Certification: MTA: HTML5 Application Development Fundamentals
Certification Full Name: Microsoft Technology Associate HTML5 Application Development Fundamentals
Certification Provider: Microsoft
Exam Code: 98-375
Exam Name: HTML5 App Development Fundamentals
98-375 Exam Product Screenshots
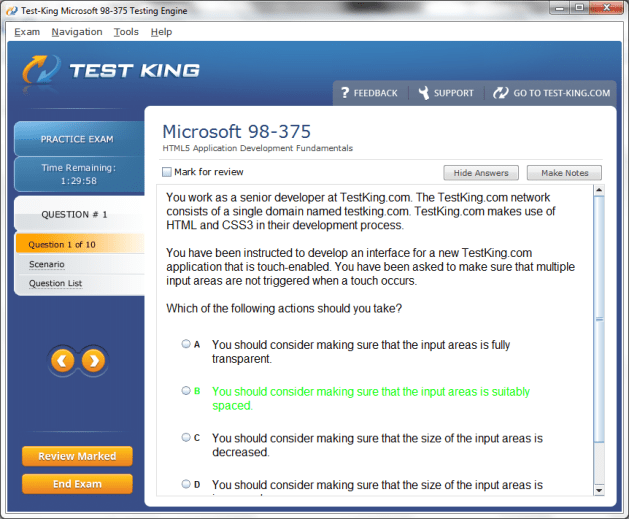
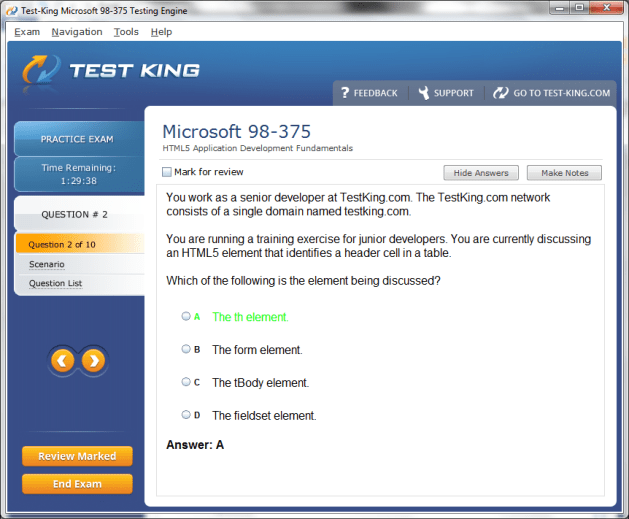
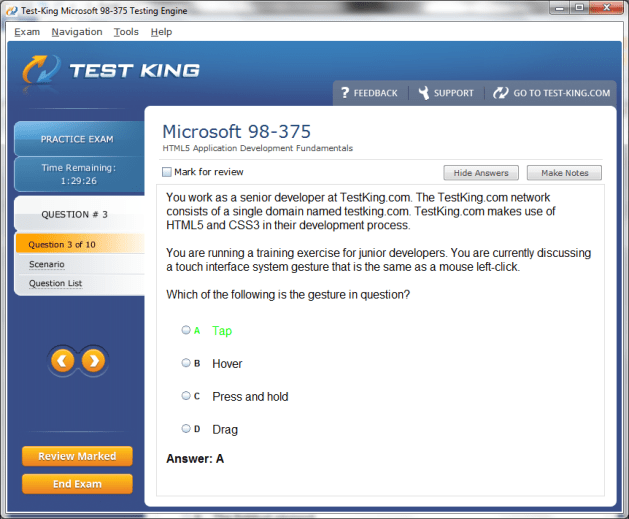
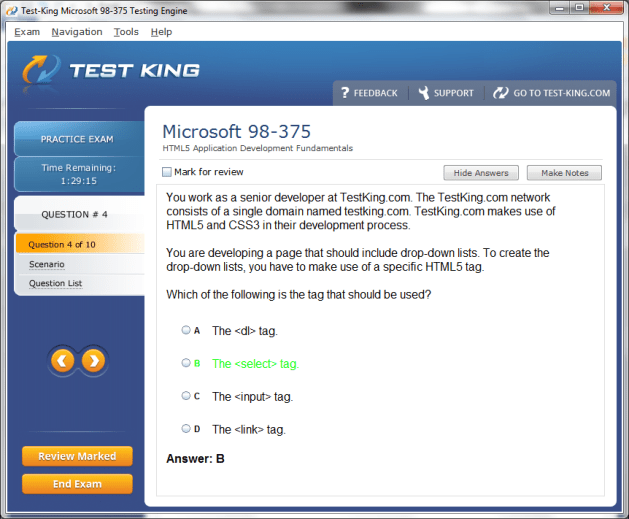
MTA: HTML5 Application Development Fundamentals Certification and Core Database Concepts and the Foundations of Data Systems
The art and science of managing data have evolved into a sophisticated discipline that underpins nearly every digital interaction in the modern world. At the center of this evolution lies the concept of the database, a meticulously structured environment designed to store, organize, and manage data efficiently. The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals framework introduces learners to this intricate realm by emphasizing essential theories, practical knowledge, and logical constructs that enable the creation and stewardship of relational databases.
A database is more than a repository; it is a living architecture that governs how information interacts within systems. To comprehend its intricacies, one must understand not only how data is stored but how it moves, transforms, and interrelates across multifarious entities. Relational databases form the nucleus of this understanding, offering a model built on tables, fields, and relations that together sustain consistency and coherence. Through this structure, vast quantities of information become manageable, reliable, and actionable.
The Essence of Relational Databases
The relational model is rooted in mathematical theory and logical precision. Its fundamental principle is simple yet profound: data is stored in tables, and relationships between these tables define how pieces of information correlate. Each table, often referred to as a relation, contains rows known as records and columns referred to as fields or attributes. This organized arrangement ensures that each element of data occupies a defined space, minimizing redundancy and enhancing clarity.
Relational databases, governed by systems known as Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS), embody this structure in action. Such systems—examples include Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle Database, and MySQL—manage the way users interact with data, ensuring integrity, accessibility, and security. The RDBMS acts as the custodian of consistency, guaranteeing that every transaction adheres to the principles of accuracy and reliability.
In the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals context, learners encounter the mechanics of these relationships through tangible examples and exercises that reflect real-world applications. Understanding why relational structures prevail requires an appreciation of normalization, primary and foreign keys, and the constraints that enforce data validity. Without these mechanisms, databases would descend into chaos, with duplication, inconsistency, and ambiguity undermining their purpose.
The Architecture of Data Storage
To master database fundamentals, it is essential to recognize how data is physically and logically stored. A database’s architecture encompasses files, pages, and extents—units that together orchestrate how information is written to disk and retrieved for processing. Logical storage represents data in abstract terms, allowing users to focus on structure without delving into the complexities of physical hardware management.
Within relational databases, data storage is intrinsically linked to efficiency. Each data type, whether numeric, textual, binary, or temporal, occupies a specific amount of space and imposes distinct performance implications. Choosing the correct data type is not a trivial decision; it directly influences how queries perform, how much storage the database consumes, and how swiftly results can be retrieved. For instance, storing a numeric value as a large integer when a smaller type would suffice leads to waste, while incorrect text encodings can result in corruption or inefficiency.
When the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals course introduces learners to data storage principles, it imparts an awareness that extends beyond syntax. Understanding data storage is an act of foresight—predicting how systems will behave under scale, how memory and disk interactions unfold, and how to align design choices with organizational goals.
Data Definition and Manipulation in Context
Databases are not static structures; they are dynamic environments shaped and reshaped by human intent and system processes. Two linguistic frameworks govern this transformation: the Data Definition Language (DDL) and the Data Manipulation Language (DML). These dialects, implemented through Transact-SQL or T-SQL, form the communicative bridge between user and database.
The DDL defines the structure of the database. It enables the creation of tables, views, schemas, and other objects that constitute the skeleton of data architecture. Through commands that establish entities and their interrelations, one determines the form that information will take. On the other hand, the DML animates this form by allowing users to insert, update, delete, and retrieve data. It is through DML that databases become functional instruments of decision-making, computation, and reporting.
Within the training, learners are introduced to the power of T-SQL, Microsoft’s extension of SQL, which offers additional control and procedural logic. Understanding the harmony between DDL and DML equips professionals with the capacity to design and refine systems that respond intelligently to the evolving demands of their organizations.
The Concept of Tables and Relationships
Tables are the bedrock of relational databases, each representing a distinct category of information. Whether describing customers, orders, products, or transactions, every table encapsulates a unique aspect of a business process. The design of these tables determines not only how easily information can be retrieved but also how resilient the database will be to change.
Relationships between tables emerge through the alignment of keys. A primary key uniquely identifies each record within a table, ensuring that no duplication occurs. A foreign key establishes a link between two tables, allowing data in one to reference data in another. These relationships create a web of dependencies and associations that mirror the real world, turning abstract data into meaningful structures.
In practice, designing relationships requires discernment. Poorly chosen keys can lead to anomalies and inefficiencies, while overly complex relationships can make queries cumbersome. The balance lies in crafting a schema that captures the essential truth of the business domain without burdening performance or maintainability.
