Certification: ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester
Certification Full Name: ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester
Certification Provider: BCS
Exam Code: ISEB-SWT2
Exam Name: ISTQB-ISEB Certified Tester Foundation Level (BH0-010)
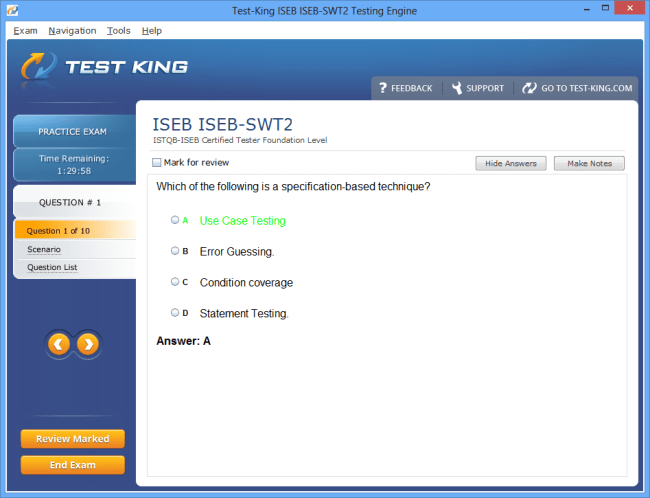
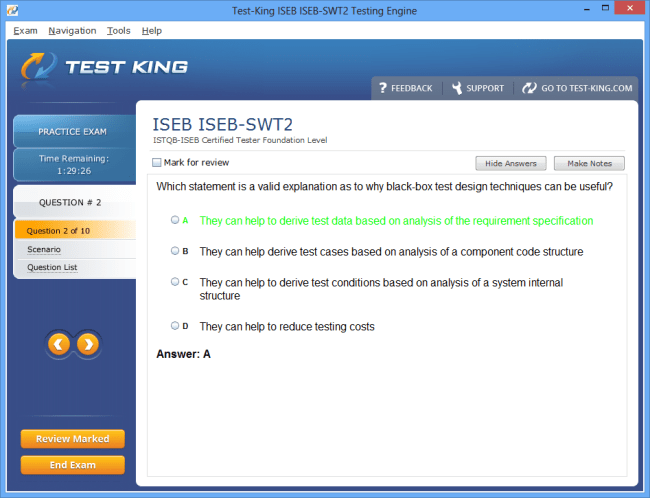
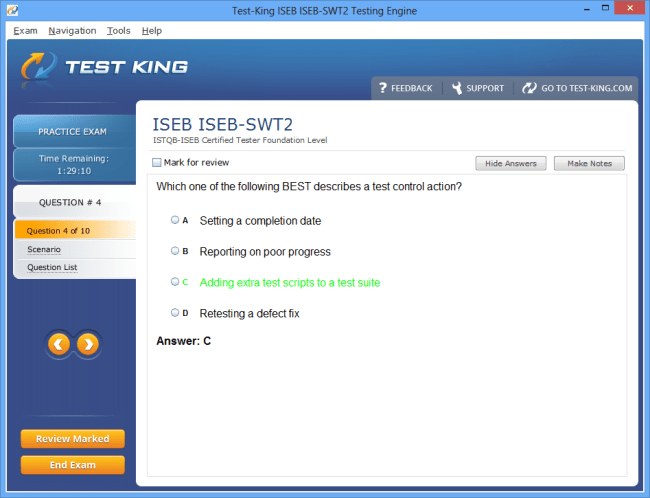
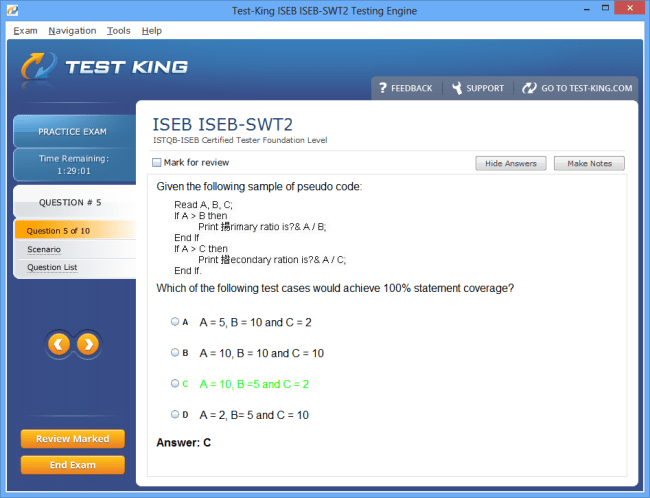
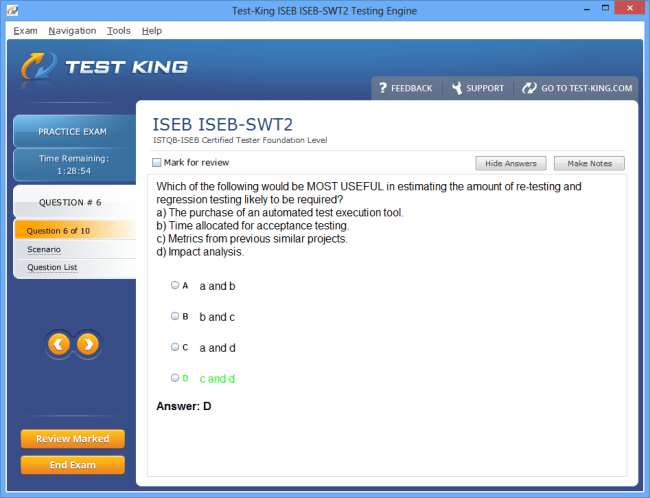
ISEB-SWT2 Exam Product Screenshots
ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester: A Comprehensive Guide for Aspiring QA Professionals
In the intricate and constantly evolving realm of software development, the significance of quality assurance cannot be overstated. The ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester credential, administered by the British Computer Society, has emerged as a globally recognized standard for evaluating and validating the expertise of software testing professionals. It is a meticulous framework designed to provide aspiring testers with the tools, methodologies, and conceptual clarity required to excel in diverse software development environments. This certification serves not merely as a testament to one’s theoretical understanding, but as a tangible validation of practical competencies that ensure software reliability, stability, and performance across various platforms.
Understanding the ISTQB-BCS Certification
At its core, the certification emphasizes a structured approach to testing, underpinned by globally acknowledged standards. Candidates are expected to assimilate a spectrum of knowledge, ranging from fundamental testing principles to advanced analytical techniques that facilitate risk-based testing, test planning, and defect management. By achieving this credential, individuals signify their ability to navigate complex testing scenarios with discernment and precision, reinforcing organizational confidence in their professional judgment.
Who Should Pursue the Certification
This certification is particularly advantageous for individuals embarking on a career in quality assurance or software testing. Novice testers, IT professionals seeking to diversify their skillset, and developers aiming to deepen their understanding of systematic testing practices find this credential especially valuable. Its utility extends beyond the individual; organizations also benefit from employing certified professionals, as structured testing practices enhance product quality, streamline workflows, and minimize the risk of software anomalies.
The ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester pathway offers an intellectual scaffold that bridges theoretical comprehension with practical application. It provides an opportunity for aspiring testers to cultivate a disciplined approach to analyzing, designing, and executing test cases. By systematically integrating quality assurance principles into their work, certified testers elevate the overall software development lifecycle, fostering reliability and reducing the likelihood of costly post-deployment defects.
