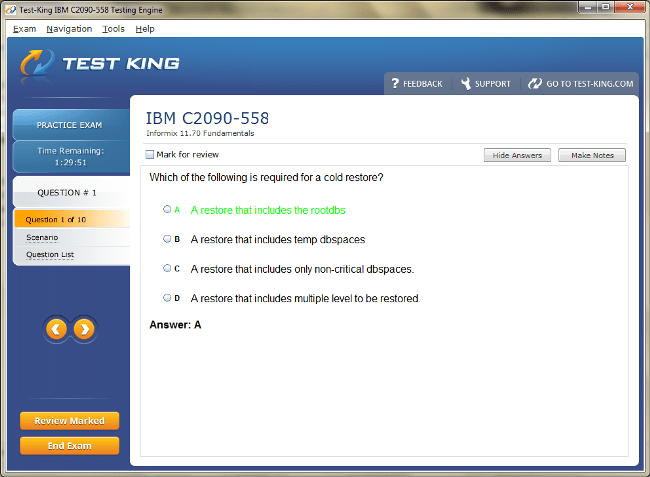
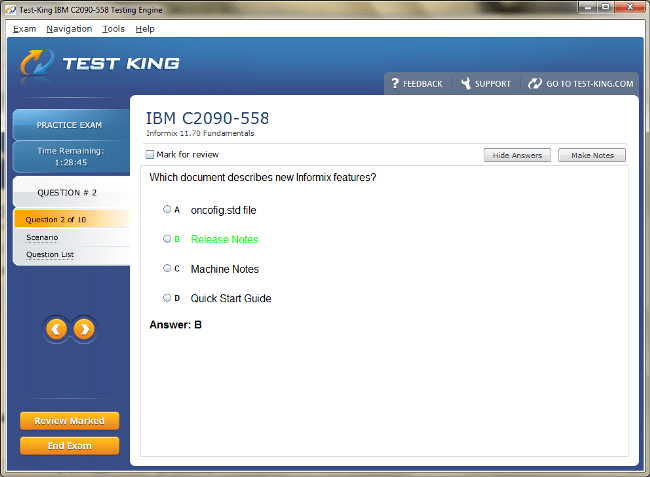
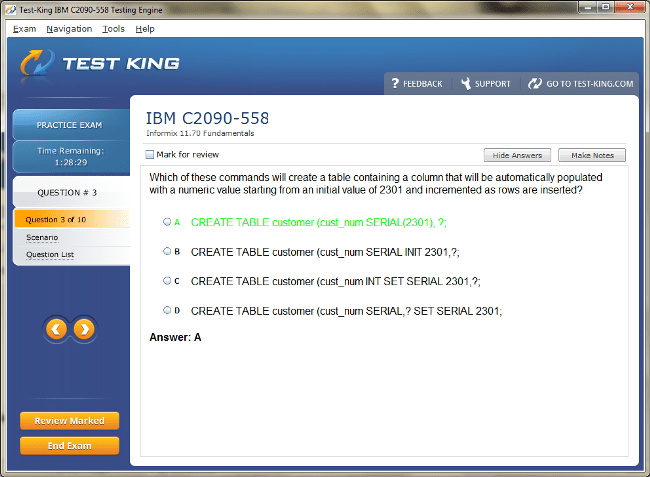
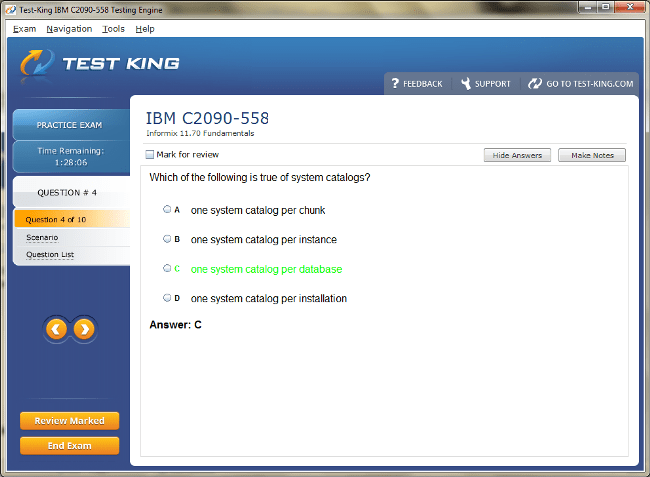
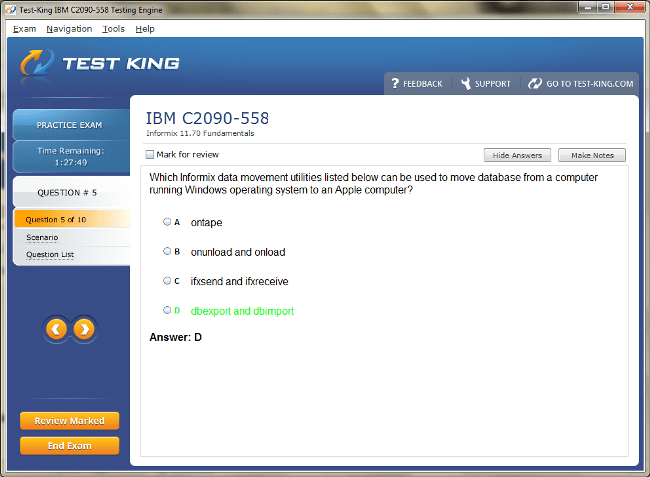
C2090-558 Exam Product Screenshots
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get the products after purchase?
All products are available for download immediately from your Member's Area. Once you have made the payment, you will be transferred to Member's Area where you can login and download the products you have purchased to your computer.
How long can I use my product? Will it be valid forever?
Test-King products have a validity of 90 days from the date of purchase. This means that any updates to the products, including but not limited to new questions, or updates and changes by our editing team, will be automatically downloaded on to computer to make sure that you get latest exam prep materials during those 90 days.
Can I renew my product if when it's expired?
Yes, when the 90 days of your product validity are over, you have the option of renewing your expired products with a 30% discount. This can be done in your Member's Area.
Please note that you will not be able to use the product after it has expired if you don't renew it.
How often are the questions updated?
We always try to provide the latest pool of questions, Updates in the questions depend on the changes in actual pool of questions by different vendors. As soon as we know about the change in the exam question pool we try our best to update the products as fast as possible.
How many computers I can download Test-King software on?
You can download the Test-King products on the maximum number of 2 (two) computers or devices. If you need to use the software on more than two machines, you can purchase this option separately. Please email support@test-king.com if you need to use more than 5 (five) computers.
