success. By mastering these competencies, the HR professional evolves into a strategist capable of orchestrating human potential across borders, crafting a legacy of ethical leadership and enduring impact.
Global Talent Management and the Cultivation of International Workforce Excellence
Global Talent Management constitutes one of the most pivotal domains for professionals pursuing the HRCI Global Professional in Human Resources credential. This discipline focuses on ensuring that organizations can attract, cultivate, retain, and deploy talent across international borders while aligning workforce capabilities with corporate strategy. Effective talent management is not merely about filling vacancies; it requires an orchestrated approach that balances organizational needs, employee aspirations, cultural diversity, and operational efficiency. Human resource professionals who excel in this arena contribute directly to a company’s global competitiveness and long-term sustainability.
A comprehensive understanding of talent management begins with evaluating the components of a robust strategy. Strategic employee planning is fundamental, as it enables organizations to anticipate future skill requirements, identify critical roles, and develop succession pipelines. Talent acquisition processes must be tailored to different geographic regions, taking into account local labor laws, cultural nuances, and market conditions. Retention strategies also require meticulous attention, incorporating performance management frameworks, continuous learning opportunities, motivational programs, and clearly defined career progression pathways. This holistic approach ensures that employees remain engaged and productive while supporting organizational objectives.
Global sourcing of talent encompasses various approaches, each offering distinct advantages. Organizations may choose to build internal capabilities, buy expertise from the external market, or borrow talent through temporary arrangements or consulting engagements. Internal transfers and mobility programs facilitate knowledge sharing and cultural integration, while recruitment process outsourcing and partnerships with specialized agencies can accelerate talent acquisition in challenging markets. Social media platforms and employee referral programs have emerged as indispensable tools in global recruitment, allowing organizations to identify high-caliber candidates efficiently while projecting a compelling employer brand.
Talent assessment is another crucial dimension. Evaluating employees for skill, potential, and cultural adaptability requires nuanced methodologies that account for regional differences and unconscious bias. Assessment tools must be valid, reliable, and culturally sensitive, enabling organizations to make informed decisions about hiring, development, and promotion. The global HR professional must also consider the logistics of administering assessments across time zones, languages, and technological infrastructures, ensuring consistency and fairness in evaluation processes.
As organizations expand internationally, alternative work arrangements become increasingly relevant. Flexible schedules, telecommuting, virtual teams, cross-border collaborations, and job-sharing initiatives allow enterprises to optimize productivity while accommodating employee needs. These arrangements demand careful consideration of legal compliance, technological capability, cost-effectiveness, and organizational culture. HR professionals must evaluate the implications of different models on engagement, retention, and overall performance, designing policies that balance organizational objectives with workforce well-being.
The use of nonemployees, such as independent contractors, consultants, and third-party vendors, introduces both opportunities and risks in global talent management. While leveraging external expertise can enhance agility and reduce operational overhead, it also exposes organizations to misclassification risks, legal liabilities, and financial obligations. Human resource leaders must establish rigorous governance frameworks to manage these relationships, ensuring adherence to labor laws, contractual obligations, and ethical standards. Clear documentation, monitoring mechanisms, and communication channels are essential to mitigate potential complications.
Learning and development initiatives form the backbone of employee growth and organizational capability. Designing programs for a global workforce entails consideration of language barriers, cultural contexts, delivery methods, and learning styles. Organizations must assess knowledge gaps and provide appropriate resources, whether through e-learning platforms, workshops, mentorship programs, or blended learning solutions. Effective learning and development not only enhance individual performance but also cultivate leadership pipelines, foster innovation, and reinforce strategic priorities.
Performance management frameworks are integral to sustaining engagement and driving accountability. Establishing clear goals, aligning expectations with business objectives, and integrating culturally sensitive appraisal methods are essential. HR professionals must ensure that systems are legally compliant and technologically optimized, enabling seamless feedback, evaluation, and recognition processes. Change management plays a critical role in embedding these frameworks, requiring communication strategies, training, and continuous monitoring to sustain effectiveness across diverse global teams.
Employee engagement is a complex yet vital aspect of global talent management. Using diagnostic tools such as onboarding surveys, engagement surveys, exit interviews, and employee net promoter scores, organizations can gauge morale, satisfaction, and commitment levels. Engagement initiatives may include peer recognition platforms, coaching and mentoring programs, internal communication strategies, and social connectivity tools. Sustaining engagement requires ongoing attention to employee needs, responsive leadership, and an environment that nurtures inclusivity and collaboration.
The influence of employee organizations, including works councils and unions, must also be considered. These entities can shape labor relations, impact strategy, and influence workplace culture at both local and global levels. HR professionals must navigate these dynamics carefully, balancing organizational objectives with compliance and ethical obligations. Similarly, the guidance of international bodies such as the International Labour Organization, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, and the United Nations informs policy design, employee rights, and strategic decision-making across borders.
Technology has become a central enabler of global talent management. Integrating HR systems and tools allows organizations to automate processes, maintain regulatory compliance, and provide a consistent user experience across multiple regions. Analytics capabilities enable the monitoring of employee performance, engagement, and workforce trends, allowing for informed decision-making. HR leaders must ensure that data is secure, privacy regulations are observed, and emerging technologies are harnessed effectively to enhance organizational outcomes.
A critical aspect of data utilization involves standardizing definitions, measurement units, and benchmarks across different geographies. Global HR professionals must ensure that analytical insights are comparable and actionable while respecting local legal constraints and cultural expectations. Data-driven decision-making enhances operational efficiency, supports talent deployment strategies, and provides measurable outcomes that link human capital initiatives to business success.
The orchestration of global talent management requires fluency in cultural intelligence. Professionals must understand the interplay of societal norms, organizational culture, and individual expectations across diverse regions. Programs for inclusion, diversity, and equity must be tailored to address cultural, religious, social, political, and legal considerations. These initiatives not only improve employee satisfaction but also enhance innovation, collaboration, and organizational reputation on the international stage.