Advantages of Obtaining the Certification
Obtaining the ISTQB-BCS credential presents a confluence of professional, cognitive, and organizational advantages. One of the most conspicuous benefits lies in employability. In a competitive marketplace where certifications are often used as a differentiating factor, the ISTQB-BCS credential signals to employers that the holder possesses verified knowledge and skills in software testing. It enhances the prospect of career advancement, facilitating entry into specialized roles, higher responsibilities, and leadership positions within quality assurance teams.
Beyond tangible career benefits, the certification nurtures an enriched understanding of the testing domain. It acquaints candidates with an extensive lexicon of testing terminologies, methodologies, and evaluative techniques. The curriculum encourages analytical rigor, meticulous observation, and methodical reasoning—attributes indispensable to both manual and automated testing scenarios. Individuals trained under this framework demonstrate an ability to systematically dissect software functionalities, detect subtle inconsistencies, and implement corrective measures in a structured manner.
Another significant advantage is the cultivation of professional confidence. For many entrants into the field, transitioning from theoretical learning to practical application can evoke uncertainty. The ISTQB-BCS framework mitigates this apprehension by offering a coherent pathway that integrates knowledge with hands-on competencies. Certified testers often report heightened assurance in decision-making, the ability to advocate for quality-centric strategies, and improved collaboration with development teams.
Examination Structure and Preparation
The examination for this certification is designed to rigorously assess both cognitive understanding and applied skills. It generally comprises multiple-choice questions that evaluate comprehension of fundamental principles, the software testing lifecycle, test design techniques, defect identification, and management strategies. The examination necessitates an amalgamation of theoretical retention and pragmatic interpretation, as candidates must often apply learned concepts to hypothetical scenarios and contextual problem-solving exercises.
Preparation for the examination is multidimensional. Candidates benefit from immersive study routines that blend guided readings, workshops, practical exercises, and discussion forums. The British Computer Society provides extensive study materials, including syllabi, illustrative examples, and sample questions that offer insight into exam expectations. Many aspirants find that mock examinations not only reinforce retention but also cultivate the analytical agility necessary to navigate the nuanced challenges of real-world testing scenarios.
Additionally, integrating practical exposure alongside theoretical study is invaluable. Engaging with testing projects, participating in internships, or simulating test environments enables aspirants to translate abstract concepts into applied expertise. This experiential learning fosters an intuitive grasp of testing strategies, allowing candidates to approach problems with both creativity and methodical rigor.
Global Recognition and Career Impact
One of the defining attributes of the ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester credential is its international recognition. Organizations across continents, ranging from small enterprises to multinational corporations, acknowledge it as a benchmark of professional competence. Certified testers frequently encounter opportunities for global employment, consulting roles, and positions that demand verified expertise in software testing. This transnational recognition reinforces the value of the certification, particularly in an era where software development transcends geographical boundaries.
Professional credibility is another pivotal outcome of certification. It signals a commitment to structured methodologies, continual learning, and adherence to high-quality standards. In domains where software failures can result in significant financial, operational, or reputational setbacks, certified testers provide a measure of assurance. Their proficiency in identifying, analyzing, and mitigating software defects contributes to organizational resilience and product dependability.
The career trajectories of certified testers often reflect accelerated growth. They tend to occupy positions of increasing responsibility, engage in strategic project planning, and participate in high-impact initiatives that influence software quality at an organizational scale. Employers recognize the tangible benefits of such certifications, integrating certified professionals into roles that require nuanced judgment, cross-functional collaboration, and systematic problem-solving skills.
Eligibility Criteria and Prerequisites
The ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester credential is designed to be accessible to a wide array of professionals, with minimal barriers to entry. Candidates typically require a foundational understanding of software development principles, although no specific degree or prior certification is mandated. This inclusivity ensures that both newcomers to the field and experienced IT practitioners can pursue the credential to augment their skillset.
However, aspirants are advised to possess analytical acumen, logical reasoning capabilities, and a predisposition for meticulous evaluation. Since software testing often demands scrutiny of minute functional details, candidates must demonstrate a capacity for sustained concentration, precision, and the ability to interpret complex systems. These intrinsic attributes, combined with dedicated preparation, significantly enhance the likelihood of certification success.
Practical Applications in the Workplace
The practical implications of holding the ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester credential extend beyond theoretical knowledge. In professional settings, certified testers employ structured methodologies to design test plans, execute test cases, and report defects systematically. They contribute to risk-based testing strategies, ensuring that software releases align with organizational standards and user expectations.
Certified testers also facilitate cross-functional communication by translating technical findings into actionable insights for development teams, project managers, and stakeholders. Their expertise underpins the iterative processes of agile and DevOps environments, where rapid development cycles necessitate precise, efficient, and reliable testing practices. Moreover, their presence fosters a culture of quality within organizations, encouraging adherence to standardized processes and the adoption of best practices in software assurance.
Continuous Learning and Advanced Opportunities
While the ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester credential represents a foundational benchmark, it also serves as a springboard for further specialization. Professionals may pursue advanced certifications, explore niche domains such as automation, security testing, or performance evaluation, and refine their skills in alignment with emerging technological paradigms. The credential cultivates a mindset of perpetual learning, equipping testers to adapt to evolving industry standards, toolsets, and methodologies.
In addition, certified testers often engage with professional communities, contribute to knowledge-sharing forums, and participate in workshops or seminars. These activities not only enhance professional visibility but also facilitate the exchange of innovative approaches, lessons learned, and pragmatic strategies that enrich the collective competence of the software testing ecosystem.
Enhancing Analytical and Cognitive Skills
One of the more subtle yet profound benefits of pursuing this certification lies in the cognitive development it fosters. The structured curriculum, combined with scenario-based problem-solving, enhances analytical thinking, critical reasoning, and decision-making skills. Certified testers are trained to dissect complex software structures, identify latent defects, and anticipate potential vulnerabilities. These cognitive faculties extend beyond technical testing, influencing strategic planning, risk assessment, and process optimization within organizational contexts.
Through continuous practice, candidates cultivate an intuitive understanding of software behavior, user expectations, and systemic interactions. This heightened perceptiveness enables them to not only detect anomalies but also recommend solutions that optimize functionality, usability, and reliability. In doing so, certified testers become indispensable contributors to both the development process and the overarching organizational mission of delivering high-quality software products.
Understanding Eligibility Requirements
Embarking on the journey toward becoming an ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester begins with understanding the eligibility parameters set by the British Computer Society. The certification is designed to accommodate a wide array of individuals, ranging from those who are taking their initial steps in software testing to experienced IT professionals aiming to consolidate and formalize their expertise. There is no rigid prerequisite in terms of formal education, making it accessible to aspirants from diverse academic backgrounds.
Although there is flexibility in formal educational qualifications, candidates are expected to demonstrate an aptitude for logical analysis, methodical reasoning, and meticulous attention to detail. These intrinsic qualities are crucial as they underpin the capacity to navigate complex software systems, design effective test scenarios, and interpret results with precision. A foundational understanding of software development processes, including familiarity with programming concepts, databases, and application architectures, is beneficial but not mandatory. This combination of accessibility and cognitive expectation ensures that the certification can accommodate a heterogeneous pool of candidates while maintaining the high standards necessary for professional validation.
Registration Process for Certification
The registration process for the ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester credential is structured yet straightforward, providing a clear pathway for candidates to formalize their participation. Registration typically commences online through the British Computer Society’s official portal, where candidates can create a personal profile and select their preferred examination date and venue. Upon registration, candidates gain access to essential resources, including syllabi, preparatory materials, and guidance on examination formats.