The Role of Normalization in Database Integrity
One of the most vital concepts in database design is normalization, a methodical process that refines data structures to eliminate redundancy and ensure logical consistency. Normalization decomposes large, unwieldy tables into smaller, more manageable ones, each focused on a single theme. Through a sequence of normal forms—typically up to the third—the database attains an elegant equilibrium where every piece of data resides in its rightful place.
The first normal form enforces atomicity, ensuring that each field contains only indivisible values. The second normal form eliminates partial dependencies, requiring that non-key attributes depend fully on the primary key. The third normal form removes transitive dependencies, so that attributes depend only on the key, not on other non-key attributes. These rules, though abstract, manifest in tangible benefits: reduced duplication, enhanced data integrity, and improved maintainability.
For those embarking on the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals path, normalization embodies the discipline of clarity. It is the antidote to confusion, compelling designers to articulate exactly how information relates and how it should evolve over time.
Querying and Data Extraction
A database’s true utility is revealed not merely in its ability to store data, but in its capacity to yield insights. Querying is the craft of extracting knowledge from structured information. Through the use of SELECT statements and logical conditions, users can summon the precise subset of data they require. This act, simple on the surface, conceals layers of complexity involving filtering, sorting, grouping, and joining.
Joins, in particular, represent the connective tissue of relational databases. They allow data from multiple tables to be combined, revealing associations that would otherwise remain hidden. Inner joins, outer joins, and self-joins each serve distinct purposes in illuminating relationships among datasets. The mastery of joins transforms a database from a passive repository into an active analytical tool.
Understanding how to craft efficient queries also demands an appreciation of indexes and query optimization. Without these mechanisms, retrieval operations could deteriorate under the weight of scale. Indexes serve as accelerators, guiding the system toward relevant data with precision, though they too must be managed judiciously to avoid excessive overhead.
Data Integrity and Transactions
Integrity is the cornerstone of any credible data system. It ensures that information remains accurate, consistent, and reliable, even amid simultaneous operations and potential failures. In relational databases, integrity is enforced through constraints and transactions. Constraints such as primary keys, foreign keys, unique indexes, and check rules guard the database against invalid or contradictory entries.
Transactions, by contrast, safeguard the process of change itself. A transaction represents a sequence of operations executed as a single logical unit. The fundamental principle—known as ACID, standing for Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability—ensures that either all operations succeed or none do. This guarantees that the database never enters an uncertain state.
When learners in the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals program encounter these concepts, they are not simply memorizing definitions; they are internalizing the ethical dimension of data management. Every constraint and transaction reflects a commitment to truth and coherence within the digital ecosystem.
Security and Data Protection
No database is complete without a strategy for security. As information becomes increasingly valuable, the need to protect it intensifies. Database security encompasses multiple layers: authentication, authorization, encryption, and auditing. Together, these mechanisms ensure that only legitimate users gain access, that their privileges are appropriate, and that every action is traceable.
User accounts and roles form the foundation of access control. Administrators define who may interact with the system and what operations they are permitted to perform. Roles simplify management by grouping permissions logically, ensuring that organizational policies are consistently enforced. Beyond these measures, encryption shields sensitive data from unauthorized exposure, whether at rest or in transit.
Backup and recovery procedures complete the security framework. Even the most robust systems are vulnerable to failure, corruption, or external attack. Full and incremental backups provide a safety net, allowing administrators to restore the database to a known, stable state. Understanding when and how to implement these strategies is an integral part of database administration, and the Microsoft certification pathway emphasizes their importance from the outset.
The Human Element in Database Administration
While technology provides the tools, it is human intellect that wields them. Database administration demands analytical acuity, foresight, and adaptability. The administrator’s role extends beyond maintenance; it involves stewardship of an organization’s most precious asset—its data.
Monitoring performance, diagnosing bottlenecks, tuning queries, and ensuring uptime are daily responsibilities. Yet, the most successful administrators also possess an awareness of the broader context. They understand how databases integrate with applications, networks, and business objectives. Their expertise bridges the technical and the strategic, transforming data systems into instruments of innovation.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals pathway introduces learners to this mindset early. It cultivates a perspective that values precision, documentation, and continuous improvement. Database administration is not merely a technical pursuit but a discipline of responsibility, demanding vigilance and intellectual rigor.
The Interplay Between Data and Application
Modern applications rely on databases not only as back-end repositories but as integral components of their logic. The interaction between application and database defines performance, scalability, and user experience. Understanding this interplay is essential for any aspiring database professional.
Applications communicate with databases through queries, stored procedures, and APIs. Efficiency in this communication is crucial; poorly designed queries or excessive round-trips can degrade responsiveness. Likewise, inadequate indexing or suboptimal schema design can hinder even the most well-constructed applications.
Through the lens of the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals framework, students learn to see beyond syntax and consider architecture holistically. They grasp that the database is not an isolated entity but a vital organ within the digital organism.
The Evolution of Database Technologies
The database landscape continues to evolve. While relational models remain dominant, alternative paradigms such as document stores, key-value databases, and graph systems have emerged to address specific needs. Understanding relational principles, however, remains indispensable, for even these new technologies often borrow their concepts of consistency, transactions, and structure from relational theory.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals certification establishes a foundation from which learners can explore this expanding universe. Mastery of core principles equips them to adapt to emerging systems, whether cloud-based, distributed, or hybrid. The discipline instilled through relational thinking translates seamlessly into diverse technological contexts.
Data as the Lifeblood of Modern Enterprise
In today’s world, data is no longer a byproduct of business activity—it is the enterprise itself. Every decision, strategy, and innovation relies upon the ability to gather, analyze, and interpret data effectively. Databases form the infrastructure of this data-driven paradigm, transforming raw information into actionable intelligence.
Organizations that understand and harness their data thrive. Those that neglect its care risk obsolescence. Learning to construct and maintain robust database systems is therefore not an academic exercise but a vital professional pursuit. The principles covered within the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals course empower individuals to contribute meaningfully to this data-centric ecosystem.
The Journey Toward Mastery
Mastering database fundamentals is akin to learning a new language—one of precision, structure, and logic. Each concept builds upon the previous, creating a framework through which the complexity of data becomes comprehensible. Understanding core database concepts is not merely about passing an examination; it is about cultivating a mindset attuned to order, efficiency, and truth in information.
The journey begins with the smallest units—tables, fields, and relationships—and expands to encompass entire systems. It involves both the tangible manipulation of data and the intangible understanding of its purpose. Those who undertake this path through the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals framework emerge not only with technical proficiency but with a deeper appreciation for the harmony between logic and reality that databases embody.
Creating Database Objects and Building Structural Foundations
Understanding how to create database objects is the cornerstone of mastering database systems and cultivating the precision required to design and sustain reliable data architectures. Every database is composed of carefully arranged elements that together form the foundation upon which data is stored, manipulated, and retrieved. Within the framework of the Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals discipline, learning to create and administer these objects becomes a formative experience—one that blends logic, structure, and creativity into a coherent practice of digital craftsmanship.
Database objects, though conceptual in essence, manifest as tangible components that define how data exists within a relational model. They embody structure through tables, enable access through views, enforce automation through stored procedures, and encapsulate reusability through functions. Understanding how to design and interrelate these objects is essential to ensuring that a database operates with harmony, efficiency, and scalability.
The Art of Defining Data Structures
At the heart of every relational database lies the table, the most fundamental and indispensable object. A table is a carefully defined construct that organizes data into rows and columns, with each column representing an attribute and each row representing a record. The creation of a table demands precision and forethought. One must determine what type of data will be stored, how it will relate to other entities, and how to guarantee its integrity.
Each column within a table must be assigned a data type that dictates the kind of information it can hold. These data types range from integers and decimals to textual and binary forms. The decision of which data type to employ is both a technical and philosophical one. It reflects not only the nature of the data but also how it will be used, queried, and compared. For instance, a column storing numeric identifiers might employ an integer type for performance and simplicity, while a field intended for descriptive text might utilize variable-length character types to accommodate variability.
An integral part of defining data structures is considering constraints. Constraints act as guardians of accuracy, ensuring that invalid or contradictory entries cannot infiltrate the system. Primary keys guarantee uniqueness, foreign keys enforce relational consistency, and check constraints validate values against specific rules. Through this lattice of safeguards, the database gains resilience, allowing it to function as a reliable repository of truth.
When learners explore this domain within the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals context, they are introduced not only to the technical syntax of creation but also to the intellectual discipline of foreseeing relationships, dependencies, and the consequences of design decisions.
Understanding Data Types and Storage Implications
The selection of data types may appear mundane to the untrained eye, yet it possesses profound implications for performance, efficiency, and scalability. Each type consumes a specific amount of storage, influences how data is indexed, and affects how queries are executed. Choosing the appropriate type for each field ensures the database remains agile, conserving both memory and processing power.
Numeric data types are often employed for quantities, identifiers, and calculations. Textual data types accommodate words, descriptions, and unstructured information. Binary types preserve multimedia or encoded data, while date and time types manage temporal values essential for chronological records. Understanding the nuances among them allows designers to create structures that align with both functional and operational needs.
For example, a column meant to store monetary values must account for precision and rounding; using a floating-point type may lead to subtle inaccuracies over time, while fixed-point numeric types provide exactness. Similarly, selecting between fixed-length and variable-length character fields can affect storage allocation and query performance.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals course emphasizes these subtleties to cultivate discernment among learners. It teaches that creating a table is not a mechanical act but a strategic decision-making process that affects every interaction with the data henceforth.