In multinational contexts, compensation and reward strategies must be synchronized with talent management objectives. Total rewards, encompassing base salary, benefits, bonuses, and equity incentives, should reflect local norms while reinforcing corporate philosophy. HR leaders must balance statutory compliance with market competitiveness, ensuring equitable and motivating packages for employees at all levels. Supplemental pay considerations, such as hazard allowances, hardship stipends, and per diems, further enhance global mobility and engagement by addressing the unique challenges of specific regions or roles.
Learning to navigate the dynamics of expatriates and cross-border mobility is intricately linked to talent management. Employees assigned to overseas positions require support through planning, orientation, cultural adaptation, and logistical assistance. The selection process must account for demographic variables, family considerations, and personal adaptability. Compensation packages must include incremental cost variables, allowances, and benefits tailored to the expatriate’s circumstances, ensuring financial equity and operational feasibility. Repatriation planning is equally crucial, as it facilitates smooth transitions back to home-country operations while maintaining career development and family stability.
The role of global HR professionals extends to monitoring legislative landscapes and ensuring compliance with employment laws in multiple jurisdictions. This involves understanding country-specific regulations, statutory obligations, and customary practices that affect recruitment, compensation, performance management, and employee relations. Navigating these complexities requires a combination of legal knowledge, cultural literacy, and strategic judgment. Failure to comply can result in legal sanctions, reputational harm, and disruption to operations.
Global talent management also entails fostering organizational agility. Workforce planning, reskilling initiatives, and leadership development must be adaptable to rapid market shifts, technological innovations, and changing competitive landscapes. HR professionals are tasked with creating mechanisms for continuous learning, scenario planning, and proactive problem-solving. These strategies enable organizations to remain resilient while preserving talent engagement, performance standards, and operational continuity.
Engagement with local communities, ethical practices, and corporate social responsibility forms a subtle yet powerful component of global talent management. HR leaders must design policies that promote ethical behavior, environmental stewardship, and social impact while maintaining alignment with corporate strategy. Employee participation in these initiatives fosters loyalty, pride, and long-term commitment, reinforcing the organization’s position as a responsible global entity.
Preparation for the GPHR examination requires integrating theoretical knowledge with practical exposure to international talent management challenges. Sample questions and practice tests provide familiarity with the format and conceptual frameworks, but true mastery derives from hands-on experience. Professionals who manage recruitment, performance, engagement, and learning initiatives across geographies acquire an intrinsic understanding that enables them to make informed, culturally sensitive decisions under real-world conditions.
In essence, global talent management embodies the intersection of strategy, culture, and operational excellence. HR professionals in this domain serve as architects of organizational capability, ensuring that talent is identified, cultivated, and mobilized effectively across international boundaries. Their expertise ensures that workforce strategies are aligned with corporate vision, responsive to local contexts, and resilient to global uncertainties. Mastery in this field not only enhances career prospects but also empowers organizations to thrive in increasingly complex and competitive global landscapes.
Human resource leaders who have internalized these principles are equipped to influence business strategy profoundly. By fostering talent pipelines, enhancing employee engagement, and leveraging technological insights, they transform human capital from a resource into a strategic advantage. This intricate balance of foresight, analytical rigor, and cultural intelligence defines the hallmark of the HRCI Global Professional in Human Resources credential and underscores the essential role of talent management in the success of international enterprises.
Global Mobility and the Dynamics of International Workforce Movement
Global Mobility is an indispensable domain within the HRCI Global Professional in Human Resources certification, emphasizing the strategic management of employees across international boundaries. It involves the planning, execution, and oversight of expatriate assignments, ensuring smooth transitions, compliance with local and international regulations, and alignment with organizational objectives. This domain is critical for multinational enterprises seeking to deploy talent effectively while mitigating risks associated with cross-border employment. Professionals who excel in global mobility act as navigators of complex geopolitical landscapes, labor regulations, and cultural intricacies.
At the heart of global mobility lies the analysis of various expatriate assignment models. Organizations utilize long-term, short-term, local plus, and hybrid assignments depending on operational requirements, business strategy, and talent objectives. Each model carries unique implications for compensation, tax obligations, relocation support, and cultural adaptation. Understanding the nuances of these assignments allows HR professionals to optimize employee performance while controlling costs and maintaining compliance. For instance, long-term assignments require comprehensive planning, including relocation logistics, family support, housing, education, and healthcare, whereas short-term or project-based assignments may prioritize agility and rapid integration into host-country operations.
Selecting the appropriate candidate for international assignment necessitates careful evaluation of demographic, cultural, and personal factors. Beyond standard professional qualifications, considerations such as religion, gender identity, family circumstances, cultural adaptability, and even pet care may influence assignment success. Human resource leaders must assess candidates holistically, ensuring that both the employee and their family can acclimate to the host-country environment while maintaining productivity and engagement. This careful selection process mitigates potential challenges, enhances employee satisfaction, and reduces the risk of assignment failure.
Financial considerations play a central role in global mobility. The primary incremental variables included in expatriate cost analyses encompass relocation expenses, housing allowances, travel costs, education stipends, home leave allowances, cost-of-living adjustments, consulting fees, and tax obligations. HR professionals must design compensation packages that are equitable, compliant with host-country regulations, and aligned with organizational policies. Detailed financial planning ensures transparency, fairness, and fiscal responsibility while fostering employee confidence and engagement.
The hiring and onboarding processes for expatriates vary significantly across countries, reflecting regulatory, statutory, and customary differences. Preemployment screenings, personally identifiable information requirements, health checks, benefit enrollment, employment agreements, and visa procedures must be navigated with precision. HR leaders must develop robust protocols to manage these processes, ensuring compliance with local labor laws while facilitating a seamless experience for the employee. Understanding these differences prevents legal complications, enhances operational efficiency, and reinforces the organization’s reputation as a responsible employer.
Visa and immigration management is another critical aspect of global mobility. Professionals must identify applicable visa types for employees and their families, navigate regulatory frameworks, and ensure timely processing. The offboarding process also varies across jurisdictions, encompassing notice periods, benefit discontinuation, government notifications, departure travel arrangements, and labor organization consultations. The ability to anticipate and address these differences is essential for maintaining compliance and ensuring positive employee experiences.