Payment for the examination is integrated into the registration process. Fees vary depending on the country and examination center, but the structured approach ensures transparency and accessibility. Candidates are encouraged to review examination schedules well in advance to accommodate personal preparation timelines, as the certification demands thorough engagement with both theoretical and practical dimensions of software testing.
The registration process also includes verification of identity and credentials to ensure the integrity of the certification system. Candidates may be required to present identification documents or professional references, particularly in cases where eligibility requires confirmation of practical experience in software development or testing roles. This ensures that the credential remains a robust and reliable benchmark of professional competence across the global IT landscape.
Recommended Experience and Background
While formal prerequisites are minimal, experience in software testing or related IT domains significantly enhances the candidate’s readiness for the certification examination. Individuals with hands-on exposure to test case design, defect logging, or software lifecycle management often find it easier to assimilate the structured knowledge and apply it effectively during examinations.
Even a modest engagement with testing processes, such as participating in small-scale project testing, assisting in quality assurance tasks, or contributing to debugging initiatives, provides practical insight that complements theoretical study. Familiarity with software testing tools, test management applications, and defect tracking systems further enriches the candidate’s preparation, allowing for a more intuitive understanding of the principles underpinning the certification syllabus.
Candidates without formal testing experience are encouraged to engage in preparatory exercises, online workshops, or internships that provide exposure to practical scenarios. By simulating testing environments or participating in collaborative projects, aspirants can cultivate the analytical mindset and procedural discipline required to excel in both the certification examination and professional testing practice.
Registration Steps and Documentation
The process of registering for the ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester examination involves several key steps that ensure both accessibility and procedural rigor. Initially, candidates must create an account on the British Computer Society’s portal, providing personal details, contact information, and relevant background information regarding their educational or professional history.
Following account creation, candidates select an examination location and date. The availability of centers across multiple regions ensures that geographical constraints do not impede access to certification. The system also provides clear information on examination formats, duration, and scoring methodologies, allowing candidates to plan preparation strategies effectively.
Payment is typically conducted online, with secure gateways ensuring the confidentiality of financial information. Upon completion, candidates receive confirmation of registration, examination instructions, and preparatory resources. These resources often include the official syllabus, sample questions, and guidance on best practices for approaching the examination.
Candidates may also be required to submit verification documents, particularly in jurisdictions where proof of professional experience or identification is mandated. This ensures the integrity of the certification process, confirming that candidates meet the established standards while maintaining accessibility for diverse aspirants.
Recommended Preparation Timeline
Preparing for the ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester examination is a meticulous endeavor that benefits from a structured timeline. Experts suggest a phased approach that combines theoretical study with practical application. Initially, candidates should familiarize themselves with the complete syllabus, understanding each topic’s scope and relevance. Following this, dedicated periods of focused study, reinforced with mock examinations, facilitate knowledge retention and application.
Practical engagement is equally vital. Allocating time to simulate testing scenarios, analyze sample defects, and design test cases strengthens comprehension and builds the analytical acumen necessary for success. Candidates are encouraged to maintain a disciplined study schedule, integrating periodic reviews and self-assessments to monitor progress and identify areas requiring additional focus.
The recommended preparation timeline may vary depending on prior experience, learning pace, and individual aptitude. However, a systematic approach that balances theoretical immersion with hands-on practice ensures comprehensive readiness and cultivates the confidence necessary for optimal performance in the examination environment.
Benefits of Meeting Eligibility and Completing Registration
Successfully navigating the eligibility and registration process represents a pivotal milestone in the professional journey of a software testing aspirant. Achieving eligibility and completing registration confirms the candidate’s commitment to structured learning and professional development. It also facilitates access to a wealth of resources designed to enhance knowledge, analytical skills, and practical capabilities.
Engaging with the preparatory materials provided by the British Computer Society equips candidates with a robust understanding of testing principles, techniques, and industry standards. The registration process itself serves as an initial orientation, introducing candidates to the formal expectations, ethical considerations, and procedural rigor that define professional testing practice.
Moreover, completing registration ensures that candidates can participate in a globally recognized certification examination, providing access to opportunities that transcend geographical boundaries. Certified professionals are often viewed as credible contributors in both local and international contexts, enabling career mobility, increased responsibility, and engagement in high-impact projects that influence organizational software quality standards.
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
A frequent misconception is that formal educational degrees or extensive professional experience are mandatory for eligibility. While advantageous, these are not prerequisites, and the certification remains accessible to a wide range of aspirants with the intellectual acumen and motivation to succeed. Another misunderstanding involves the complexity of the registration process, which is often perceived as cumbersome. In reality, the process is streamlined and guided, with clear instructions, online support, and resource access integrated into each step.
Candidates also sometimes underestimate the importance of early registration. Given that examination slots can fill rapidly and preparatory timelines are critical, initiating registration well in advance ensures optimal scheduling and adequate time for comprehensive study. By addressing these misconceptions, aspirants can approach the eligibility and registration process with clarity, confidence, and strategic foresight, laying a solid foundation for subsequent learning and examination success.
Enhancing Readiness Through Early Engagement
Early engagement with preparatory materials, including the official syllabus, sample exercises, and exploratory projects, significantly enhances readiness for the certification. This proactive approach allows candidates to identify areas requiring deeper understanding, assimilate testing terminology, and develop a procedural mindset conducive to structured analysis.
Participating in workshops, online tutorials, and peer discussions fosters a collaborative dimension, enabling aspirants to exchange insights, clarify doubts, and gain exposure to diverse testing scenarios. Such early engagement not only strengthens comprehension but also cultivates the professional demeanor and analytical rigor characteristic of certified testers.
Navigating the Registration Experience Globally
The global nature of the ISTQB-BCS certification ensures that aspirants from multiple regions can access the registration process and examination facilities. Examination centers are strategically distributed, accommodating diverse geographical locations while maintaining standardized evaluation criteria. This international accessibility reinforces the credential’s recognition and facilitates equitable opportunities for candidates worldwide.
The registration experience is designed to be user-centric, offering guidance through every step, from profile creation to examination confirmation. Candidates are encouraged to leverage online portals, resource repositories, and customer support mechanisms to navigate the process efficiently, ensuring clarity, accuracy, and readiness for subsequent stages of certification preparation.
Integrating Practical Preparation During Registration
Even during the registration phase, candidates can initiate practical preparation. Reviewing sample questions, analyzing testing scenarios, and familiarizing themselves with the format and expectations of the examination cultivate a mindset attuned to structured problem-solving. This early integration of practical engagement alongside administrative completion establishes a rhythm of disciplined learning that continues through the study period, enhancing both confidence and competence.
Understanding the Syllabus Framework
The ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester syllabus is meticulously crafted to provide a comprehensive understanding of software testing principles, techniques, and methodologies. It is designed to equip candidates with both theoretical knowledge and practical acumen required for professional testing roles. The curriculum encapsulates core concepts of testing, emphasizing analytical thinking, structured problem-solving, and a methodical approach to ensuring software quality.
At its heart, the syllabus is organized to build a progressive understanding of software testing, beginning with fundamental principles and advancing through test planning, design, execution, and reporting. Candidates are introduced to a structured vocabulary that not only enhances comprehension but also aligns with globally recognized standards. Each learning area is interrelated, forming an intricate tapestry that enables testers to systematically evaluate software behavior, detect anomalies, and propose effective remedies.