Establishing Keys and Relationships
The creation of relationships between tables transforms a collection of isolated entities into an interconnected web of meaning. Keys are the conduits through which these relationships flow. A primary key serves as the singular identifier for each record, while a foreign key establishes a linkage to another table, forging a relationship that binds data together across structures.
Establishing a relationship requires alignment between corresponding columns in different tables, ensuring compatibility in data types and constraints. The enforcement of referential integrity guarantees that no orphaned records can exist—every reference must point to a valid and existing entry.
Designing these relationships involves more than technical knowledge; it demands a conceptual understanding of the underlying domain. One must envision how entities interact within the context of the real world. For instance, in a system tracking customers and orders, a relationship between the customers table and the orders table must capture the fact that each order originates from a specific customer. Without such clarity, the database would fail to represent the logic of its domain accurately.
Keys, indexes, and relationships thus form the skeletal framework upon which the vitality of the database depends. Mastering their creation marks a pivotal step toward becoming proficient in relational thinking and structured design.
Creating Views for Data Abstraction
In a complex database, raw tables often contain more data than users or applications need to access directly. Views provide a solution by offering a filtered, customized perspective of the underlying tables. A view acts as a virtual table derived from a query, presenting a subset of data tailored to specific requirements.
Creating views is an exercise in both security and clarity. By abstracting certain columns or rows, one can restrict access to sensitive information while presenting only the necessary details to users. Views also simplify complex queries by encapsulating logic into a reusable object, making it easier to retrieve data without rewriting lengthy statements.
For example, a business analyst might require a view that consolidates customer information and their corresponding purchase totals, drawn from multiple tables. By creating such a view, the analyst gains direct access to meaningful insights without navigating the intricacies of the underlying schema.
Through the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals framework, learners are guided to appreciate views as instruments of abstraction, enabling them to build layered architectures that balance accessibility and protection.
The Function and Creation of Stored Procedures
Stored procedures represent a higher level of database logic, encapsulating sequences of commands into reusable routines. They can perform operations ranging from simple data retrieval to complex transactional workflows. Their existence within the database itself allows them to execute more efficiently than ad hoc queries, as they are precompiled and optimized by the system.
Creating stored procedures involves defining parameters, logic, and the operations to be performed. They can accept inputs, return results, and even enforce business rules. This capability transforms the database from a passive data store into an active participant in application logic.
The advantages of stored procedures extend beyond performance. They enhance consistency by centralizing logic that might otherwise be duplicated across multiple applications. They also strengthen security by restricting direct access to tables, permitting users to interact with data only through controlled procedures.
Within the context of the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals pathway, understanding how to craft and manage stored procedures equips learners with the ability to design self-sufficient, maintainable systems that support organizational objectives efficiently and securely.
Creating and Utilizing Functions
Functions share similarities with stored procedures but are primarily designed to return a single value or result set based on input parameters. They serve as the analytical tools within a database, transforming data through calculation, formatting, or aggregation.
The creation of functions allows for modular and reusable logic. By defining a function once, developers can invoke it across multiple queries, ensuring consistency and reducing redundancy. For instance, a function that calculates tax or discounts can be applied to numerous operations without rewriting the formula each time.
Functions also promote clarity in query construction. Instead of embedding complex expressions within statements, one can reference a function to make queries more readable and maintainable. When used judiciously, functions become integral to a database’s design philosophy—concise, elegant, and purposeful.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals curriculum integrates the concept of functions as a vital step toward writing efficient and maintainable T-SQL code, reinforcing the notion that simplicity and reusability lie at the heart of robust database systems.
Managing Schema and Ownership
Every database object resides within a schema, a logical container that defines its namespace and ownership. Schemas provide structure and security, organizing objects in a way that reflects their function and relevance. For example, one schema might contain tables related to finance, while another hosts data concerning human resources.
Creating and managing schemas is essential for maintaining order within expansive databases. It also assists in enforcing access control, as permissions can be granted at the schema level, ensuring that users can interact only with the data pertinent to their role.
Understanding how to manage schema ownership also mitigates risks related to object modification and deletion. It clarifies accountability and supports a cleaner separation of responsibilities within teams that manage databases collaboratively.
Through the study of the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals, learners acquire the perspective that organization extends beyond data values; it encompasses the structure and governance of the objects themselves.
Integrating Constraints and Defaults
Constraints ensure that the data entering a table adheres to predefined rules. They represent the moral compass of a database, guiding it toward consistency and veracity. A check constraint, for instance, might ensure that a numeric value remains within a sensible range, while a default constraint automatically assigns values to fields when none are specified.
The creation of constraints transforms a database from a passive receptacle into a self-regulating environment. It no longer relies solely on applications or external validation but enforces its own integrity internally. This reduces errors, simplifies maintenance, and ensures that data remains trustworthy.
When coupled with defaults, constraints create a harmonious balance between flexibility and control. They anticipate human error and provide safety nets that preserve accuracy without stifling functionality. The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals training immerses learners in these subtleties, encouraging them to design systems that are both resilient and adaptable.
Indexing for Performance Optimization
As databases grow in size, retrieving information efficiently becomes paramount. Indexes serve as navigational aids, accelerating access to data by maintaining auxiliary structures that guide the system to relevant records. Creating indexes requires discernment, as each index improves retrieval speed but consumes additional storage and may slow down data modification operations.
There are two primary types of indexes—clustered and non-clustered. A clustered index determines the physical order of data within a table, effectively defining how rows are stored on disk. A non-clustered index, by contrast, maintains a separate structure that references the data indirectly, providing flexibility for multiple indexing strategies.
The act of indexing represents the pursuit of equilibrium. Too few indexes result in sluggish performance, while too many burden the system with overhead. Understanding how to strike this balance is part of the wisdom imparted through the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals framework. It encourages a nuanced appreciation for optimization rather than reliance on arbitrary rules.
Triggers and Automation
In the orchestration of data systems, automation plays a crucial role. Triggers exemplify this principle by executing predefined actions automatically in response to specific events. When data is inserted, updated, or deleted, a trigger can perform supplementary tasks such as logging, validation, or synchronization with other tables.
Triggers enhance consistency by ensuring that critical operations occur without manual intervention. They embody the concept of reactive programming within the database, enabling it to respond dynamically to change. However, with great power comes responsibility; poorly designed triggers can introduce complexity and performance challenges.
Learning to design efficient triggers within the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals discipline teaches restraint as well as capability. It instills an understanding that automation should simplify, not complicate, the system’s behavior.
Data Integrity Through Referential Enforcement
Referential integrity is the assurance that relationships among tables remain valid. When a foreign key references a primary key, the system must ensure that no record violates this bond. Attempting to delete or modify a record that would break a relationship triggers constraints that prevent data corruption.
Maintaining referential integrity fosters stability. It guarantees that the database reflects reality—that every reference points to something that exists. This discipline mirrors ethical integrity in human systems; it is the database’s promise to uphold the truth of its data.
Within the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals course, enforcing referential integrity is portrayed as a central responsibility of every designer and administrator. It is the invisible thread that binds data together, ensuring coherence even amid growth and complexity.
Building Scalable Structures
As organizations evolve, so too must their databases. Scalability ensures that systems can accommodate expanding volumes of data and increasing user demands without degradation of performance. Creating scalable database objects involves foresight in design—anticipating future requirements, modularizing structures, and avoiding rigid dependencies.
Partitioning data, distributing workloads, and designing efficient relationships all contribute to scalability. Equally important is the human element: documentation, naming conventions, and consistent standards ensure that as databases grow, they remain intelligible and maintainable.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals training instills the philosophy that scalability is not an afterthought but a design principle woven into the very act of creating objects.
The Synergy of Design and Functionality
Creating database objects is an act of synthesis where design and functionality converge. Each decision—every key, constraint, and index—represents a negotiation between precision and adaptability. The most successful databases are those whose architecture harmonizes technical rigor with real-world usability.
To achieve this harmony, designers must think both abstractly and concretely. They must consider not only how data is stored but why it exists and how it will be used. In doing so, they transcend the mechanics of creation and enter the realm of architecture, where each object contributes to a coherent and purposeful system.
The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals pathway cultivates this vision by transforming learners into architects of order in a world awash with information. It teaches that every table, view, and procedure is not merely a construct but a manifestation of logic and intent, a testament to the enduring human pursuit of clarity in complexity.
Manipulating Data and the Dynamics of Information Flow
Within the intricate world of databases, manipulation of data is the heartbeat that keeps the entire system alive and responsive. The capacity to insert, update, delete, and retrieve information defines the very essence of a functional data environment. Without the power of manipulation, even the most meticulously structured database would remain inert—an empty vessel devoid of purpose. In the framework of the Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals discipline, understanding how to manipulate data becomes a vital competence, merging analytical reasoning with technical execution.
Manipulating data is more than an exercise in modifying values; it is a method of maintaining the integrity, fluidity, and relevance of information within a relational ecosystem. Every operation, whether the extraction of insights or the alteration of existing records, carries implications for performance, consistency, and accuracy. The mastery of these interactions is essential for anyone seeking to comprehend how relational databases operate in both theoretical and practical dimensions.