Successful repatriation is as crucial as expatriation itself. Planning for the return of employees from overseas assignments involves integrating them into new roles, supporting family reacclimation, managing visa and immigration requirements, and ensuring career continuity. Effective repatriation strategies preserve institutional knowledge, maintain engagement, and reinforce organizational loyalty. HR professionals must anticipate potential challenges, such as reverse culture shock, compensation adjustments, and career progression expectations, to facilitate a smooth transition.
Localization of expatriates demands attention to practical, legal, and cultural considerations. Housing arrangements, children’s education, compensation alignment, and compliance with local labor laws are central to successful integration. HR leaders must navigate these variables with sensitivity and precision, ensuring that employees feel supported and valued while meeting organizational objectives. This holistic approach to localization enhances employee retention, performance, and satisfaction.
Global mobility also requires a sophisticated understanding of cross-border tax regulations and cost management. HR professionals must coordinate with financial and legal advisors to address issues such as double taxation, totalization agreements, and tax equalization policies. Effective management of these elements ensures financial compliance, reduces risk exposure, and provides equitable treatment for expatriates. Organizations benefit from streamlined operations, predictable budgeting, and enhanced strategic planning by integrating these considerations into mobility programs.
Cultural intelligence is indispensable for international assignments. HR leaders must educate and prepare employees for host-country norms, workplace etiquette, and social expectations. Pre-departure training, language instruction, and cultural immersion programs enhance adaptability and minimize misunderstandings. Effective preparation fosters productive relationships with local colleagues, clients, and stakeholders while supporting organizational cohesion. Employees who are culturally attuned are better equipped to navigate challenges, contribute meaningfully, and act as ambassadors for the organization.
Logistical planning forms the backbone of global mobility execution. This includes relocation services, housing arrangements, travel logistics, visa and immigration documentation, and family support. HR professionals must coordinate with relocation agencies, legal advisors, and internal stakeholders to ensure that all elements align with company standards and regulatory requirements. Precision and attention to detail are essential, as missteps can result in financial loss, operational disruption, or diminished employee satisfaction.
Global mobility strategies also involve continuous evaluation and monitoring. Tracking assignment progress, assessing employee engagement, and analyzing cost-effectiveness allow organizations to refine policies and practices. Key performance indicators such as assignment completion rates, expatriate satisfaction, and return-on-investment metrics provide actionable insights. Analytics-driven oversight enables HR professionals to adjust strategies proactively, optimize outcomes, and ensure alignment with organizational objectives.
Employee support extends beyond logistical and financial considerations. Mental well-being, family integration, social support networks, and access to healthcare resources are critical to assignment success. HR leaders must develop programs that address these dimensions, fostering resilience and stability among expatriates and their families. Comprehensive support enhances retention, productivity, and overall engagement while mitigating stress-related risks associated with relocation.
Strategic alignment of mobility with organizational objectives is a core responsibility. HR professionals must ensure that the deployment of talent abroad contributes directly to business goals, such as market expansion, project execution, knowledge transfer, and leadership development. Assignments should be designed to maximize value both for the employee and the organization. Alignment involves continuous communication with business leaders, operational units, and international offices to integrate mobility plans into broader corporate strategy.
Policy development is central to managing international assignments. HR leaders must craft policies that address eligibility criteria, assignment duration, compensation frameworks, benefits administration, repatriation procedures, and compliance requirements. Clear and coherent policies provide consistency, fairness, and transparency, reducing ambiguity and promoting trust among employees. Policies must be flexible enough to accommodate unique circumstances while maintaining alignment with organizational standards.
Technology serves as an essential enabler of global mobility. HR information systems, data analytics platforms, and digital communication tools streamline assignment management, reporting, and monitoring. Leveraging technology allows professionals to track expatriate progress, manage documentation, and communicate effectively across time zones. Data-driven insights facilitate predictive planning, risk mitigation, and informed decision-making, enhancing operational efficiency and assignment success.
Risk management is another critical dimension. Expatriate assignments involve inherent risks related to political instability, health and safety, regulatory compliance, and financial exposure. HR professionals must implement frameworks to identify, assess, and mitigate these risks proactively. Contingency planning, emergency response protocols, and continuous monitoring ensure that employees are protected while organizational objectives are maintained.
Training and development programs specifically tailored for international assignees are indispensable. These programs include cultural awareness workshops, leadership development, language training, and technical skill enhancement. By equipping employees with the necessary tools and knowledge, organizations enhance productivity, reduce adaptation time, and foster positive cross-cultural interactions. Continuous development during assignments sustains engagement and supports long-term organizational objectives.
Compensation design for international assignments must be equitable and competitive. This includes base salary adjustments, cost-of-living allowances, housing stipends, tax equalization, and supplementary benefits. Properly structured compensation packages ensure fairness, support mobility objectives, and maintain motivation among employees. HR professionals must also account for host-country regulations, market practices, and organizational policies to ensure alignment and compliance.
Cross-border assignments often necessitate collaboration with legal, financial, and operational teams. HR leaders coordinate with internal and external stakeholders to ensure smooth transitions, regulatory compliance, and employee well-being. Effective collaboration fosters synergy, reduces operational friction, and enhances the overall success of mobility programs.
Global mobility professionals must also focus on repatriation readiness. Planning for reintegration into home-country roles involves assessing career trajectories, providing coaching and mentoring, and facilitating knowledge transfer. Repatriation ensures that valuable experience gained abroad contributes to organizational growth, strengthens leadership pipelines, and enhances retention. Preparing employees and their families for return is essential to minimize culture shock, retain engagement, and support professional development.
Monitoring and evaluation form an ongoing cycle within global mobility. Metrics such as assignment success rates, cost analysis, employee satisfaction, and compliance adherence provide critical insights. HR professionals leverage this information to refine processes, adjust policies, and optimize program effectiveness. Analytical rigor ensures that mobility initiatives are not only efficient but also strategically aligned with organizational priorities.