What is a PDF Version?
PDF Version is a pdf document of Questions & Answers product. The document file has standart .pdf format, which can be easily read by any pdf reader application like Adobe Acrobat Reader, Foxit Reader, OpenOffice, Google Docs and many others.
Can I purchase PDF Version without the Testing Engine?
PDF Version cannot be purchased separately. It is only available as an add-on to main Question & Answer Testing Engine product.
What operating systems are supported by your Testing Engine software?
Our testing engine is supported by Windows. Andriod and IOS software is currently under development.
Top IBM Exams
- C1000-156 - QRadar SIEM V7.5 Administration
- C1000-074 - IBM FileNet P8 V5.5.3 Deployment Professional
- C1000-132 - IBM Maximo Manage v8.0 Implementation
- C1000-150 - IBM Cloud Pak for Business Automation v21.0.3 Administration
- C1000-142 - IBM Cloud Advocate v2
- C1000-194 - IBM Cloud Pak for Business Automation v24.0.0 Solution Architect - Professional
IBM Informix 11.70 Fundamentals (C2090-558): Complete Syllabus Breakdown Exam
The IBM Informix 11.70 Fundamentals examination, identified by the exam code C2090-558, is a foundational certification designed to measure one’s proficiency in working with IBM Informix database environments. This certification validates an individual’s understanding of the essential components that constitute an Informix system, including its architecture, storage mechanisms, SQL operations, and administrative utilities. It represents the preliminary step in a larger continuum of expertise that connects data management, optimization, and application development within the IBM ecosystem.