The Conceptual Landscape of Data Manipulation
Before delving into the mechanisms of manipulation, it is essential to appreciate the philosophical foundation of the process. Data is not static; it is a constantly evolving representation of real-world phenomena. Businesses grow, transactions occur, relationships change, and all these transformations must be mirrored within the database. The relational model was conceived precisely to accommodate this dynamic nature, ensuring that information remains synchronized with the evolving reality it represents.
Manipulating data involves four primary operations: inserting new data, updating existing data, deleting obsolete data, and selecting data for analysis or presentation. These operations are executed through the use of the Data Manipulation Language, commonly abbreviated as DML. Implemented through Transact-SQL or T-SQL, DML forms the expressive syntax through which humans communicate intentions to the database management system.
Every command executed through DML triggers a cascade of actions within the relational structure. Rows are created, altered, or removed; indexes are adjusted; constraints are verified; and relationships are maintained. Understanding this intricate choreography of operations requires both conceptual clarity and technical precision.
Inserting Data into Relational Tables
The insertion of data is the initial act of populating a database, transforming an abstract schema into a living collection of information. Each record introduced represents a new instance of an entity—a customer, product, employee, or transaction—that contributes to the broader data narrative.
When inserting data, one must ensure adherence to all structural and integrity constraints defined within the database. Every primary key must be unique, foreign keys must correspond to existing values in related tables, and each field must conform to its designated data type and format. Failure to respect these rules disrupts the delicate equilibrium of relational integrity.
The act of insertion, though seemingly straightforward, carries strategic significance. The order in which data is inserted can affect dependencies among tables, particularly when referential constraints are in play. Inserting parent records before child records preserves logical coherence and prevents violations. Moreover, understanding the implications of triggers, defaults, and computed columns allows for seamless automation of routine insertions.
Within the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals learning path, the process of insertion is explored not merely as a technical operation but as an exercise in discipline and foresight. Each row introduced into the system becomes part of an interconnected web whose stability depends on meticulous attention to structure.
Updating Data to Reflect Change
Change is the constant companion of any living system, and databases are no exception. Updating data enables the system to evolve, reflecting new realities as they emerge. Whether modifying a customer’s address, adjusting an employee’s salary, or revising inventory counts, updates ensure that stored information remains accurate and relevant.
However, with this power comes responsibility. Updating data requires a delicate balance between precision and caution. Careless updates can introduce inconsistencies or cascade unintended effects across related tables. For instance, altering a key value that serves as a foreign reference may disrupt the relationships that maintain logical continuity between entities.
The efficiency of updates is also influenced by indexing and query optimization. A well-indexed column allows updates to be targeted efficiently, while poor indexing can lead to unnecessary scanning of large datasets. Understanding how indexes interact with update operations is therefore vital to maintaining system performance.
In the realm of the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals framework, learners are taught to approach updates with a sense of stewardship. Every modification to data should serve the purpose of improving accuracy and supporting decision-making, never compromising the coherence of the database.
Deleting Data and Preserving Integrity
Deleting data is a paradoxical act: it removes information, yet when done correctly, it preserves the purity and order of the database. Deletion is necessary to eliminate redundant, obsolete, or erroneous records, ensuring that the database remains a faithful representation of the current state of affairs.
However, the removal of data carries inherent risk. Deleting a record that serves as a reference for other tables can create orphaned entries, violating referential integrity. To prevent this, relational databases employ constraints and cascading rules that dictate how deletions propagate. A cascading delete, for instance, automatically removes dependent records, ensuring consistency without manual intervention.
The decision to delete should be guided by a deep understanding of dependencies and consequences. In certain contexts, logical deletion—marking a record as inactive rather than physically removing it—provides a safer alternative, preserving historical data for auditing and analysis.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals perspective treats deletion not as a destructive act but as a method of refinement. It is the pruning that allows the data tree to grow healthily, unencumbered by redundancy or contradiction.
Retrieving Data through Querying
While insertion, updating, and deletion shape the structure of data, querying reveals its meaning. The process of retrieving data through queries transforms static records into dynamic insights. Through the use of the SELECT statement, users extract precise subsets of information according to specific criteria, allowing them to analyze patterns, generate reports, and support decisions.
Querying lies at the heart of database utility. It allows users to ask questions of their data, combining logic and mathematics to uncover relationships and trends. Conditions, filters, aggregations, and sorting mechanisms refine the output, while joins enable data from multiple tables to be combined into cohesive results.
Understanding how to craft effective queries requires not only knowledge of syntax but also an appreciation of logic and structure. A query is an argument—a logical statement that must be both accurate and efficient. Poorly written queries can burden the system, consuming excessive resources and slowing down performance. Optimized queries, on the other hand, achieve clarity and speed, delivering results swiftly and precisely.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals course places special emphasis on querying as a cognitive skill. It transforms the student into a data interpreter, capable of translating raw numbers into knowledge and insight.
The Role of Joins in Combining Data
Relational databases derive their strength from relationships. Joins are the mechanism that allows these relationships to be expressed in queries, bringing together data from multiple tables based on shared attributes. Through joins, disparate fragments of information coalesce into a unified whole, mirroring the interconnectedness of the real world.
There are several types of joins, each serving a distinct purpose. An inner join retrieves records that have matching values in both tables, ensuring that only related data appears in the result. Outer joins, whether left, right, or full, include unmatched records from one or both tables, revealing gaps and exceptions. Self-joins, meanwhile, enable comparisons within the same table, useful for hierarchical or recursive relationships.
The logic of joins extends beyond mere syntax; it embodies relational thinking itself. By understanding how data entities relate, one can design queries that reflect real-world associations with elegance and precision.
Through the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals discipline, learners develop fluency in using joins to weave complex narratives from simple components, transforming scattered facts into coherent knowledge.
Combining Result Sets and Aggregating Data
In many analytical contexts, information from multiple sources must be combined to produce comprehensive insights. Combining result sets through constructs such as union or intersection enables the merging or comparison of different query outputs. A union gathers the results of two compatible queries into a single dataset, while an intersection isolates only those records that appear in both. These operations expand the expressive capacity of database queries, allowing analysts to explore relationships between diverse datasets.
Aggregation, meanwhile, condenses vast volumes of data into meaningful summaries. Through aggregate functions such as counting, averaging, or summing, one can extract high-level insights from granular information. Grouping mechanisms allow these aggregates to be applied across categories, enabling patterns to emerge from complexity.
The practice of aggregation and combination transforms the database from a passive storage medium into an active analytical engine. It bridges the gap between data management and data intelligence. The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals pathway cultivates this analytical sensibility, emphasizing the importance of clarity, precision, and interpretive skill in crafting queries that inform rather than obscure.
Transactions and Consistency
When manipulating data, maintaining consistency across multiple operations is paramount. Transactions provide the framework for ensuring that related changes are treated as a single, atomic unit of work. Within a transaction, all operations either succeed collectively or fail collectively, preserving the integrity of the database even in the face of errors or interruptions.
The concept of transactions is governed by the ACID properties: atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability. Atomicity ensures that each transaction is indivisible; consistency guarantees adherence to constraints; isolation prevents interference between concurrent operations; and durability ensures that once committed, changes persist even after system failures.
Understanding transactions transforms data manipulation from a set of isolated actions into a disciplined process governed by logical coherence. It ensures that the database remains stable and reliable, reflecting a consistent truth at every moment.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals curriculum instills this understanding early, teaching learners to view transactions as the ethical framework of database manipulation—a contract between system and user that promises order amid complexity.
Data Validation and Error Handling
Manipulating data inevitably involves encountering anomalies, conflicts, and errors. Data validation acts as the first line of defense, ensuring that inputs conform to expected formats, ranges, and relationships. Validation may occur at multiple levels—within the application, through constraints, or via stored procedures and triggers.
When errors arise, graceful handling becomes crucial. A robust system anticipates failure and responds constructively, rolling back incomplete transactions and preserving data consistency. Error-handling mechanisms provide feedback, allowing users and administrators to diagnose problems and implement corrective measures.
Validation and error management elevate the quality of data manipulation, transforming it from a mechanical process into a thoughtful dialogue between user and system. The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals approach emphasizes that integrity is not achieved through perfection but through the capacity to detect, correct, and learn from deviation.
Performance and Optimization in Data Manipulation
As data volumes expand, efficiency becomes a central concern. The performance of manipulation operations—whether insertion, update, deletion, or retrieval—depends on a symphony of factors: indexing, query design, hardware resources, and concurrency control.
Optimization begins with understanding how the database engine processes commands. Execution plans reveal the sequence of operations, the indexes used, and the costs associated with each step. By analyzing these plans, one can identify bottlenecks and redesign queries for improved performance.
Batch processing, partitioning, and caching also play significant roles in optimizing manipulation. Efficiently designed systems minimize contention, reduce redundancy, and balance workloads across resources.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals framework encourages learners to view optimization not as a one-time adjustment but as an ongoing pursuit of equilibrium between speed, accuracy, and maintainability.
Automation and Data Transformation
Beyond direct manipulation, databases often require automation to handle repetitive or scheduled operations. Automated processes, whether through jobs, triggers, or procedures, ensure that data remains synchronized and up to date without constant human intervention.