Global mobility also requires understanding the interplay of ethical, legal, and social considerations. Professionals must navigate issues related to labor standards, anti-discrimination laws, human rights, and cultural sensitivities. Ensuring ethical practices strengthens corporate reputation, fosters trust, and aligns mobility programs with broader organizational values.
The role of HR leaders in global mobility transcends administrative management; it encompasses strategic foresight, cultural stewardship, financial acumen, and operational dexterity. By integrating these competencies, professionals create mobility frameworks that enhance talent deployment, support organizational growth, and cultivate a resilient, adaptable workforce. The domain of global mobility reflects the complexity, dynamism, and strategic importance of human capital in a globalized business environment, positioning certified professionals as indispensable architects of international organizational success.
Workplace Culture, Ethics, and Corporate Responsibility in Global HR
Workplace culture forms a cornerstone of the HRCI Global Professional in Human Resources certification, encompassing the creation of inclusive environments, ethical practices, and corporate responsibility on a global scale. HR professionals must understand the subtle interplay between organizational objectives, employee engagement, and cultural dynamics, as these factors significantly influence productivity, innovation, and long-term sustainability. Cultivating a culture that integrates ethical behavior, social responsibility, and cross-cultural competence is essential for multinational organizations seeking to thrive in diverse and competitive environments.
Understanding global cultural frameworks is fundamental to shaping workplace culture. The models developed by Hofstede and Trompenaars provide insights into how national values, societal norms, and communication styles influence behavior, decision-making, and collaboration within organizations. HR leaders must apply these frameworks to design policies, programs, and practices that accommodate cultural differences while fostering cohesion and inclusivity. Recognizing variations in power distance, individualism versus collectivism, uncertainty avoidance, and other cultural dimensions allows professionals to anticipate challenges, mediate conflicts, and facilitate effective teamwork across borders.
Designing HR programs that respect cultural nuances requires attention to potential differences in work ethics, communication preferences, and societal expectations. Strategies for promoting diversity and inclusion must account for religious practices, gender norms, political structures, social hierarchies, and legal requirements. HR professionals are tasked with integrating these considerations into recruitment, onboarding, training, performance management, and employee engagement initiatives, ensuring that programs resonate with local sensibilities while aligning with global objectives.
Corporate social responsibility and ethics programs are integral to establishing trust, reputation, and organizational legitimacy. HR leaders must implement initiatives that support ethical conduct, environmental stewardship, community engagement, and regulatory compliance. Such programs encompass risk management, adherence to international laws, and alignment with principles like the US Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, the UK Bribery Act, and Safe Harbor Privacy Principles. Ensuring that employees understand their responsibilities and have access to ethical guidance fosters a workplace environment that prioritizes integrity and accountability.
The influence of ethical leadership on workplace culture cannot be overstated. Leaders who model ethical behavior, transparency, and fairness inspire trust and commitment among employees. HR professionals play a key role in developing leadership programs that embed these values, offering coaching, mentorship, and training to cultivate ethical decision-making across hierarchical levels. By embedding ethical considerations into leadership development, organizations reinforce cultural norms that support compliance, engagement, and performance excellence.
Managing cultural diversity involves designing programs that encourage collaboration and mitigate potential conflicts arising from differing values, communication styles, and workplace expectations. HR professionals must develop mechanisms to facilitate dialogue, encourage mutual respect, and resolve disputes constructively. Training initiatives that enhance cultural intelligence, empathy, and conflict resolution skills equip employees to navigate complex interactions, promoting harmony and productivity in global teams.
The implementation of inclusion strategies extends beyond representation. HR leaders must foster an environment where all employees feel valued, heard, and empowered to contribute meaningfully. Policies and programs should address barriers to participation, provide equitable opportunities for advancement, and ensure that performance evaluations are fair and culturally aware. By creating inclusive workplaces, organizations enhance innovation, retention, and employee satisfaction, ultimately reinforcing their competitive advantage.
Ethical and responsible conduct in global organizations involves continuous monitoring and adaptation. HR professionals must establish mechanisms to identify potential risks, audit compliance with policies, and address emerging ethical dilemmas. Proactive engagement with legal advisors, internal auditors, and compliance officers ensures that the organization operates within regulatory frameworks and maintains reputational integrity. This vigilance extends to areas such as anti-bribery, anti-corruption, privacy protection, and fair labor practices, reflecting the organization’s commitment to principled operations.
Workplace culture also intersects with employee engagement and motivation. HR leaders must design programs that encourage collaboration, recognize achievements, and provide meaningful opportunities for professional growth. Peer recognition platforms, mentoring, coaching, and transparent communication channels foster a sense of belonging and reinforce desired behaviors. Engagement initiatives must be tailored to cultural expectations and workforce diversity to maximize their impact across different regions and organizational levels.
Corporate social responsibility initiatives provide employees with opportunities to contribute to broader societal goals, enhancing organizational reputation and employee morale. HR professionals may facilitate volunteer programs, sustainability projects, community partnerships, and educational initiatives. These programs not only strengthen organizational legitimacy but also reinforce values that employees can internalize and champion, creating a culture of purpose and accountability.
Ethical frameworks are critical in guiding employee behavior and organizational decisions. HR professionals must design policies and training that emphasize integrity, fairness, and transparency in interactions with colleagues, clients, and external stakeholders. By embedding these principles into everyday operations, organizations cultivate a culture where ethical considerations are prioritized alongside business objectives, creating a resilient and trusted corporate identity.
The integration of workplace culture, ethics, and corporate responsibility requires alignment with broader human resource strategies. HR leaders must ensure that diversity, equity, and inclusion, ethical behavior, and CSR initiatives are interconnected with talent management, performance systems, mobility programs, and compensation strategies. This holistic integration ensures that cultural and ethical imperatives reinforce organizational goals rather than operate as isolated initiatives.
Monitoring and assessment are essential to maintain and enhance workplace culture. HR professionals employ surveys, focus groups, engagement metrics, and qualitative feedback to evaluate cultural climate, ethical awareness, and employee perceptions. Insights from these assessments guide program adjustments, leadership interventions, and policy enhancements. Data-driven evaluation enables organizations to identify strengths, address gaps, and sustain a workplace environment that aligns with global standards and organizational vision.