Fundamental Principles of Testing
The foundation of the ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester curriculum is the fundamental principles of software testing. These principles elucidate the rationale behind testing, highlighting its necessity, objectives, and underlying philosophies. Testing is recognized as a critical activity that enhances software reliability and mitigates risk by detecting defects before deployment. Candidates are expected to grasp the conceptual framework that distinguishes testing from mere verification or debugging, appreciating its role in the broader software development lifecycle.
The curriculum emphasizes that testing cannot exhaustively cover all possible scenarios but should focus on strategically selected areas to maximize defect detection and resource efficiency. This approach requires analytical foresight, prioritization skills, and the ability to evaluate software risk in a systematic manner. Understanding these principles ensures that testers adopt a balanced perspective, integrating thoroughness with practicality in their work.
Test Design and Techniques
A significant component of the syllabus focuses on test design techniques. Candidates are introduced to diverse strategies for creating effective test cases that comprehensively evaluate software functionality. These techniques include equivalence partitioning, boundary value analysis, decision table testing, state transition testing, and exploratory approaches. Each method provides a structured means to identify critical test scenarios, reduce redundancy, and enhance defect detection efficiency.
Equivalence partitioning and boundary value analysis encourage candidates to analyze inputs systematically, grouping similar conditions and identifying edge cases that may trigger defects. Decision tables and state transition testing promote logical reasoning, helping testers capture complex system behaviors and interactions. Exploratory testing fosters creativity, allowing professionals to investigate software behavior dynamically while drawing on experience, intuition, and analytical observation.
Test Planning and Management
Test planning and management represent another essential learning area, emphasizing the strategic and organizational aspects of software testing. Candidates gain insight into developing test plans, defining objectives, estimating effort, allocating resources, and scheduling activities. The curriculum highlights the importance of aligning testing objectives with project goals, ensuring that testing activities are both efficient and effective.
Risk assessment is a recurring theme, with candidates learning to prioritize testing based on potential impact, likelihood of defect occurrence, and business criticality. Effective communication of test strategies, resource utilization, and progress tracking are integral elements, fostering collaboration among testers, developers, and project managers. This learning area cultivates organizational acumen, enabling certified testers to contribute meaningfully to project planning and execution.
Types of Testing and Their Applications
The syllabus delineates the diverse types of testing that candidates must understand and apply. Functional testing examines whether software behaves according to specified requirements, encompassing system, integration, and acceptance testing. Non-functional testing evaluates performance, security, usability, and reliability aspects, ensuring that software meets broader quality criteria.
Regression testing, often highlighted in the syllabus, emphasizes the need to verify that modifications do not introduce new defects, reinforcing the iterative and adaptive nature of software development. Exploratory and ad hoc testing are also examined, underscoring the importance of experience-driven investigation and creative problem-solving in uncovering subtle defects. Candidates learn to discern the appropriate testing type based on project context, risk assessment, and stakeholder requirements.
Test Execution and Defect Management
Practical execution of tests is a central theme, encompassing test case execution, result documentation, and defect reporting. Candidates are trained to meticulously observe software behavior, compare actual outcomes with expected results, and identify deviations that may indicate defects. Emphasis is placed on clarity, precision, and reproducibility of test documentation, ensuring that findings are actionable and comprehensible to stakeholders.
Defect management, another critical learning area, involves classification, prioritization, and tracking of identified issues. Candidates gain an understanding of defect lifecycle processes, including logging, investigation, resolution, and verification. This knowledge ensures that defects are managed systematically, supporting continuous improvement and fostering accountability within development and testing teams.
Tools and Automation Awareness
The syllabus also introduces candidates to testing tools and automation concepts, highlighting the advantages of leveraging technology to enhance testing efficiency. While the certification primarily focuses on foundational principles, familiarity with test management tools, defect tracking systems, and basic automation frameworks is encouraged. Candidates gain insight into how automation can complement manual testing, facilitate repetitive tasks, and enable consistent regression verification.
Understanding the selection and application of appropriate tools fosters strategic thinking. Certified testers learn to evaluate tools based on project requirements, scalability, and integration with existing development workflows. This awareness ensures that technology serves as an enabler rather than a replacement, enhancing the overall effectiveness of testing initiatives.
Quality Standards and Best Practices
An integral component of the syllabus is the study of quality standards and best practices. Candidates explore internationally recognized frameworks, such as ISO standards for software testing, and understand how adherence to these principles ensures consistency, reliability, and credibility. Best practices include systematic test planning, comprehensive documentation, peer reviews, risk-focused testing, and continuous learning.
Emphasizing standards instills a professional ethos, encouraging testers to approach their work with rigor, ethical responsibility, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Candidates learn that quality assurance is not merely a procedural activity but a mindset that informs every stage of software development, from requirement analysis to deployment.
Metrics and Measurement in Testing
Measuring testing effectiveness and efficiency is another critical learning area. Candidates are introduced to metrics that quantify coverage, defect density, test execution progress, and overall quality levels. Understanding and interpreting these metrics enables testers to provide objective insights, inform decision-making, and demonstrate the value of testing activities to stakeholders.
The curriculum emphasizes that metrics must be contextualized within project objectives. Blind adherence to quantitative measures without qualitative analysis can lead to misleading conclusions. Certified testers are encouraged to integrate metrics with observational insights, ensuring that measurements reflect actual software quality and project realities.
Integrating Theory with Practical Application
Throughout the syllabus, there is a consistent emphasis on bridging theoretical knowledge with practical application. Candidates are encouraged to apply learned techniques to sample projects, case studies, and simulation exercises. This integration cultivates a holistic understanding, enabling testers to navigate real-world complexities while adhering to structured methodologies.
Analytical reasoning, attention to detail, and systematic documentation are continually reinforced, ensuring that candidates emerge with a well-rounded skill set. This dual focus on theory and practice distinguishes certified testers as professionals capable of delivering consistent quality assurance outcomes across varied software landscapes.
Preparing for Advanced Concepts
While the certification emphasizes foundational knowledge, it also introduces aspirants to concepts that serve as a gateway to advanced testing competencies. Understanding principles of test automation, risk-based testing, and integration within agile and DevOps methodologies provides a scaffold for future specialization. Candidates gain a forward-looking perspective, recognizing how foundational skills underpin advanced practices in specialized testing domains.
This orientation encourages a mindset of perpetual learning, equipping candidates to adapt to evolving technologies, emerging testing tools, and shifting industry standards. Certified testers are thereby prepared to engage in continuous professional development, ensuring long-term relevance and career growth in the software testing ecosystem.
Analytical Thinking and Cognitive Skill Enhancement
A unique attribute of the syllabus is its focus on cultivating cognitive and analytical capabilities. Candidates are trained to dissect complex software architectures, anticipate potential vulnerabilities, and design testing strategies that maximize defect detection. This mental discipline extends beyond testing scenarios, influencing broader problem-solving, risk assessment, and strategic decision-making skills within professional contexts.
Through sustained engagement with the curriculum, candidates refine their observational acuity, logical reasoning, and systematic documentation abilities. These cognitive enhancements position certified testers as indispensable contributors, capable of translating technical insights into actionable recommendations that improve software reliability and organizational outcomes.
Understanding the Preparation Framework
Preparing for the ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester examination is a meticulous endeavor that requires a structured approach combining theoretical understanding and practical application. The examination evaluates a candidate’s ability to comprehend fundamental testing principles, apply analytical reasoning, and implement structured methodologies in varied scenarios. Consequently, preparation demands not only memorization of concepts but also the development of critical thinking skills, problem-solving acumen, and disciplined study habits.