Transformation, meanwhile, involves reshaping data for new purposes—integrating it into reports, feeding it into analytical models, or migrating it between systems. The capacity to transform data effectively depends on understanding its structure, lineage, and meaning.
Automation and transformation together extend the power of manipulation beyond immediate interaction, allowing databases to function as self-sustaining ecosystems that respond dynamically to their environments. The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals training imparts this understanding, preparing learners to design systems that are both autonomous and adaptable.
The Philosophy of Responsible Data Manipulation
Ultimately, manipulating data is not merely a technical skill but an ethical practice. Every insertion, update, deletion, or query alters the narrative of the data universe. With each change comes the responsibility to maintain truth, coherence, and transparency.
Responsible manipulation involves foresight—anticipating consequences before executing commands—and humility—recognizing the fallibility of both human and machine. It is through this balance that the database remains not just a tool of computation but an instrument of knowledge and trust.
The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals foundation cultivates this mindset, guiding learners to engage with data not as mere technicians but as custodians of information, aware that each operation contributes to the enduring structure of collective understanding.
Understanding Data Storage and the Architecture of Relational Systems
The inner workings of data storage are the unsung foundation upon which the entire edifice of relational databases stands. Every structured system, from a modest business database to a colossal enterprise architecture, relies upon meticulous methods of storing, retrieving, and protecting information. To understand data storage is to delve into the very anatomy of the digital world, where each byte occupies a purpose and each relation reinforces meaning. Within the scope of the Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals discipline, the comprehension of how data is stored, organized, and optimized becomes indispensable to every aspiring professional who seeks mastery over the art of database management.
The Concept of Data Storage and its Underlying Purpose
At the core of database systems lies the need to represent real-world entities in a digital format. The process of data storage is not simply about placing information into a container; it is an exercise in designing a harmonious structure where efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility coexist. Every value inserted into a database table is preserved in a manner that ensures both its immediate availability and its long-term integrity.
Relational databases, in particular, follow a structured methodology wherein data is distributed across interrelated tables. Each table holds rows, each row represents an instance of an entity, and each column defines a property of that entity. This structured form of organization is what allows the relational model to thrive. By abstracting data into related entities, databases minimize redundancy and ensure logical consistency across the system.
The data storage process begins with schema design, a stage in which architects define the blueprint for how information will be organized. The schema governs relationships, keys, constraints, and indexes, thereby dictating how efficiently data can be stored and accessed. The physical storage of this data, meanwhile, depends upon underlying mechanisms within the database management system that manage blocks, pages, and files.
The Philosophy of Normalization
Normalization is the intellectual heartbeat of data storage design. It is the process of structuring a database to reduce redundancy and improve data integrity. The relational model’s elegance stems from its ability to separate data into logical units, ensuring that each piece of information is stored only once and referenced where needed.
Normalization operates through a series of progressive refinements known as normal forms. The first normal form ensures that all data is atomic—meaning each field contains indivisible values. The second normal form eliminates partial dependencies, ensuring that non-key attributes depend upon the whole primary key. The third normal form removes transitive dependencies, guaranteeing that each attribute depends only upon the key and nothing else.
Beyond the third level, higher normal forms such as Boyce-Codd, fourth, and fifth normal forms introduce further refinements, each designed to handle increasingly complex relationships. Though these higher forms are less frequently encountered in basic systems, their conceptual rigor serves as a philosophical guide for advanced data architects.
The act of normalization is not merely mechanical. It is a balancing act between efficiency and practicality. Over-normalization can lead to excessive fragmentation of data, making queries cumbersome. Therefore, designers often seek a middle ground, known as denormalization, where selective redundancy enhances performance without sacrificing integrity. The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals approach encourages understanding this balance as both an art and a science.
The Significance of Primary and Foreign Keys
In the architecture of relational databases, keys act as the connective tissue that binds data together. A primary key uniquely identifies each record in a table, ensuring that no two entries can occupy the same logical space. It embodies the concept of identity—each entity represented in a table must be distinguishable from all others.
Foreign keys, on the other hand, establish relationships between tables. They reference primary keys in other tables, creating the relational fabric that defines the database. Through foreign keys, data across tables remains interconnected, enabling the database to maintain consistency and enforce referential integrity.
Choosing the right key requires strategic thought. A primary key must be stable, unique, and immutable over time. Natural keys, which derive from inherent properties such as identification numbers or codes, often serve this purpose well, though surrogate keys—artificial identifiers such as auto-incremented numbers—provide flexibility in evolving systems.
The relationship between primary and foreign keys is what transforms isolated tables into a coherent relational structure. Within the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals curriculum, learners explore how these keys interact, how constraints enforce their rules, and how they form the backbone of query operations and data integrity.
Indexes and Their Role in Performance Optimization
While normalization ensures logical clarity, indexing ensures physical efficiency. An index serves as a roadmap that allows the database engine to locate specific data quickly without scanning entire tables. Like the index of a book guiding readers to precise pages, database indexes direct queries to exact rows.
There are two principal forms of indexes: clustered and non-clustered. A clustered index determines the physical order of data within a table, aligning storage with the index’s structure. Each table can have only one clustered index because data can be physically ordered in only one way. Non-clustered indexes, in contrast, act as separate structures that reference data stored elsewhere, allowing multiple indexes to coexist for various columns.
Understanding when and where to create indexes is a critical skill. Too few indexes lead to sluggish queries; too many can slow down data modification operations, as each insertion or update must also modify the indexes. Proper indexing strategy is thus a delicate dance between speed and resource consumption.
The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals framework delves deeply into these principles, teaching learners to read execution plans, assess query performance, and apply indexing strategies that harmonize speed with stability.
Data Types and Storage Efficiency
Every piece of data stored in a database occupies physical space, and the choice of data type determines how efficiently that space is used. Data types define not only the format of stored values but also their storage requirements, comparison behavior, and potential for precision.
Numeric data types are suited for quantitative information, offering varying levels of precision and scale. Character data types store textual information, with fixed-length and variable-length options influencing space allocation. Date and time types provide temporal precision, allowing for chronological computation and sequencing. Binary types, meanwhile, accommodate non-textual data such as images or files.
The art of choosing the correct data type extends beyond simple compatibility. It requires foresight into how the data will be used, how it might grow, and how it interacts with other fields. Overly generous data types waste space; overly restrictive ones risk truncation and errors.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals learning experience encourages precision in data type selection, recognizing that storage efficiency and system performance hinge upon these seemingly minute choices.
Understanding Data Files, Pages, and Extents
Beneath the logical structures of tables and indexes lies the physical reality of data storage. Databases store information in files, which are divided into pages and extents. Pages represent the smallest unit of storage, typically eight kilobytes in size. Each page can contain multiple rows of data, depending on the size of each row.
Extents are collections of pages grouped together for allocation efficiency. When a table or index grows, the database engine allocates additional extents to accommodate the new data. This granular approach allows for fine-tuned management of storage space while minimizing fragmentation.
The arrangement of data across pages and extents influences performance. Sequential data access benefits from contiguous storage, while random access patterns can lead to scattered reads and reduced efficiency. Database administrators often use filegroups and partitioning to manage how and where data is stored, optimizing both performance and recoverability.
These internal mechanisms may seem abstract, yet they embody the craftsmanship that distinguishes effective database design. The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals curriculum provides insight into these low-level structures, bridging the gap between logical design and physical implementation.
The Principles of Data Integrity
Integrity lies at the heart of reliable data storage. It ensures that information remains accurate, consistent, and trustworthy over time. There are several dimensions to data integrity: entity integrity, referential integrity, and domain integrity.
Entity integrity is enforced through primary keys, guaranteeing that each record remains unique. Referential integrity ensures that relationships between tables remain valid—no foreign key should point to a non-existent primary key. Domain integrity governs the validity of individual values, ensuring that each entry falls within an acceptable range or format.
These principles are implemented through constraints—rules embedded within the database schema that automatically validate data. Check constraints, unique constraints, and default values all contribute to maintaining integrity.
In the Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals perspective, integrity is viewed not as an optional feature but as an essential pillar of system reliability. Without it, even the most sophisticated database becomes an unreliable repository of uncertainty.
Storage Optimization and Performance Tuning
As data accumulates, storage optimization becomes a perpetual concern. Databases that neglect optimization eventually succumb to bloat, inefficiency, and sluggish performance. Optimization involves analyzing access patterns, refining indexes, reorganizing storage, and monitoring fragmentation.
Compression is one effective strategy for optimization, reducing the physical footprint of data without altering its logical form. Partitioning allows large tables to be divided into manageable units, enhancing both performance and maintainability.
Regular maintenance tasks such as index rebuilding, statistics updating, and file defragmentation ensure that the database remains agile. The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals framework emphasizes proactive maintenance as a means of sustaining long-term efficiency.
The Role of Backups in Data Preservation
While optimization focuses on performance, backups safeguard persistence. No matter how robust a database may be, hardware failures, human errors, and unforeseen disasters can threaten the integrity of stored information. Backups provide the means to recover from such events, restoring the database to a known, consistent state.
Full backups capture the entire database, while differential and incremental backups record only changes since the last backup. Transaction log backups preserve the sequence of operations, enabling point-in-time recovery.
A well-designed backup strategy balances redundancy with practicality, ensuring that recovery is both possible and timely. The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals approach treats backups not as an administrative afterthought but as a vital component of data stewardship.