Training and development in workplace culture focus on equipping employees with the skills and knowledge necessary to navigate diverse environments, act ethically, and contribute to corporate responsibility initiatives. Workshops on cultural intelligence, ethics, unconscious bias, and inclusive leadership prepare employees to handle challenges effectively. These programs cultivate a workforce capable of functioning in complex, multicultural contexts while reinforcing organizational values.
The role of HR professionals extends to crisis management and ethical decision-making in challenging situations. They must anticipate potential cultural misunderstandings, compliance violations, and ethical dilemmas, developing response strategies that protect employees and organizational interests. By fostering a proactive, principled approach, HR leaders ensure that workplace culture remains resilient even in the face of adversity.
Global workplace culture also involves the harmonization of policies across regions. While respecting local customs and laws, organizations must maintain core principles related to ethics, inclusion, and corporate responsibility. HR professionals navigate this balance by adapting practices to local contexts without compromising global standards, ensuring coherence and consistency in organizational behavior.
Employee well-being is a central consideration in cultivating an ethical and responsible workplace culture. Programs addressing mental health, work-life balance, physical safety, and social support are integral to employee engagement and productivity. HR leaders must design initiatives that are culturally appropriate and responsive to local norms while aligning with the organization’s broader ethical and operational objectives.
Communication strategies are vital in embedding culture and ethics within organizations. Transparent, consistent, and culturally sensitive communication ensures that employees understand expectations, policies, and organizational values. HR professionals must leverage multiple channels, including digital platforms, town halls, training sessions, and written guidelines, to reinforce desired behaviors and cultural norms. Effective communication promotes accountability, fosters engagement, and strengthens organizational cohesion across geographically dispersed teams.
Ethical leadership development programs emphasize decision-making frameworks, accountability mechanisms, and mentorship structures. HR professionals guide leaders in modeling behavior that aligns with organizational values, promoting integrity in operations, and cultivating a culture of trust. By prioritizing ethical conduct at the leadership level, organizations set the tone for behavior across all levels, reinforcing a culture that supports compliance, diversity, and social responsibility.
Workplace culture also intersects with corporate governance. HR professionals collaborate with boards, executives, and operational managers to ensure that policies and practices support ethical decision-making, legal compliance, and strategic alignment. Governance structures provide oversight, establish accountability, and enable corrective action when deviations occur, safeguarding organizational reputation and operational integrity.
Global HR professionals must also consider the role of technology in shaping culture and ethical behavior. Digital tools facilitate training, monitoring, communication, and engagement initiatives. Platforms for ethical reporting, feedback, and recognition allow employees to participate actively in sustaining a positive workplace culture. Technology enhances accessibility, efficiency, and effectiveness in embedding ethical and responsible practices throughout the organization.
In addition, fostering innovation and continuous improvement within the workplace requires cultivating a culture that encourages experimentation, learning from mistakes, and cross-cultural collaboration. HR professionals guide employees in embracing adaptive mindsets while ensuring that ethical and corporate responsibility standards are maintained. This balance between innovation and principled conduct is crucial for sustaining competitive advantage and organizational credibility.
Finally, HR leaders must continuously evaluate the evolving global landscape to maintain relevance in workplace culture strategies. Social, political, technological, and economic changes influence employee expectations, regulatory requirements, and cultural norms. By staying attuned to these shifts, professionals can anticipate challenges, seize opportunities, and implement initiatives that reinforce inclusivity, ethics, and corporate responsibility in dynamic global environments.
Mastery of workplace culture, ethics, and corporate responsibility enables HR professionals to shape organizations that are resilient, principled, and globally competitive. Their role in embedding inclusive practices, guiding ethical behavior, and fostering social responsibility ensures that multinational enterprises can thrive while creating meaningful value for employees, communities, and stakeholders alike.
Total Rewards and Compensation Strategies in Global Human Resources
Total rewards constitute a pivotal domain in the HRCI Global Professional in Human Resources certification, encompassing the design and administration of compensation, benefits, and recognition systems that align with organizational objectives and workforce expectations. The globalized business environment demands that HR professionals craft reward strategies that balance competitiveness, compliance, equity, and cultural nuances across diverse geographies. A sophisticated understanding of total rewards enables HR leaders to attract, retain, and motivate talent while reinforcing organizational goals and sustaining operational efficiency.
Developing comprehensive reward strategies begins with evaluating the statutory and market requirements of each location where the organization operates. HR professionals must consider legal mandates, labor regulations, taxation frameworks, and customary practices while designing compensation packages. These packages often integrate base salary, performance-based incentives, equity compensation, retirement benefits, health and welfare programs, and supplementary allowances. The ability to harmonize global consistency with local relevance is essential, ensuring that employees perceive fairness and competitiveness while the organization remains compliant and fiscally prudent.
Expatriate compensation philosophies require particular attention. Home-country-based models anchor remuneration to the employee’s original country, often adjusted for cost-of-living differences and purchasing power parity, while host-country-based models align pay with local market standards. HR leaders must weigh these approaches carefully, considering factors such as tax implications, currency fluctuations, and employee expectations. Strategic decisions in this area influence retention, engagement, and organizational reputation, making it imperative to design packages that are transparent, equitable, and aligned with assignment objectives.
Supplemental pay represents another critical dimension of total rewards. These additional payments may include hazard pay, hardship allowances, per diems, relocation stipends, and specialized benefits for employees operating in challenging or high-risk environments. HR professionals must identify circumstances warranting such compensation, such as political unrest, extreme climates, safety risks, or demanding work schedules. Tailoring supplemental pay to individual and situational needs ensures employees feel supported, valued, and motivated while reinforcing organizational commitment.
Retirement plans constitute a foundational component of total rewards strategy. HR leaders must navigate the complexities of defined benefit and defined contribution schemes, evaluating statutory requirements, voluntary contributions, and cross-border considerations. Employees may participate in home-country, host-country, or hybrid retirement programs, requiring careful coordination to ensure compliance, minimize tax exposure, and provide clarity for beneficiaries. By integrating retirement planning into broader total rewards frameworks, organizations foster long-term financial security for employees while enhancing employer value proposition.