Understanding the Core Structure and Concepts of IBM Informix 11.70 Fundamentals
Informix 11.70, being a highly adaptive and resilient database platform, emphasizes performance optimization and stability across heterogeneous computing environments. Its architecture is crafted to support continuous availability, minimal downtime, and high scalability, making it ideal for businesses requiring dependable data handling. The fundamentals examination is not just a measure of theoretical comprehension; it also assesses practical awareness of how database components interact to sustain performance and reliability.
The syllabus for this certification delves into several intertwined domains: understanding database concepts, navigating Informix tools, implementing data types, executing SQL operations, managing storage and space allocation, configuring server parameters, monitoring performance, and handling security and user privileges. Each of these domains encapsulates both conceptual frameworks and procedural knowledge essential to administrating or developing within an Informix environment.
At its core, the IBM Informix 11.70 Fundamentals exam seeks to evaluate an individual’s capacity to integrate structured query language proficiency with the operational features of Informix systems. While SQL forms the linguistic backbone of database manipulation, the environment in which it functions—governed by the Informix engine—defines its behavior, speed, and data integrity. Hence, mastering the fundamentals entails more than memorizing syntax; it requires a cognitive assimilation of how Informix interprets, optimizes, and executes instructions within its server landscape.
One of the key expectations in this exam is an understanding of Informix architecture. Informix follows a layered configuration, which encompasses the database server, storage spaces, logs, and communication interfaces. The server core, often referred to as Dynamic Server or IDS, is responsible for managing the logical and physical structure of data. It orchestrates interactions between user requests, SQL commands, and data files while ensuring transactional consistency. The architecture allows the database to maintain durability even during unexpected interruptions, making it a trustworthy platform for enterprise-grade applications.
Within the examination’s syllabus, candidates are expected to possess knowledge of database terminology, such as chunks, dbspaces, sbspaces, and blobspaces. These components represent the physical storage units that underlie the database structure. Understanding how data is segmented across these spaces, and how Informix allocates resources dynamically, is vital to both system performance and space utilization. For instance, dbspaces house standard tables and indexes, while sbspaces and blobspaces are designated for large object storage. Informix distinguishes itself by enabling flexible allocation, allowing databases to expand or redistribute storage with minimal administrative intervention.
In addition to architecture, a crucial aspect of this exam involves the study of system configuration and environment setup. Informix 11.70 operates through a series of configuration files, such as onconfig and sqlhosts, which define system parameters, memory distribution, and connectivity protocols. Candidates preparing for the C2090-558 exam should have an intuitive grasp of how these files interact to shape runtime behavior. For instance, understanding how to tune the buffer pool, adjust log file sizes, or modify CPU virtual processors directly impacts performance outcomes.
Beyond setup, the exam syllabus emphasizes database creation and management. Informix provides multiple command-line tools and utilities, including dbaccess, oninit, and onstat, that allow administrators and developers to interface directly with the server. The dbaccess tool, for example, serves as both a query interface and an administrative console, enabling database creation, schema design, and data manipulation. A candidate must not only be aware of such utilities but also comprehend their context of use. Knowing when to use onmode to manage server modes, or onmonitor to observe activity levels, reflects the applied understanding that this certification seeks to validate.
An equally critical domain within the syllabus concerns SQL fundamentals and data manipulation. The examination expects familiarity with the core SQL operations used in the Informix environment—SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE—along with advanced elements such as joins, subqueries, and set operations. The Informix implementation of SQL adheres to ANSI standards while incorporating proprietary extensions that enhance performance and flexibility. Candidates must also recognize how query optimization occurs internally, such as the role of indexes and the optimizer’s selection of access paths. Understanding how to construct efficient queries, minimize resource overhead, and maintain data integrity forms an indispensable component of exam readiness.