Data Storage in Modern Contexts
In contemporary environments, data storage extends beyond traditional on-premises architectures. Cloud-based databases and distributed systems introduce new paradigms of scalability and resilience. Storage is no longer confined to a single machine; it spans clusters, data centers, and even continents.
Yet the principles of relational design remain constant. Whether hosted on physical servers or virtualized environments, databases still rely on normalization, keys, indexes, and integrity constraints. The evolution of technology has only expanded the scale and speed at which these principles operate.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals philosophy prepares learners to navigate this expanding landscape, where data storage merges with cloud architectures, replication strategies, and hybrid deployments.
The Interplay Between Storage and Security
Data storage is inseparable from security. Every byte stored within a database must be protected from unauthorized access, corruption, or misuse. Security mechanisms operate at multiple levels: authentication controls who can access the system, authorization defines what actions they can perform, and encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable.
Encryption at rest protects stored data, while encryption in transit secures communication between clients and servers. Role-based access controls assign permissions based on function rather than individual identity, simplifying management while enforcing discipline.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals learning journey integrates security within the discussion of storage, underscoring the idea that safe data is the only meaningful data. Storage without security is merely a repository of potential risk.
Evolving Paradigms of Data Storage
As the digital age advances, new paradigms emerge to redefine storage. Columnar storage, in-memory databases, and hybrid transactional-analytical systems challenge traditional assumptions about how data should be stored and retrieved. These innovations aim to reconcile the age-old trade-off between speed and scalability.
Columnar databases, for example, store data by columns rather than rows, making them ideal for analytical workloads. In-memory systems keep data in volatile memory rather than disk, achieving unparalleled speed at the cost of persistence.
The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals grounding offers a conceptual foundation upon which learners can explore these innovations. Understanding the relational model equips them with the intellectual tools to evaluate new technologies critically and adapt them to practical needs.
The Continuum of Storage and Knowledge
Ultimately, the study of data storage transcends technicality. It represents humanity’s effort to capture, preserve, and understand its collective experience. Each database, no matter how mundane its purpose, participates in this larger pursuit of memory and meaning.
Through meticulous design, disciplined normalization, careful indexing, and vigilant preservation, we transform ephemeral information into enduring knowledge. The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals curriculum reminds us that beneath every query and command lies a deeper aspiration—to impose order upon chaos, to make sense of the unseen patterns that govern our digital reality.
Administering a Database and the Discipline of Secure Management
The stewardship of a database extends far beyond its creation or design; it encompasses the perpetual guardianship of its health, performance, and security. Administering a database is both an art and a science—an endeavor that requires vigilance, precision, and a deep understanding of relational systems. To administer a database is to maintain equilibrium between accessibility and protection, ensuring that information remains available, accurate, and safeguarded against both internal inconsistency and external threat. Within the academic and practical framework of Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals, database administration stands as one of the most vital competencies, blending strategic thinking with methodical execution.
The Essence of Database Administration
At its core, database administration is the orchestration of all activities that sustain a database from inception through its operational lifespan. It involves configuring environments, managing user access, maintaining performance, enforcing integrity, and ensuring recoverability. The database administrator serves as both architect and guardian, responsible not only for the structural soundness of the system but also for its continual evolution in response to changing organizational demands.
A well-administered database mirrors the stability of a finely tuned instrument. Every adjustment, whether in indexing, storage allocation, or user privilege, influences the overall harmony of the system. The administrator must balance competing priorities: speed against safety, accessibility against confidentiality, and automation against oversight.
In the context of Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals, administration is portrayed as a holistic process that integrates management with governance. It requires both technical mastery and ethical sensibility, for the administrator holds dominion over the organization’s most valuable resource—its data.
Understanding Database Security Concepts
Security forms the moral and operational foundation of database administration. Without it, the entire system remains vulnerable to corruption, theft, and misuse. Database security involves a layered approach, combining authentication, authorization, encryption, auditing, and compliance mechanisms.
Authentication ensures that only legitimate users can access the database. This process verifies identity, often through credentials such as usernames, passwords, certificates, or integrated network authentication systems. Authorization, on the other hand, governs what those authenticated users can do once access is granted. Through role-based or object-level permissions, administrators can define precise boundaries of control, ensuring that users see and modify only what they are entitled to.
Encryption provides the final layer of defense. Data encryption at rest protects stored information from unauthorized reading, while encryption in transit ensures that data remains unreadable during transmission between systems. This dual protection is vital in environments where sensitive data, such as personal records or financial details, must remain inviolate even in the event of interception or theft.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals learning framework approaches security not as an optional consideration but as an intrinsic responsibility. The safeguarding of data is portrayed as both a technical mandate and a moral obligation.
Managing User Accounts and Roles
The administration of user accounts lies at the heart of security management. Each user who interacts with the database is represented by an account that defines their identity and privileges. Through these accounts, administrators can monitor activity, trace responsibility, and enforce accountability.
In small environments, individual account management may suffice, but in larger enterprises, it becomes impractical to assign and manage permissions manually for each user. Roles address this challenge by grouping privileges according to job function or responsibility. A role might define permissions for analysts, developers, administrators, or auditors, and users are then assigned to roles based on their duties.
The granularity of role design affects both security and efficiency. Too broad a role introduces unnecessary exposure; too narrow a one creates administrative overhead. The task of the administrator is to define roles that are both precise and pragmatic.
The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals perspective highlights role management as a cornerstone of sustainable administration. It teaches future administrators to design hierarchies of access that reflect organizational structures while preserving the sanctity of sensitive data.
Backup Strategies and Data Recovery
Even the most meticulously managed system is vulnerable to unforeseen events—hardware failures, software corruption, human error, or malicious intrusion. Backup and recovery mechanisms exist to mitigate these risks, ensuring that data remains resilient in the face of adversity.
A comprehensive backup strategy involves multiple layers of protection. Full backups capture the entire database in its current state, while differential backups record only changes since the last full backup. Incremental backups, meanwhile, track changes since the last backup of any type, optimizing storage efficiency. Transaction log backups preserve the chronological record of operations, allowing administrators to restore the database to a precise point in time.
Effective recovery depends not only on having backups but also on verifying their integrity and practicing restoration procedures. A backup that cannot be restored is merely an illusion of safety. Therefore, administrators regularly test restoration scenarios to ensure readiness for real-world emergencies.
In the Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals context, backup and recovery are taught as vital rituals of stewardship. They embody the discipline of foresight, reminding administrators that preservation is as essential as creation.
Monitoring and Performance Management
Performance is the pulse of a database system. A healthy database responds swiftly to queries, processes transactions efficiently, and scales gracefully under load. Monitoring performance involves observing metrics such as response time, throughput, resource utilization, and concurrency.
Administrators use tools and dashboards to track performance indicators, identifying bottlenecks in queries, indexing, or resource allocation. By analyzing execution plans, they can detect inefficient queries and restructure them for better optimization. Hardware considerations, such as memory, CPU, and disk I/O, also influence performance and must be balanced carefully.
Caching strategies, partitioning, and indexing play integral roles in performance management. The administrator’s challenge lies in tuning these elements without compromising stability or data integrity.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals learning philosophy introduces learners to the principles of performance analysis and the strategies used to maintain equilibrium between responsiveness and reliability.
Database Maintenance and Automation
Regular maintenance is the unseen labor that sustains the longevity of a database. Tasks such as index rebuilding, statistics updating, and log file management prevent degradation and preserve efficiency. Over time, data fragmentation, obsolete records, and bloated indexes can erode performance if not addressed.
Automation transforms maintenance from a manual chore into a systematic routine. Scheduled jobs, scripts, and alerts allow administrators to ensure continuous health monitoring without constant supervision. Automated processes can also handle repetitive activities such as backups, report generation, and data purging.
However, automation demands oversight. Blind reliance on automation can lead to complacency, where unnoticed failures accumulate. The administrator must remain the sentinel, ensuring that automated systems perform as intended.
The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals discipline presents maintenance as a form of ritualized care—a reflection of diligence and respect for the living organism that is the database system.
Security Auditing and Compliance
Beyond daily administration, databases exist within a larger framework of governance and compliance. Regulations concerning data privacy, financial reporting, and security accountability require that every access and modification be traceable. Auditing mechanisms record who did what, when, and from where.
Audit logs serve as both a deterrent and a diagnostic tool. They discourage misuse by introducing accountability and provide forensic evidence when investigating anomalies or breaches. Proper configuration of auditing ensures that logs capture relevant events without overwhelming the system with excessive data.
Compliance standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO directives dictate specific obligations regarding data handling and retention. Administrators must ensure that the database conforms to these mandates while maintaining operational flexibility.
In the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals framework, auditing is portrayed as an ethical necessity as much as a regulatory requirement. It reinforces the principle that transparency and accountability are the cornerstones of trust in digital systems.
Managing Concurrency and Transactions
In multi-user environments, concurrency introduces complex challenges. Multiple users may attempt to read or modify the same data simultaneously, leading to conflicts or inconsistencies. Concurrency control mechanisms ensure that transactions occur in a manner that preserves logical coherence.