Performance-based incentives are instrumental in driving organizational objectives and employee engagement. HR professionals design metrics-aligned bonus structures, recognition programs, and career development pathways that reward high performance while promoting collaboration and innovation. Implementing transparent and measurable performance criteria ensures that employees understand expectations and recognize the connection between their contributions and organizational success. Such systems also facilitate succession planning, talent retention, and knowledge transfer across geographies.
Health and welfare benefits represent another critical pillar within total rewards. Comprehensive programs may include medical coverage, mental health support, wellness initiatives, insurance schemes, and employee assistance programs. HR leaders must ensure that benefits are culturally relevant, compliant with local regulations, and accessible to all employees, including expatriates. Tailored health and welfare programs enhance productivity, reduce absenteeism, and reinforce a culture of care and engagement within the organization.
Payroll management across global operations presents unique challenges. Variations in currency, taxation, labor laws, and payment schedules necessitate precise coordination. HR professionals must implement systems and processes that ensure accurate, timely, and compliant payroll administration. Automation and digital platforms facilitate efficiency, reduce errors, and provide transparency for employees. Effective payroll management supports employee trust, operational reliability, and strategic planning.
Equity compensation strategies are increasingly utilized to align employee interests with organizational performance. Stock options, restricted stock units, and other equity instruments incentivize employees to contribute to long-term business success. HR professionals must navigate legal, financial, and regulatory considerations, ensuring that equity awards are appropriately structured, communicated, and managed across jurisdictions. Equity compensation strengthens retention, fosters a sense of ownership, and encourages commitment to organizational goals.
Cost-of-living adjustments and location-specific allowances are crucial in managing the mobility of employees. HR leaders must analyze economic conditions, purchasing power, and inflation rates to determine appropriate adjustments for expatriates and globally mobile employees. Properly calibrated adjustments ensure fairness, maintain motivation, and prevent disparities that could undermine engagement or performance.
Taxation and compliance considerations permeate all aspects of total rewards. HR professionals coordinate with financial and legal advisors to manage corporate obligations, employee tax liabilities, and reporting requirements. Strategies may include tax equalization, withholding management, and adherence to international agreements such as double taxation treaties. Compliance safeguards the organization from legal exposure while ensuring that employees receive equitable treatment and clarity regarding financial obligations.
Recognition programs complement monetary compensation by reinforcing desired behaviors, achievements, and organizational values. Peer-to-peer recognition, performance awards, milestone celebrations, and public acknowledgment foster motivation, engagement, and a positive organizational culture. HR professionals must design recognition programs that are culturally sensitive, equitable, and integrated with broader performance and reward strategies to maximize their impact.
Communication of total rewards is essential for employee understanding, engagement, and perception of fairness. HR leaders must articulate compensation philosophies, benefit structures, and recognition programs clearly and consistently. Transparency fosters trust, reduces misunderstandings, and enhances the perceived value of the total rewards package. Communication strategies may include training sessions, digital portals, informational guides, and personalized consultations to address employee inquiries effectively.
Benchmarking and market analysis are integral to designing competitive total rewards programs. HR professionals must collect and analyze data on industry standards, geographic variations, and emerging trends to ensure that compensation packages remain attractive, equitable, and aligned with organizational objectives. Benchmarking also informs strategic decisions regarding pay adjustments, benefit enhancements, and talent retention initiatives.
Total rewards strategy must be closely aligned with talent management initiatives. Compensation and benefits programs support recruitment, retention, performance management, learning and development, and succession planning. HR leaders integrate total rewards with organizational goals to create a cohesive human capital framework that enhances engagement, drives results, and positions the organization as an employer of choice.
Global mobility further intersects with total rewards, requiring HR professionals to design packages that accommodate international assignments, repatriation, and localization. This involves harmonizing base pay, allowances, benefits, and recognition mechanisms across borders while accounting for cultural, legal, and economic differences. A well-structured global rewards program ensures continuity, fairness, and strategic alignment throughout the employee lifecycle.
Metrics and analytics are increasingly vital in managing total rewards effectively. HR professionals utilize data to assess cost-effectiveness, employee satisfaction, engagement levels, and alignment with strategic objectives. Key performance indicators, surveys, and analytical models inform decision-making, enabling continuous refinement and optimization of reward programs. Evidence-based insights enhance organizational agility, accountability, and strategic impact.
Incentive programs designed to promote strategic behaviors require careful calibration. HR leaders must link rewards to measurable outcomes, organizational priorities, and individual performance. Incentives may target innovation, cross-functional collaboration, leadership development, or customer satisfaction. Structuring incentives thoughtfully ensures alignment with organizational values while encouraging desired employee actions.
Flexibility and adaptability are crucial in managing total rewards in diverse environments. HR professionals must respond to evolving market conditions, regulatory changes, and workforce expectations. This includes adjusting benefit offerings, compensation levels, and recognition programs to meet emerging needs while maintaining equity and compliance. Adaptive strategies foster organizational resilience, employee loyalty, and long-term sustainability.
Employee engagement is deeply influenced by the perceived fairness and competitiveness of total rewards. HR leaders must ensure that employees feel valued, motivated, and recognized through both tangible and intangible rewards. Engagement strategies linked to total rewards enhance productivity, reduce turnover, and strengthen organizational culture. Tailored initiatives that account for cultural and demographic diversity maximize impact across global teams.
Technology plays a critical role in the administration and communication of total rewards. Digital platforms streamline payroll, benefits management, performance tracking, recognition, and reporting. HR professionals leverage technology to enhance efficiency, provide real-time insights, and ensure accessibility for employees across regions. Effective use of technology supports transparency, accuracy, and data-driven decision-making.
Strategic integration of total rewards with business objectives ensures that compensation and benefits programs contribute directly to organizational success. HR professionals must align reward strategies with financial goals, operational needs, and talent priorities. Cohesion between rewards and strategy reinforces employee motivation, supports organizational performance, and sustains competitive advantage.