A comprehensive preparation strategy begins with an understanding of the examination format and syllabus. Candidates are expected to be familiar with core testing principles, test design techniques, defect management processes, and quality assurance best practices. Awareness of these elements allows aspirants to prioritize study areas, allocate time efficiently, and approach the examination with clarity and confidence.
Creating an Effective Study Plan
An effective study plan is a cornerstone of successful preparation. Candidates are encouraged to design a timeline that balances the assimilation of theoretical knowledge with practical exercises. Initial stages should involve thorough reading of the official syllabus, understanding each learning objective, and familiarizing oneself with testing terminology and principles. This foundational comprehension provides a framework upon which deeper analytical skills can be developed.
Following the initial study phase, candidates should engage in focused practice through exercises, scenario analysis, and self-assessment quizzes. Allocating time for revision and reinforcing areas of difficulty ensures that knowledge gaps are addressed systematically. Flexibility within the study plan is essential, allowing candidates to adapt based on progress, comprehension levels, and personal aptitude. A disciplined, yet adaptable approach fosters consistent engagement and prevents cognitive fatigue, enhancing retention and practical application.
Utilizing Official Study Materials
Official study materials provided by the British Computer Society constitute a primary resource for preparation. The syllabus offers comprehensive coverage of testing concepts, structured explanations of test design techniques, and illustrative examples to facilitate understanding. Sample questions included in these resources familiarize candidates with examination style, question complexity, and expected analytical rigor.
In addition to the syllabus, candidates benefit from official practice papers, guides, and explanatory notes. These materials encourage reflective learning, allowing aspirants to analyze reasoning behind correct answers, identify common pitfalls, and develop a systematic approach to problem-solving. Regular engagement with these resources builds familiarity with examination patterns and reinforces the conceptual framework necessary for effective test execution and defect analysis.
Engaging in Mock Examinations
Mock examinations are a pivotal aspect of preparation, providing both evaluative feedback and experiential learning. By simulating examination conditions, candidates cultivate time management skills, analytical agility, and resilience under assessment pressure. Mock tests allow candidates to apply theoretical knowledge to realistic scenarios, enhancing confidence and sharpening critical thinking abilities.
Analyzing performance in mock examinations is as important as completing them. Candidates should review incorrect responses to identify underlying misconceptions, refine understanding of testing principles, and adjust study strategies accordingly. Continuous iteration between practice and review fosters progressive mastery, ensuring that preparation is both targeted and comprehensive.
Leveraging Practical Experience
While theoretical study is essential, integrating practical experience significantly enhances preparation. Candidates are encouraged to engage with sample projects, simulate testing scenarios, and analyze software behavior systematically. Hands-on practice allows for the application of test design techniques, defect logging, and risk-based testing in controlled environments, reinforcing conceptual understanding.
Exposure to real-world scenarios fosters intuitive reasoning, enabling candidates to anticipate potential defects, identify critical areas for testing, and develop efficient strategies for defect detection and reporting. This experiential learning complements theoretical study, ensuring that candidates are adept at translating knowledge into actionable testing strategies.
Collaborative Learning and Peer Discussion
Collaborative learning offers a valuable dimension to preparation, providing opportunities for discussion, clarification, and diverse perspectives. Study groups, online forums, and workshops facilitate the exchange of insights, practical tips, and problem-solving approaches. Interaction with peers enhances comprehension, exposes candidates to alternative strategies, and fosters the analytical flexibility necessary for tackling complex examination questions.
Engaging in peer discussion also cultivates professional communication skills. Articulating reasoning, defending analytical choices, and evaluating differing viewpoints simulate real-world professional interactions, preparing candidates for collaborative environments in testing roles. This social dimension of preparation enriches understanding while promoting confidence and adaptability.
Integrating Test Design Techniques in Practice
A significant component of preparation involves mastery of test design techniques. Candidates should practice equivalence partitioning, boundary value analysis, decision tables, and state transition testing through exercises that mirror practical testing scenarios. Applying these techniques in simulated or real environments enhances analytical acumen, enabling candidates to create effective test cases, anticipate edge cases, and prioritize critical functional areas.
Exploratory testing, another key element, cultivates creative problem-solving skills. By investigating software without predefined scripts, candidates develop intuition, observational acuity, and adaptive reasoning abilities. Integrating structured and exploratory approaches ensures comprehensive readiness, equipping aspirants to navigate both expected and unforeseen examination challenges.
Time Management and Focused Study
Effective time management is crucial during preparation. Candidates should allocate dedicated intervals for focused study, practical exercises, revision, and mock tests. Structured sessions minimize cognitive overload, enhance retention, and foster sustained engagement. Prioritizing high-impact topics, addressing areas of difficulty, and maintaining regular revision cycles optimize preparation outcomes.
Equally important is cultivating mental focus and minimizing distractions. Concentrated study periods, interspersed with reflective breaks, reinforce cognitive processing and consolidate knowledge. Mindfulness techniques, short analytical exercises, and scenario-based problem-solving can augment concentration, ensuring that preparation remains productive and insightful.
Utilizing Online Resources and Tutorials
The digital landscape offers a wealth of supplementary resources that complement official materials. Online tutorials, video lectures, interactive exercises, and discussion forums provide alternative explanations, visualizations, and real-world examples. These resources cater to diverse learning styles, enabling candidates to assimilate concepts through auditory, visual, or kinesthetic modalities.
Engaging with online communities also provides exposure to frequently asked questions, emerging industry trends, and practical insights from certified professionals. Candidates benefit from observing how theoretical principles are applied in professional contexts, enhancing comprehension and bridging the gap between examination preparation and practical application.
Analyzing Previous Examination Patterns
Studying past examination patterns provides valuable insight into the types of questions, level of analytical complexity, and recurring thematic areas. Candidates gain an understanding of how testing principles are assessed, enabling targeted preparation and strategic allocation of study effort. Recognizing patterns facilitates anticipation of question scenarios, allowing candidates to approach unfamiliar problems with structured reasoning and confidence.
Analysis of previous examinations also highlights common pitfalls, misconceptions, and areas requiring reinforced understanding. By systematically addressing these gaps, candidates enhance accuracy, reduce errors, and cultivate the precision necessary for successful examination performance.
Stress Management and Examination Readiness
Preparation extends beyond knowledge acquisition to include mental and emotional readiness. Stress management techniques, such as deep-breathing exercises, focused meditation, and time-bound practice sessions, enhance concentration and mitigate anxiety. Candidates are encouraged to simulate examination conditions, including timed sessions and controlled environments, to acclimate to assessment pressures.
Developing resilience ensures that candidates can maintain analytical clarity, make informed decisions, and respond adaptively to complex or ambiguous questions. Integrating cognitive, emotional, and practical preparation strategies establishes holistic readiness, positioning candidates for optimal performance in the ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester examination.
Continuous Review and Iterative Learning
Preparation is an iterative process that benefits from continuous review and refinement. Candidates should periodically revisit the syllabus, reassess understanding of complex concepts, and adjust study strategies based on evolving comprehension and feedback from practice exercises. This cyclical approach ensures that knowledge is reinforced, analytical skills are sharpened, and examination readiness is progressively enhanced.
Iterative learning also cultivates adaptability, allowing candidates to incorporate new insights, reflect on problem-solving approaches, and integrate practical experiences into their conceptual framework. By maintaining a dynamic and reflective preparation strategy, candidates develop both the depth and flexibility of understanding necessary for success.