Locks are the primary instruments of concurrency control. Shared locks allow multiple readers to access data simultaneously, while exclusive locks prevent conflicts during modification. Deadlocks, where two transactions block each other indefinitely, represent one of the most intricate challenges for administrators to resolve.
Transaction isolation levels define how much visibility one transaction has into another’s changes. Stricter isolation provides greater accuracy but may reduce performance; looser isolation improves speed but risks temporary anomalies. The administrator’s task is to select an appropriate balance based on the system’s nature and priorities.
Through Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals, learners acquire a deep understanding of these mechanisms, cultivating the capacity to foresee and mitigate conflicts before they impact system stability.
Implementing Security Policies and Encryption Strategies
Security policies encapsulate the organizational philosophy toward safeguarding data. They dictate password requirements, access protocols, encryption standards, and incident response procedures. Effective policies integrate technical enforcement with human awareness, ensuring that both system and personnel adhere to best practices.
Encryption strategies extend protection into the very fabric of data storage and transmission. Transparent data encryption secures entire databases, while column-level encryption safeguards particularly sensitive fields. Hashing ensures the confidentiality of authentication data, preventing the reversal of passwords even in the event of exposure.
Administrators must also consider key management, as the loss or compromise of encryption keys renders even the most advanced cryptography useless. Secure key storage and rotation policies are essential to maintaining the effectiveness of encryption.
The Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals approach emphasizes that security cannot be retrofitted; it must be intrinsic to every stage of administration. Each policy and practice reflects an attitude of reverence toward data stewardship.
Managing Storage and Resource Allocation
As data grows, so too does the demand for efficient storage and resource management. The administrator must allocate disk space, memory, and processing capacity in proportion to the system’s workload. Storage architectures such as RAID, filegroups, and partitioned tables enable scalability and redundancy.
Monitoring storage usage allows administrators to anticipate capacity issues before they become crises. Compression and archiving reduce physical space requirements, while tiered storage strategies balance cost with performance.
Resource allocation also encompasses the configuration of memory buffers, caching, and connection pools. Each parameter affects how the database handles concurrent requests and maintains responsiveness.
Within Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals, storage management is portrayed as a continuous negotiation between finite resources and infinite data demands, requiring foresight and adaptability.
Handling Database Migration and Upgrades
As technology evolves, databases must adapt. Migration involves transferring data, schema, and configurations from one environment to another—perhaps from an on-premises server to a cloud platform or from one database version to a newer release.
Successful migration requires careful planning, validation, and testing. Compatibility issues must be identified, data integrity preserved, and performance benchmarks re-evaluated. Administrators often employ transitional stages, where systems run in parallel until stability is assured.
Upgrades, meanwhile, introduce new features, security improvements, and performance enhancements. Yet they also carry risks, as deprecated features or altered behaviors can disrupt existing processes.
Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals imparts the procedural rigor necessary for these transformations. Learners are taught to approach migration as an act of renewal—a way to rejuvenate systems while preserving their accumulated wisdom.
Database Documentation and Knowledge Continuity
The administrative wisdom of a database must not reside solely in the mind of its custodian. Documentation ensures that processes, configurations, and policies remain accessible to others who may one day assume responsibility. Comprehensive documentation includes architectural diagrams, configuration details, maintenance schedules, and recovery procedures.
Knowledge continuity protects against loss caused by turnover or absence. It also promotes collaboration, allowing teams to share understanding and coordinate actions. The documentation process itself encourages reflection, revealing inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement.
In the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals ethos, documentation is viewed not as an afterthought but as an integral part of the administrative cycle. It transforms tacit expertise into institutional memory.
The Administrator’s Ethic of Responsibility
To administer a database is to exercise profound trust. The administrator stands as the intermediary between human intention and digital truth. Their actions shape the reliability of systems that sustain organizations, communities, and societies.
This responsibility demands an ethic of care—an awareness that every configuration, permission, and backup influences the integrity of the data universe. Vigilance, transparency, and humility become the virtues of administration.
The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals framework cultivates these virtues by embedding them in practice. It recognizes that mastery of database administration is not measured merely in technical competence but in the steadfast commitment to protect, preserve, and perfect the systems that embody collective knowledge.
Pathways to Mastery: Certification, Professional Growth, and the Evolution of Database Expertise
The world of information management is built upon the silent order of databases. Beneath every digital experience, transaction, or analytical insight lies the structure of carefully designed data repositories. As technology evolves, so too does the demand for individuals capable of understanding, securing, and optimizing these complex systems. The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals certification stands as a portal into this realm—a credential designed to guide aspiring professionals into the discipline of database architecture, administration, and stewardship. It is not merely an examination of skill but a rite of passage toward professional maturity in the digital sciences.
To achieve excellence in the field of data, one must embrace a holistic approach that fuses technical mastery with ethical awareness, conceptual understanding with practical dexterity, and curiosity with consistency. This exploration of certification and growth unveils the intellectual, procedural, and aspirational dimensions of the journey from novice to expert.
Understanding the Role of Certification in Modern Data Careers
In contemporary industries, data has become the lifeblood of decision-making and innovation. Organizations depend upon structured repositories of information to fuel their strategies and to ensure resilience in uncertain times. The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals certification serves as a foundational affirmation that a candidate comprehends the principles underpinning these repositories—relational design, data manipulation, normalization, storage mechanisms, and security management.
Certification provides both recognition and structure. It formalizes knowledge through standardized evaluation, ensuring that practitioners share a common understanding of essential concepts. Beyond the credential itself, the pursuit of certification fosters discipline and curiosity. Candidates internalize principles of relational database management systems, practice T-SQL queries, and refine their ability to analyze schema design.
For employers, certification acts as a signal of competence and reliability. It demonstrates that the holder has achieved a baseline proficiency validated by Microsoft’s rigorous standards. For individuals, it represents entry into a global community of data practitioners—a fraternity bound by shared learning and continuous evolution.
Preparation and Study Methodology
Preparation for the Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals examination demands a deliberate and structured approach. Candidates begin by familiarizing themselves with the key domains of knowledge: understanding core database concepts, creating database objects, manipulating data, managing data storage, and administering security. Each domain intertwines with the others, forming a network of interconnected understanding.
A disciplined study schedule is crucial. Candidates benefit from combining conceptual learning with applied practice. Interactive simulations, sample exercises, and virtual labs allow learners to translate theory into experience. Revisiting core topics such as normalization, relational integrity, and indexing deepens intuition and builds analytical agility.
Self-assessment serves as an indispensable component of preparation. Mock examinations and scenario-based questions reveal areas of weakness that require reinforcement. Reviewing these areas consolidates understanding and enhances recall under exam conditions. The process is not solely about memorization but about developing mental agility—learning to interpret, reason, and deduce efficiently.
In the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals course, the preparation methodology is guided by a pedagogy that integrates visual, auditory, and kinesthetic modes of learning. Through this multi-sensory approach, learners internalize principles with greater permanence and comprehension.
Cultivating Analytical Thinking and Precision
The study of databases cultivates analytical acuity. Every query, constraint, and schema design requires exactitude. Students of database fundamentals learn to think structurally, perceiving data as interconnected entities rather than as isolated fragments.
Analytical precision extends beyond the mechanical act of writing queries. It manifests in the ability to conceptualize how data flows through systems, how dependencies shape relationships, and how anomalies disrupt coherence. The mastery of relational integrity instills habits of methodical reasoning that extend far beyond the realm of databases.
Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals emphasizes that a database professional must not only understand how to manipulate data but also why certain structures behave as they do. Through continuous exposure to problem-solving exercises, learners develop an intellectual reflex for detecting inefficiencies and inconsistencies.
Building Professional Resilience Through Continuous Learning
Technology evolves with relentless velocity. Concepts once considered advanced soon become fundamental, and new paradigms emerge that redefine the landscape of information systems. The true value of the Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals certification lies in its role as a launching platform for lifelong learning.
Certified individuals gain the foundation upon which advanced competencies can be built. Many continue their education by pursuing higher-level Microsoft certifications such as Azure Database Administrator Associate or Data Analyst Associate. Others expand horizontally into complementary fields like cybersecurity, data analytics, or cloud infrastructure.
Professional resilience is born from adaptability. The habits developed during certification preparation—discipline, reflection, and analytical rigor—become enduring traits that empower individuals to navigate change with confidence. In the digital age, learning is no longer episodic; it is perpetual.
The Ethical Dimension of Data Stewardship
In the realm of data management, ethics is inseparable from expertise. Administrators and developers hold custodial authority over information that may define lives, reveal identities, and influence decisions. The integrity of these professionals determines the integrity of the systems they maintain.
The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals philosophy encourages practitioners to view their role not merely as technical operators but as stewards of truth. Protecting data from corruption, unauthorized access, and misuse is an act of moral responsibility. Administrators must uphold principles of confidentiality, accuracy, and accountability in every operation.
As organizations increasingly rely on data-driven automation and machine learning, the ethical considerations surrounding bias, privacy, and transparency intensify. Certified professionals must therefore integrate ethical discernment into their daily practice, ensuring that efficiency never compromises humanity.
Employability and Industry Relevance
The modern job market prizes individuals who combine theoretical knowledge with practical capability. Database fundamentals represent a universal skill set that transcends industries. From finance and healthcare to e-commerce and government administration, the demand for data proficiency continues to escalate.