Finally, HR professionals must continuously evaluate and refine total rewards programs. Emerging trends in employee expectations, market conditions, and regulatory frameworks require proactive adaptation. By analyzing feedback, monitoring outcomes, and implementing iterative improvements, HR leaders maintain the relevance, competitiveness, and effectiveness of total rewards initiatives across global operations.
Mastery of total rewards enables HR professionals to design comprehensive, equitable, and strategic compensation and benefits programs that attract and retain top talent, foster engagement, and drive organizational performance in an increasingly complex and interconnected global environment.
Risk Management, Compliance, and Strategic Integration in Global Human Resources
Risk management and compliance form the culmination of expertise required for the HRCI Global Professional in Human Resources credential, focusing on safeguarding employees, maintaining legal conformity, and protecting organizational integrity on a global scale. In an interconnected and rapidly evolving business landscape, HR professionals must develop proactive strategies to anticipate and mitigate risks while ensuring adherence to diverse regulatory frameworks. Mastery of this domain enables leaders to foster secure, ethical, and efficient workplaces that enhance both employee well-being and organizational resilience.
Developing a comprehensive strategy for global employee safety begins with identifying potential hazards across physical, operational, and geopolitical contexts. HR leaders must evaluate environmental conditions, regional threats, organizational vulnerabilities, and workforce-specific risks to establish prevention and mitigation measures. This may involve designing emergency protocols, conducting risk assessments, and coordinating with security specialists, medical services, and travel advisors to ensure a safe working environment for employees operating domestically and internationally.
Global mobility introduces unique considerations for risk management. Employees on international assignments may encounter legal, cultural, and environmental challenges that require meticulous planning. HR professionals must provide guidance and resources for expatriates, addressing aspects such as health and safety, visa compliance, family welfare, and integration into host-country environments. Proactive support reduces potential disruptions, fosters engagement, and protects both the employee and the organization from avoidable liabilities.
Security management includes the implementation of internal controls designed to protect employees and organizational assets. Audits, segregation of duties, multi-level approval processes, exception reporting, and external accreditation mechanisms help maintain compliance and minimize operational vulnerabilities. HR professionals coordinate with internal audit, finance, and compliance teams to ensure these controls are effective, consistently applied, and tailored to the global operational landscape.
Anti-discrimination, anti-harassment, and anti-bullying policies are critical to cultivating a safe and respectful workplace. HR leaders must develop and enforce guidelines that comply with regional regulations while promoting cultural sensitivity and inclusivity. Training programs, reporting mechanisms, and consistent enforcement ensure that employees understand their rights and responsibilities and that violations are addressed swiftly and appropriately. These measures foster a culture of respect and accountability that aligns with global organizational standards.
Investigations into workplace incidents require careful planning and execution. HR professionals must select qualified investigators, adhere to regional legal requirements, maintain impartiality, and document outcomes accurately. Effective investigation protocols mitigate risks, reinforce ethical standards, and preserve organizational credibility. Cultural differences must be considered when conducting investigations to ensure fairness, transparency, and compliance with local norms.
Data privacy and protection are increasingly critical in the management of global human resources. HR leaders must implement practices that comply with international standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation, while safeguarding sensitive employee information. Principles including lawfulness, fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, data minimization, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity, and accountability must guide data collection, storage, processing, and reporting. A robust data governance framework builds trust with employees and ensures organizational compliance with regulatory expectations.
Managing compliance requires an understanding of international labor standards and local legal obligations. HR professionals must navigate differences in employment law, statutory benefits, reporting requirements, and labor relations practices. By maintaining up-to-date knowledge and collaborating with legal advisors, HR leaders ensure that policies and practices comply with applicable regulations while minimizing risk exposure. This approach enhances organizational credibility and reduces the potential for costly disputes or reputational damage.
Proactive risk management integrates with talent management, mobility, workplace culture, and total rewards strategies to ensure holistic organizational resilience. HR professionals assess potential vulnerabilities in each functional area, applying preventive measures and contingency plans to maintain continuity and mitigate disruptions. By linking risk management to broader human capital strategies, organizations reinforce strategic alignment, operational stability, and employee confidence.
Training and development play a pivotal role in preparing employees to navigate risks and comply with regulations. Programs addressing safety protocols, ethical behavior, anti-discrimination, harassment prevention, data protection, and crisis response equip employees with knowledge and practical skills. HR professionals tailor these programs to cultural contexts, job roles, and regional regulations to maximize their effectiveness and relevance. Continuous reinforcement through workshops, simulations, and digital learning ensures that employees remain informed and prepared.
The use of technology enhances risk management and compliance capabilities. Digital tools facilitate monitoring, reporting, data analysis, and communication, enabling HR professionals to identify trends, detect potential issues, and implement timely interventions. Platforms for incident reporting, compliance tracking, and policy dissemination streamline processes and ensure consistency across global operations. Technology supports efficiency, accuracy, and transparency in managing organizational risk and regulatory adherence.
Employee engagement and organizational culture intersect with risk management in profound ways. A culture of accountability, ethical behavior, and inclusivity reduces the likelihood of misconduct, enhances reporting of potential issues, and promotes adherence to policies. HR professionals cultivate such cultures by modeling ethical behavior, recognizing compliant conduct, and embedding ethical considerations into decision-making frameworks. Engaged employees are more likely to act responsibly and contribute to a safe, compliant, and high-performing workplace.
Global HR professionals must also anticipate and respond to emerging risks. Economic volatility, geopolitical shifts, natural disasters, technological disruptions, and evolving regulatory landscapes require agile risk management strategies. Scenario planning, predictive analytics, and continuous monitoring allow HR leaders to identify potential threats and develop contingency plans that maintain business continuity and employee safety. This proactive approach strengthens organizational resilience and adaptability.
Integration of risk management with other HR domains ensures coherence and strategic impact. For example, compliance considerations influence global talent management by dictating hiring practices, mobility programs, and performance evaluation frameworks. Workplace culture initiatives intersect with risk management by promoting ethical behavior, respect, and inclusivity. Total rewards strategies may incorporate risk-based incentives or hazard-related compensation adjustments. By embedding risk awareness across HR functions, professionals create a unified, risk-conscious organizational framework.