Integrating Conceptual and Applied Knowledge
A central principle of preparation is the integration of conceptual understanding with applied practice. Candidates must be able to not only recall theoretical principles but also apply them effectively to realistic scenarios. This dual focus strengthens analytical reasoning, enhances decision-making capabilities, and ensures that knowledge is both actionable and deeply internalized.
By consistently applying learned concepts to exercises, simulations, and case studies, candidates cultivate a professional mindset attuned to systematic analysis, risk assessment, and quality assurance. This integration bridges the gap between academic study and practical competence, establishing a robust foundation for both examination success and professional application.
Integrating Certification Knowledge into Project Work
The ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester credential equips professionals with a structured understanding of software testing principles, methodologies, and best practices, which can be directly applied to real-world projects. Certified testers bring a systematic approach to project work, emphasizing meticulous planning, risk assessment, and comprehensive coverage of functional and non-functional requirements. Their knowledge allows them to design tests that not only verify system functionality but also anticipate potential defects, thereby enhancing overall project reliability and stability.
In practical project environments, certified testers act as both analysts and facilitators, bridging communication between developers, project managers, and stakeholders. Their expertise ensures that testing activities align with project objectives, timelines, and quality expectations. By employing rigorous test design techniques, including equivalence partitioning, boundary value analysis, and decision tables, testers can create structured test cases that systematically evaluate critical software components.
Enhancing Risk-Based Testing Approaches
One of the salient applications of the certification is the adoption of risk-based testing strategies. Certified testers are trained to identify areas of highest potential impact, prioritize test scenarios accordingly, and allocate resources efficiently. In real-world projects, where time and budgets are often constrained, this approach ensures that the most critical functionalities are thoroughly evaluated, reducing the likelihood of high-impact defects going undetected.
Risk-based testing also requires analytical foresight, enabling testers to anticipate potential failure points based on previous experiences, historical data, and architectural understanding. Certified testers employ qualitative and quantitative assessment techniques to evaluate risk levels, ensuring that testing efforts are both focused and effective. This methodology enhances project efficiency while maintaining high standards of software quality.
Supporting Agile and DevOps Environments
Modern software development increasingly relies on iterative methodologies such as Agile and DevOps, where rapid development cycles demand swift and accurate testing practices. Certified testers bring structured methodologies to these dynamic environments, integrating seamlessly with development sprints, continuous integration pipelines, and automated testing workflows.
In Agile projects, certified testers collaborate closely with cross-functional teams to define test criteria, execute test cases, and provide timely feedback. Their systematic approach ensures that even in fast-paced cycles, testing remains comprehensive, reproducible, and aligned with project objectives. Within DevOps pipelines, testers contribute to continuous delivery practices, validating software changes and ensuring consistent quality across iterations. Their proficiency in both manual and automation-adjacent testing techniques allows projects to maintain high-quality standards while accelerating delivery timelines.
Improving Defect Management and Reporting
Effective defect management is another critical application of ISTQB-BCS certification in projects. Certified testers are trained to document defects accurately, classify them based on severity and priority, and track resolution through structured workflows. Their expertise ensures that issues are communicated clearly to developers, project managers, and stakeholders, facilitating timely remediation and minimizing rework.
Beyond identification, certified testers contribute to the analysis of defect patterns, providing insights that inform process improvement initiatives. By monitoring recurring defects, evaluating root causes, and suggesting preventive measures, testers help organizations refine development practices, enhance software quality, and reduce defect recurrence. This analytical perspective transforms defect management from a reactive process into a proactive strategy for long-term project improvement.
Applying Test Design Techniques Practically
Certified testers leverage test design techniques in real-world projects to optimize coverage, reduce redundancy, and maximize defect detection efficiency. Techniques such as equivalence partitioning allow testers to categorize input data and identify representative test cases, while boundary value analysis targets potential edge cases that may trigger unexpected behavior. Decision tables and state transition testing support logical evaluation of complex scenarios, ensuring that multiple conditions and interactions are systematically verified.
These techniques are not merely theoretical; in project environments, they inform the creation of executable test plans, guide prioritization of test cases, and facilitate structured analysis of system behavior. By applying these methods consistently, certified testers enhance both the accuracy and efficiency of testing activities, contributing to robust and reliable software deliverables.
Enhancing Quality Assurance Processes
The presence of ISTQB-BCS certified testers in project teams strengthens overall quality assurance processes. Their knowledge of testing standards, best practices, and systematic methodologies ensures that testing activities are conducted with rigor and consistency. They advocate for comprehensive test planning, thorough documentation, and objective measurement of outcomes, fostering a culture of quality within the team.
Certified testers also provide mentorship and guidance to less experienced team members, disseminating knowledge of testing principles, techniques, and project-specific practices. This educational role enhances team competence, promotes adherence to quality standards, and cultivates an environment where continuous improvement is embedded into daily workflows.
Leveraging Tools and Automation Knowledge
While the certification emphasizes foundational principles, certified testers often apply their knowledge of testing tools and automation frameworks in practical projects. Familiarity with test management systems, defect tracking platforms, and basic automation scripts allows testers to streamline processes, improve reporting accuracy, and increase testing efficiency.
In real-world scenarios, leveraging appropriate tools ensures reproducibility of tests, consistent execution, and traceability of results. Certified testers evaluate tool applicability based on project requirements, integrating them strategically to complement manual testing efforts rather than replacing critical analytical judgment. This balanced approach optimizes resource utilization and enhances project quality outcomes.
Facilitating Communication and Collaboration
Certified testers serve as pivotal communicators within project teams. Their structured understanding of testing processes enables them to articulate findings, explain test strategies, and provide actionable recommendations to diverse stakeholders. Effective communication ensures that developers comprehend defect reports, project managers understand risk implications, and decision-makers can prioritize actions based on reliable data.
In collaborative project environments, certified testers also foster alignment between development and quality assurance teams. By mediating expectations, clarifying objectives, and providing transparent insights into testing outcomes, they promote cohesion, reduce misunderstandings, and enhance overall project efficiency.
Integrating Metrics for Project Insights
Metrics are integral to demonstrating testing effectiveness in real-world projects. Certified testers apply measurement techniques to quantify coverage, defect density, and test execution progress. These metrics provide objective insights into software quality, facilitate informed decision-making, and demonstrate the value of testing activities to stakeholders.
Analyzing metrics allows certified testers to identify trends, evaluate the effectiveness of testing strategies, and recommend process improvements. For instance, high defect density in specific modules may indicate design vulnerabilities, necessitating focused reviews or process adjustments. By integrating metrics with analytical interpretation, testers transform data into actionable intelligence that drives continuous project improvement.
Adapting to Diverse Project Contexts
ISTQB-BCS certified testers are equipped to apply their knowledge across a wide spectrum of project types, from small-scale applications to complex enterprise systems. Their training emphasizes adaptability, analytical reasoning, and systematic problem-solving, allowing them to navigate diverse technological environments, varying team structures, and evolving project requirements.
In complex projects, certified testers assess dependencies, evaluate system integrations, and design comprehensive testing strategies that address both functional and non-functional requirements. In smaller projects, they prioritize efficiency, focusing on critical functionalities and risk-prone areas while maintaining adherence to quality standards. This versatility ensures that certified testers provide value across different organizational contexts and project scales.
Supporting Continuous Improvement
Certified testers contribute to continuous improvement initiatives by analyzing testing outcomes, identifying process inefficiencies, and recommending enhancements. Their expertise allows organizations to refine test strategies, adopt effective methodologies, and reduce recurring defects. By providing structured feedback, evaluating tool effectiveness, and monitoring testing practices, certified testers help establish a culture of iterative learning and process optimization.