Employers seek candidates who can manage relational systems, understand SQL commands, implement data security, and optimize queries. The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals certification serves as a testament to these abilities. It verifies not only that a candidate has studied but that they have demonstrated mastery under examination.
Moreover, certification enhances career mobility. It enables professionals to transition into roles such as database developer, data analyst, or systems administrator. For those entering the workforce, it provides a competitive edge that distinguishes them from peers. For seasoned professionals, it serves as formal validation of experience accumulated over years of practice.
Integration with Cloud and Modern Data Platforms
The contemporary database ecosystem is increasingly intertwined with cloud-based platforms. Microsoft Azure, in particular, has revolutionized how data is stored, accessed, and managed. Concepts introduced in Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals—such as T-SQL, relational models, and security protocols—find direct application in cloud environments.
Cloud databases introduce additional dimensions of scalability, elasticity, and automation. Administrators must understand not only how to design efficient schemas but also how to distribute workloads across regions, ensure high availability, and implement redundancy. The principles of indexing, normalization, and backup strategies remain relevant but evolve in their execution.
Learning these fundamentals equips professionals to adapt to hybrid architectures that blend on-premises databases with cloud-hosted systems. As organizations continue their digital transformation journeys, certified individuals become indispensable intermediaries between legacy infrastructures and emerging technologies.
The Pedagogy of the Microsoft MTA Database Fundamentals Approach
The educational design behind Microsoft’s database fundamentals curriculum reflects an intricate balance between conceptual clarity and applied practice. The course does not merely deliver content; it cultivates understanding through immersion.
Each topic—from data manipulation to security administration—is presented through incremental exploration. Learners engage with relational models, construct queries, design storage strategies, and manage access controls. Through these exercises, abstract principles are translated into tangible experiences.
The program’s structure emphasizes active engagement. Rather than passively consuming information, learners are encouraged to hypothesize, test, and refine. This iterative process builds confidence and autonomy, transforming instruction into self-discovery.
In an age of superficial learning, this pedagogy reinstates depth. It insists that understanding must precede application and that proficiency arises from repeated, deliberate practice.
Professional Networking and Community Engagement
Certification opens gateways not only to employment but also to community. The global network of Microsoft-certified professionals forms an ecosystem of collaboration, mentorship, and shared advancement. Through forums, conferences, and digital platforms, certified individuals exchange insights, troubleshoot challenges, and participate in collective growth.
Engagement in professional communities strengthens learning retention and exposes practitioners to diverse perspectives. It cultivates a sense of belonging that transforms solitary study into communal progress. Within these circles, knowledge circulates freely, enriched by the experiences of peers who have navigated similar challenges.
The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals credential thus becomes more than an academic symbol; it becomes an identity—a declaration of membership in a global fellowship of data guardians.
Career Advancement and Leadership Pathways
Earning certification marks the beginning of a trajectory toward leadership. As professionals deepen their expertise, they often evolve into roles that blend technical proficiency with strategic vision. Database administrators become architects, analysts become data scientists, and developers ascend into managerial or consultancy positions.
Leadership in data disciplines demands more than technical expertise; it requires foresight, empathy, and communication. Certified professionals learn to articulate complex concepts in accessible language, bridging the gap between technical teams and executive decision-makers.
As they guide projects, design infrastructures, and mentor newcomers, their influence extends beyond systems into the human domain of collaboration and trust. The foundations laid by Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals prepare them for these higher responsibilities, where decision-making impacts entire organizations.
Evaluating Personal Progress and Mastery
Mastery in database fundamentals is not measured by completion alone but by transformation. The process of study, practice, and certification reshapes one’s cognitive architecture. Concepts that once appeared abstract become intuitive; tasks that once required conscious effort become second nature.
Reflection serves as a vital companion to progress. By periodically reviewing one’s learning journey, professionals can identify how their perspectives have evolved and which areas merit further exploration. This metacognitive awareness distinguishes proficient technicians from true masters of their craft.
The discipline encourages a spirit of inquiry that persists long after the examination is passed. Mastery thus becomes not a destination but a perpetual horizon—a state of continuous refinement.
Conclusion
To embark on the path of database mastery through Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals is to engage in an intellectual and moral apprenticeship. It is an immersion into the logic of systems that govern modern civilization and a pledge to uphold the principles of precision, security, and stewardship.
Certification serves as both compass and credential. It validates one’s competence while guiding further exploration into advanced realms of data science, analytics, and architecture. More profoundly, it nurtures qualities that transcend technology—discipline, curiosity, and ethical awareness.
In mastering the fundamentals of relational databases, one gains more than a technical skill; one acquires a lens through which to perceive order in complexity, structure in chaos, and meaning in data. The database professional becomes a custodian of truth within the digital universe, translating information into insight and structure into wisdom.
The journey from learning to mastery, from certification to leadership, reflects the timeless principle that knowledge, once awakened, seeks expression through service. The Microsoft Certified MTA Database Fundamentals qualification is not merely an academic milestone—it is a commitment to excellence, integrity, and perpetual growth in the boundless world of data.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get the products after purchase?
All products are available for download immediately from your Member's Area. Once you have made the payment, you will be transferred to Member's Area where you can login and download the products you have purchased to your computer.
How long can I use my product? Will it be valid forever?
Test-King products have a validity of 90 days from the date of purchase. This means that any updates to the products, including but not limited to new questions, or updates and changes by our editing team, will be automatically downloaded on to computer to make sure that you get latest exam prep materials during those 90 days.
Can I renew my product if when it's expired?
Yes, when the 90 days of your product validity are over, you have the option of renewing your expired products with a 30% discount. This can be done in your Member's Area.
Please note that you will not be able to use the product after it has expired if you don't renew it.
How often are the questions updated?
We always try to provide the latest pool of questions, Updates in the questions depend on the changes in actual pool of questions by different vendors. As soon as we know about the change in the exam question pool we try our best to update the products as fast as possible.
How many computers I can download Test-King software on?
You can download the Test-King products on the maximum number of 2 (two) computers or devices. If you need to use the software on more than two machines, you can purchase this option separately. Please email support@test-king.com if you need to use more than 5 (five) computers.
What is a PDF Version?
PDF Version is a pdf document of Questions & Answers product. The document file has standart .pdf format, which can be easily read by any pdf reader application like Adobe Acrobat Reader, Foxit Reader, OpenOffice, Google Docs and many others.
Can I purchase PDF Version without the Testing Engine?
PDF Version cannot be purchased separately. It is only available as an add-on to main Question & Answer Testing Engine product.
What operating systems are supported by your Testing Engine software?
Our testing engine is supported by Windows. Andriod and IOS software is currently under development.
Top Microsoft Exams
- AZ-104 - Microsoft Azure Administrator
- AI-900 - Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals
- AZ-305 - Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- AI-102 - Designing and Implementing a Microsoft Azure AI Solution
- DP-700 - Implementing Data Engineering Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- MD-102 - Endpoint Administrator
- AZ-900 - Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
- PL-300 - Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst
- MS-102 - Microsoft 365 Administrator
- SC-300 - Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator
- AZ-500 - Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
- SC-200 - Microsoft Security Operations Analyst
- SC-401 - Administering Information Security in Microsoft 365
- AZ-700 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft Azure Networking Solutions
- DP-600 - Implementing Analytics Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- AZ-204 - Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure
- SC-100 - Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect
- PL-200 - Microsoft Power Platform Functional Consultant
- SC-900 - Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals
- AZ-140 - Configuring and Operating Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop
- AZ-400 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
- PL-400 - Microsoft Power Platform Developer
- AZ-800 - Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure
- MS-900 - Microsoft 365 Fundamentals
- DP-300 - Administering Microsoft Azure SQL Solutions
- PL-600 - Microsoft Power Platform Solution Architect
- GH-300 - GitHub Copilot
- AB-730 - AI Business Professional
- MB-280 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Experience Analyst
- AZ-801 - Configuring Windows Server Hybrid Advanced Services
- MS-700 - Managing Microsoft Teams
- PL-900 - Microsoft Power Platform Fundamentals
- MB-330 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
- MB-800 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Functional Consultant
- DP-900 - Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
- AB-100 - Agentic AI Business Solutions Architect
- AB-731 - AI Transformation Leader
- MB-310 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance Functional Consultant
- DP-100 - Designing and Implementing a Data Science Solution on Azure
- MB-820 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Developer
- MS-721 - Collaboration Communications Systems Engineer
- MB-230 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Service Functional Consultant
- GH-900 - GitHub Foundations
- PL-500 - Microsoft Power Automate RPA Developer
- MB-700 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Solution Architect
- MB-500 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Developer
- MB-335 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management Functional Consultant Expert
- GH-200 - GitHub Actions
- MB-240 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Field Service
- DP-420 - Designing and Implementing Cloud-Native Applications Using Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
- GH-500 - GitHub Advanced Security
- GH-100 - GitHub Administration
- AZ-120 - Planning and Administering Microsoft Azure for SAP Workloads
- DP-203 - Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
- SC-400 - Microsoft Information Protection Administrator
- AZ-303 - Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies
- MB-910 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Customer Engagement Apps (CRM)
- 98-383 - Introduction to Programming Using HTML and CSS
- MO-100 - Microsoft Word (Word and Word 2019)
- MB-210 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Sales
- MB-920 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Finance and Operations Apps (ERP)