Strategic decision-making in global HR relies on the synthesis of risk, compliance, and operational data. HR leaders utilize metrics and analytics to assess exposure, evaluate program effectiveness, and inform policy development. Key indicators may include incident frequency, regulatory compliance rates, employee engagement scores, turnover related to safety concerns, and audit outcomes. Data-driven insights enable continuous improvement and evidence-based interventions.
Ethical considerations permeate all aspects of risk management and compliance. HR professionals ensure that policies, practices, and decision-making frameworks reflect integrity, fairness, and respect for human rights. Ethical leadership guides organizational conduct, shapes culture, and reinforces employee trust. By embedding ethical principles into strategic planning and operational execution, HR leaders maintain organizational legitimacy and foster sustainable success.
Collaboration with internal and external stakeholders enhances risk management effectiveness. HR professionals work alongside legal teams, finance, operations, security specialists, and regulatory bodies to ensure comprehensive coverage of potential risks. Partnerships with local authorities, industry associations, and international organizations provide guidance, best practices, and compliance frameworks that support global operations. This cooperative approach strengthens organizational capabilities and mitigates vulnerabilities.
Crisis management represents a critical component of risk and compliance strategy. HR leaders must develop protocols for responding to emergencies, including health incidents, natural disasters, political unrest, cyber threats, or other disruptions. Planning encompasses communication strategies, employee evacuation, resource allocation, and continuity of operations. Effective crisis management minimizes impact, safeguards employees, and maintains organizational reputation.
Employee relations play a central role in maintaining compliance and managing risk. HR professionals monitor workplace dynamics, address grievances, mediate disputes, and implement corrective actions. Proactive engagement with employee representatives, unions, and local labor authorities ensures that policies are adhered to and that potential conflicts are resolved constructively. Effective employee relations contribute to a harmonious, productive, and legally compliant workforce.
Legal compliance extends to contractual obligations, labor agreements, immigration regulations, and employment law. HR professionals must navigate complex international frameworks, balancing organizational objectives with employee rights. Compliance audits, policy reviews, and continuous education ensure that HR practices remain aligned with evolving legal requirements. Attention to detail and vigilance are paramount to avoiding sanctions, fines, and reputational damage.
Monitoring and evaluation of risk management and compliance initiatives enable continuous refinement. HR leaders assess the effectiveness of policies, procedures, and interventions through audits, surveys, incident analyses, and performance reviews. Feedback mechanisms inform improvements, identify emerging risks, and enhance overall organizational resilience. By maintaining a cycle of evaluation and adaptation, HR professionals ensure that strategies remain robust and responsive.
Strategic integration ensures that risk management and compliance are not isolated functions but are embedded into the broader human capital framework. Alignment with workforce planning, mobility programs, talent management, total rewards, and workplace culture ensures coherence, efficiency, and maximal impact. HR leaders must view risk and compliance as integral to organizational strategy, influencing decisions and shaping outcomes across all domains of human resource management.
The interplay between risk management, compliance, and other HR domains underscores the complexity of global human resources. By cultivating expertise in this area, professionals can anticipate challenges, mitigate risks, and foster secure, ethical, and efficient workplaces. This capability enhances organizational resilience, employee well-being, and the capacity to achieve strategic objectives in a complex, dynamic, and interconnected world.
Mastery of risk management and compliance, coupled with expertise in total rewards, global mobility, talent management, and workplace culture, positions HR professionals as indispensable strategic partners. The integration of these competencies ensures that organizations can navigate global challenges effectively, maintain ethical and legal standards, and optimize human capital to achieve sustainable competitive advantage.
The HRCI GPHR certification validates this comprehensive expertise, demonstrating an individual's ability to operate at the highest level of strategic human resource management. Professionals who attain this credential not only gain recognition for their knowledge but also enhance their capability to drive organizational success across diverse international contexts.
Conclusion
Achieving the HRCI Global Professional in Human Resources certification represents a pinnacle of professional accomplishment, affirming a deep understanding of strategic HR practices, global talent management, workplace culture, total rewards, and risk management. Candidates who successfully navigate the exam demonstrate the ability to integrate complex concepts into practical solutions, fostering organizational resilience, compliance, and ethical governance. The knowledge and skills gained through preparation for the GPHR credential empower HR professionals to lead with insight, innovation, and integrity, positioning them as strategic architects of global human capital and indispensable contributors to multinational organizational success.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get the products after purchase?
All products are available for download immediately from your Member's Area. Once you have made the payment, you will be transferred to Member's Area where you can login and download the products you have purchased to your computer.
How long can I use my product? Will it be valid forever?
Test-King products have a validity of 90 days from the date of purchase. This means that any updates to the products, including but not limited to new questions, or updates and changes by our editing team, will be automatically downloaded on to computer to make sure that you get latest exam prep materials during those 90 days.
Can I renew my product if when it's expired?
Yes, when the 90 days of your product validity are over, you have the option of renewing your expired products with a 30% discount. This can be done in your Member's Area.
Please note that you will not be able to use the product after it has expired if you don't renew it.
How often are the questions updated?
We always try to provide the latest pool of questions, Updates in the questions depend on the changes in actual pool of questions by different vendors. As soon as we know about the change in the exam question pool we try our best to update the products as fast as possible.
How many computers I can download Test-King software on?
You can download the Test-King products on the maximum number of 2 (two) computers or devices. If you need to use the software on more than two machines, you can purchase this option separately. Please email support@test-king.com if you need to use more than 5 (five) computers.
What is a PDF Version?
PDF Version is a pdf document of Questions & Answers product. The document file has standart .pdf format, which can be easily read by any pdf reader application like Adobe Acrobat Reader, Foxit Reader, OpenOffice, Google Docs and many others.
Can I purchase PDF Version without the Testing Engine?
PDF Version cannot be purchased separately. It is only available as an add-on to main Question & Answer Testing Engine product.
What operating systems are supported by your Testing Engine software?
Our testing engine is supported by Windows. Andriod and IOS software is currently under development.