This proactive approach not only enhances current project quality but also strengthens organizational capability for future endeavors. Certified testers serve as catalysts for knowledge dissemination, standardization of practices, and integration of innovative approaches, ensuring that testing becomes a dynamic and evolving discipline within the project environment.
Promoting Risk Awareness and Mitigation
A critical contribution of certified testers in practical projects is fostering risk awareness. By systematically identifying potential failure points, evaluating their impact, and prioritizing test coverage accordingly, testers help project teams anticipate challenges and mitigate risks proactively. This strategic perspective enhances decision-making, resource allocation, and project planning, ensuring that high-priority areas receive adequate scrutiny and potential disruptions are minimized.
Risk mitigation extends beyond technical considerations. Certified testers evaluate process vulnerabilities, communication gaps, and testing coverage limitations, providing holistic insights that inform management decisions and promote robust project outcomes.
Cultivating Professionalism and Ethical Standards
Certified testers uphold high standards of professionalism and ethical conduct, which directly influence project outcomes. They ensure transparency in reporting, objectivity in defect analysis, and adherence to standardized testing practices. By maintaining integrity in their assessments, certified testers foster trust among stakeholders, enhance accountability, and contribute to a culture of reliability and excellence.
Their ethical approach also guides decision-making in situations involving conflicting priorities, limited resources, or complex risk scenarios. This professional grounding ensures that testing activities remain aligned with both organizational goals and broader industry standards, supporting sustainable project success.
Bridging Theoretical Knowledge with Applied Practice
The practical application of ISTQB-BCS certification embodies the fusion of theoretical knowledge and applied problem-solving. Certified testers translate learned concepts into actionable strategies, adapting methodologies to suit specific project needs. This bridging of theory and practice ensures that testing activities are not only systematic but also responsive to real-world complexities, resulting in software that is both reliable and user-centric.
By continuously applying analytical reasoning, structured planning, and meticulous execution, certified testers demonstrate the tangible benefits of certification in enhancing project quality, efficiency, and overall software reliability. Their contributions permeate multiple dimensions of project work, from technical evaluation to strategic decision-making, cementing the value of professional certification in practical settings.
Expanding Professional Horizons through Certification
Earning the ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester credential signifies far more than a technical milestone; it marks the beginning of an expansive professional evolution. The certification positions a tester within a recognized global framework of quality assurance excellence. In a marketplace where digital ecosystems evolve at breathtaking speed, certified professionals become dependable anchors of reliability and precision. Employers regard this credential as tangible proof of structured analytical ability and disciplined quality control.
Within organizations, certified testers often progress from entry-level positions to roles of strategic influence. They may begin by executing predefined test cases but quickly transition into designing test strategies, managing automation frameworks, or leading cross-functional quality initiatives. This upward mobility stems from the methodological foundation instilled by the certification. A professional who masters the underlying principles of defect prevention, test design, and risk assessment becomes indispensable in safeguarding business continuity.
Mapping the Journey of Career Advancement
Career progression for an ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester typically unfolds along two complementary trajectories: technical specialization and managerial development. On the technical side, certified professionals delve deeper into advanced testing domains such as performance analysis, security validation, usability evaluation, and automation architecture. Each discipline requires not only dexterity with tools but also conceptual understanding of how quality assurance integrates with development lifecycles. Certified testers who pursue these paths often evolve into subject-matter experts, guiding teams through complex testing landscapes.
Managerial progression, meanwhile, draws on the communication, planning, and leadership capabilities honed through structured testing practice. Many certified testers ascend to roles such as test lead, quality assurance manager, or project quality consultant. In these capacities, they orchestrate testing schedules, mentor junior analysts, allocate resources, and align quality goals with organizational strategy. Their ability to interpret metrics, balance risk with efficiency, and articulate findings to executives distinguishes them as pivotal contributors to corporate governance.
Salary Trajectories and Market Recognition
Remuneration patterns for ISTQB-BCS Certified Testers reflect both regional economics and the global demand for verified competence. Across continents, salary surveys consistently indicate that certified testers command higher compensation than their non-certified peers. Employers justify this premium on the grounds that certification reduces onboarding time, minimizes project errors, and ensures consistent testing standards.
In established technology hubs, a newly certified tester often earns a competitive starting package that increases substantially with experience and additional certifications. Professionals who transition into automation or performance testing witness marked salary growth due to the scarcity of multi-disciplinary expertise. Those advancing to managerial positions enjoy remuneration that reflects responsibility for budgets, timelines, and stakeholder satisfaction.
Beyond salary, certified testers reap intangible rewards: enhanced employability, international mobility, and professional prestige. Many multinational firms stipulate certification as a prerequisite for certain quality roles, granting certified candidates immediate eligibility for global opportunities.
Long-Term Industry Relevance
The enduring value of the ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester credential lies in its adaptability to shifting technological paradigms. As artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and microservice architectures redefine software engineering, the fundamental testing principles embedded in the certification remain pertinent. Certified testers learn to evaluate not only functional correctness but also performance, scalability, and user experience—attributes increasingly critical in contemporary systems.
This adaptability ensures sustained relevance even as tools and methodologies evolve. Certified testers approach new technologies with structured curiosity, decomposing unfamiliar systems into testable components. Their ability to apply established frameworks to novel contexts preserves consistency in quality standards across technological transitions.
Influence on Organizational Growth and Culture
Within corporate environments, certified testers act as custodians of quality culture. They champion disciplined verification processes, advocate for preventive rather than reactive quality control, and demonstrate how systematic testing mitigates financial and reputational risk. Over time, their influence shapes organizational attitudes toward quality assurance, transforming it from a peripheral activity into a central pillar of product development.
Through mentorship, documentation, and knowledge sharing, certified testers nurture new generations of professionals. They design training sessions, curate internal best-practice repositories, and guide teams through audits and compliance initiatives. This mentorship role amplifies their strategic value and creates a self-sustaining ecosystem of continuous improvement within the organization.
Building Analytical Acumen and Decision-Making Capacity
A profound benefit of the ISTQB-BCS framework is the refinement of analytical thinking. Certified testers learn to dissect requirements, trace dependencies, and anticipate cascading effects of defects. This analytical discipline extends beyond testing into broader decision-making contexts. Many professionals find that the same reasoning used to evaluate test coverage helps them assess project feasibility, vendor proposals, and risk mitigation plans.
As careers mature, this analytical prowess becomes a differentiator in leadership positions. Executives with testing backgrounds exhibit exceptional precision in evaluating technical trade-offs and forecasting the implications of quality compromises. Thus, the intellectual rigor developed through certification underpins long-term managerial effectiveness.
Cross-Industry Mobility and Global Acceptance
Software permeates every industry, from finance to healthcare, logistics to entertainment. Because the ISTQB-BCS certification adheres to international testing standards, its holders possess competencies transferable across sectors. A certified tester who has worked on e-commerce platforms can readily transition to testing medical software or automotive systems by applying the same systematic principles.
This cross-industry mobility translates into job security and career diversity. Certified testers may explore consulting roles, freelance quality auditing, or positions in regulatory compliance. The credential’s global recognition also facilitates relocation: companies across Europe, Asia, and North America interpret it as evidence of standardized expertise. Professionals seeking to broaden their horizons therefore find the certification an effective passport to new opportunities.
Networking and Professional Community
Becoming a certified tester opens gateways to a vibrant international community. Professional associations, conferences, and online forums bring together experts who exchange methodologies, case studies, and innovations. Active participation in these circles enhances visibility, fosters collaboration, and keeps practitioners abreast of evolving best practices.
This sense of community has tangible career benefits. Networking often leads to collaborations on research papers, invitations to industry panels, or recruitment referrals. Furthermore, exposure to diverse practices enriches one’s approach to problem-solving. A tester who learns how peers in different regions handle automation or compliance challenges acquires a multifaceted perspective that strengthens future projects.
Enduring Educational Pathways
The ISTQB-BCS Certified Tester credential serves as an academic gateway to advanced specializations. After mastering the foundation level, professionals may pursue advanced modules covering test analysis, test management, or technical test design. These advanced certifications deepen subject mastery and validate strategic competencies.
Each successive level broadens intellectual horizons while reinforcing the practical wisdom gained from real-world application. For lifelong learners, the certification’s modular structure provides a clear, incremental roadmap for continuous education. This structured progression ensures that certified testers remain at the forefront of evolving technologies and methodologies throughout their careers.
Economic Impact on Employers and Industries
From an organizational viewpoint, employing certified testers yields measurable economic advantages. Reduced defect rates translate into lower maintenance costs and faster time-to-market. Quality assurance teams led by certified professionals deliver more predictable results, allowing management to plan releases with confidence. The reputation of consistently delivering robust software strengthens client trust and directly influences revenue growth.
Industries that embrace certification standards benefit collectively as well. When a critical mass of professionals adheres to standardized testing practices, interoperability and compliance across companies improve. This shared discipline fosters reliability throughout supply chains, from software vendors to service providers. The cumulative outcome is a more stable digital economy supported by professionals who uphold verifiable quality norms.
Elevating Credibility in Consulting and Freelance Work
Independent consultants and freelancers derive substantial advantage from ISTQB-BCS certification. Clients evaluating external testers often seek objective proof of competence; certification serves as an unequivocal credential. It assures clients that the consultant adheres to internationally recognized testing frameworks and ethical guidelines.
Certified freelancers typically command higher hourly rates and secure longer-term engagements because their methodology yields demonstrable results. Their ability to produce structured documentation, measurable quality metrics, and traceable testing outcomes differentiates them from uncertified counterparts. Over time, this credibility cultivates client loyalty and recurring business.
Alignment with Emerging Technologies
Technological evolution continuously reshapes the quality assurance landscape. Automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics are transforming testing workflows. Certified testers, grounded in fundamental principles, adapt to these shifts by integrating new tools without abandoning methodological rigor. They understand that automation augments rather than replaces analytical judgment.
In artificial intelligence contexts, for example, certified testers evaluate model accuracy, bias, and robustness through structured experimentation. In cloud environments, they apply risk-based testing to distributed architectures. The certification’s emphasis on systematic reasoning enables testers to approach innovation with critical discernment, ensuring that technology adoption enhances rather than jeopardizes quality.
Contribution to Governance and Compliance
Modern enterprises operate within stringent regulatory frameworks. Whether in finance, healthcare, or telecommunications, compliance failures can result in substantial penalties. Certified testers contribute to regulatory assurance by validating that software systems adhere to prescribed standards. Their meticulous documentation, traceability matrices, and audit readiness safeguard organizations from compliance breaches.
Furthermore, their awareness of quality metrics aligns with governance frameworks such as ISO and ITIL. Certified testers often participate in internal audits, risk assessments, and quality reviews, ensuring that testing processes meet both internal and external regulatory expectations. This governance contribution elevates their professional stature within corporate hierarchies.
Sustaining Motivation and Professional Identity
Beyond tangible rewards, certification instills a profound sense of professional identity. The structured learning journey fosters pride, confidence, and motivation to pursue excellence. Certified testers perceive themselves not merely as executors of tasks but as stewards of product integrity. This mindset influences everyday decisions, encouraging diligence, ethical rigor, and continuous curiosity.
Over years of practice, this internalized professionalism translates into resilience against burnout. Testers who view their work as a craft derive satisfaction from meticulous analysis and incremental improvement. The credential thus serves as a psychological anchor, reminding practitioners of their contribution to technological reliability and societal trust.
Global Trends and Future Outlook
The global demand for skilled quality professionals continues to expand as software systems underpin critical infrastructure. Organizations investing in digital transformation recognize that innovation without quality assurance is unsustainable. Consequently, ISTQB-BCS certification remains a benchmark for recruitment and promotion decisions.
Emerging trends indicate that certified testers will increasingly collaborate with artificial intelligence systems, orchestrating hybrid testing ecosystems that combine human insight with machine precision. Their role will evolve from defect detection to quality engineering, emphasizing preventive design, observability, and customer experience validation. Certification ensures that testers are prepared for these transitions through enduring principles adaptable to technological change.
Cultivating Long-Term Financial and Intellectual Rewards
The lifetime value of certification extends beyond immediate salary gains. Certified testers often experience accelerated career progression, resulting in compounded financial growth over time. Their reputation for reliability opens doors to leadership roles, consulting opportunities, and entrepreneurial ventures in quality services.
Equally significant are the intellectual rewards. Continuous engagement with testing methodologies nurtures analytical agility applicable across professional and personal endeavors. Certified testers approach challenges with structured reasoning, whether designing test cases or managing complex projects. This intellectual enrichment sustains curiosity and adaptability throughout their careers.
Conclusion
A mature certified tester contributes to the profession’s legacy by sharing accumulated wisdom. Many transition into training, authorship, or advisory roles, shaping the next generation of testers. Through workshops, publications, and mentorship, they propagate the principles of systematic quality assurance that define the ISTQB-BCS ethos.
Their influence extends beyond technical instruction; they exemplify a mindset of disciplined inquiry and ethical responsibility. By cultivating future professionals, they ensure that the collective competence of the testing community continues to elevate industry standards. This generational transfer of expertise constitutes one of the most enduring benefits of certification.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get the products after purchase?
All products are available for download immediately from your Member's Area. Once you have made the payment, you will be transferred to Member's Area where you can login and download the products you have purchased to your computer.
How long can I use my product? Will it be valid forever?
Test-King products have a validity of 90 days from the date of purchase. This means that any updates to the products, including but not limited to new questions, or updates and changes by our editing team, will be automatically downloaded on to computer to make sure that you get latest exam prep materials during those 90 days.
Can I renew my product if when it's expired?
Yes, when the 90 days of your product validity are over, you have the option of renewing your expired products with a 30% discount. This can be done in your Member's Area.
Please note that you will not be able to use the product after it has expired if you don't renew it.
How often are the questions updated?
We always try to provide the latest pool of questions, Updates in the questions depend on the changes in actual pool of questions by different vendors. As soon as we know about the change in the exam question pool we try our best to update the products as fast as possible.
How many computers I can download Test-King software on?
You can download the Test-King products on the maximum number of 2 (two) computers or devices. If you need to use the software on more than two machines, you can purchase this option separately. Please email support@test-king.com if you need to use more than 5 (five) computers.
What is a PDF Version?
PDF Version is a pdf document of Questions & Answers product. The document file has standart .pdf format, which can be easily read by any pdf reader application like Adobe Acrobat Reader, Foxit Reader, OpenOffice, Google Docs and many others.
Can I purchase PDF Version without the Testing Engine?
PDF Version cannot be purchased separately. It is only available as an add-on to main Question & Answer Testing Engine product.
What operating systems are supported by your Testing Engine software?
Our testing engine is supported by Windows. Andriod and IOS software is currently under development.