Informix distinguishes itself through its versatile support for data types. Unlike systems that restrict developers to basic numeric or character types, Informix extends its schema definition to include complex and user-defined data types. Candidates are tested on their ability to differentiate between basic types like INTEGER, CHAR, and DATE, and more sophisticated ones such as collections, distinct types, and large objects. Informix also supports spatial and time series data, enabling diverse applications from financial analytics to geographic information systems. Mastery of these data types includes knowing how they are stored, indexed, and retrieved, as well as how their use affects performance.
Transaction management and logging constitute another integral topic in the exam. Informix employs a robust mechanism for ensuring atomicity and durability through logical logs and physical logs. Logical logs record transactional activities, allowing the system to roll back incomplete operations or roll forward committed ones after a failure. Physical logs, on the other hand, capture page-level changes, serving as a complement to logical recovery. Understanding how to monitor, back up, and restore these logs ensures data resilience. Candidates are expected to comprehend the significance of checkpoints, fast recovery, and backup utilities such as ontape and onbar, which facilitate both snapshot-based and incremental backups.
Performance monitoring and tuning form a more advanced area of the syllabus. Informix 11.70 includes a variety of diagnostic tools that allow administrators to observe real-time behavior and historical performance patterns. Commands like onstat provide granular visibility into system resources, lock activity, and buffer usage. Tuning in Informix is both an art and a science, involving the adjustment of configuration parameters such as shared memory size, thread allocation, and I/O distribution. Candidates should understand how to interpret statistical outputs and translate them into practical tuning decisions. For instance, excessive lock contention or slow I/O operations can often be mitigated through intelligent reallocation of resources or query plan refinement.
Security management and user privileges represent another pillar within the IBM Informix 11.70 Fundamentals exam. Informix enforces a layered security model encompassing authentication, authorization, and auditing. Authentication verifies user identities through host-based or server-based mechanisms, while authorization determines the privileges granted to each user or role. Informix allows fine-grained control, enabling administrators to specify access rights at the database, table, or column level. Moreover, the audit subsystem can be configured to record security-related events, ensuring traceability and compliance. Understanding how to create users, assign roles, and safeguard data through access control mechanisms is crucial to maintaining an uncompromised environment.
In the context of client connectivity, Informix employs network protocols and configuration files that dictate how applications communicate with the server. The sqlhosts file defines connectivity options such as server names, protocols, and host addresses. Candidates should understand how to configure these settings for local and remote clients and how connectivity parameters influence performance and reliability. Additionally, awareness of the Informix Client Software Development Kit (CSDK) helps bridge the gap between database administration and application development.
Storage management within Informix is another domain that demands close attention. The system organizes its physical storage through chunks, which are continuous spaces on disk assigned to dbspaces or blobspaces. Understanding how to create, extend, and monitor these storage units helps ensure optimal resource utilization. Informix also implements automatic space expansion, enabling the server to add chunks dynamically as space runs low. Candidates should appreciate the interplay between physical design and logical schema, recognizing how storage layout affects I/O efficiency.
An often-overlooked yet important area in the syllabus is data integrity and constraints. Informix supports primary keys, foreign keys, unique constraints, and check constraints, each contributing to maintaining consistency and validity. The database engine enforces these constraints automatically during data operations, preventing anomalies such as duplicate entries or orphaned records. The exam expects a conceptual understanding of when to apply each constraint type, how constraints influence performance, and how they interact with transactional operations.
Informix’s approach to indexing and query optimization also forms part of the core syllabus. Indexes accelerate data retrieval by maintaining ordered structures that guide the optimizer. Informix supports B-tree, functional, and R-tree indexes, among others. Knowing when to use each type and how to manage index fragmentation or rebuilding is essential for sustaining long-term efficiency. The optimizer itself is cost-based, meaning it evaluates multiple access paths and chooses the most efficient execution plan. Understanding how statistics, distribution histograms, and update frequencies influence optimizer decisions enables candidates to interpret and enhance query behavior.
Another area of focus is the management of database objects, such as tables, views, synonyms, and sequences. Informix provides tools for creating and modifying these objects dynamically. The syllabus requires familiarity with how each object functions and interacts with others. Views, for example, allow developers to abstract complex queries into reusable entities, while synonyms simplify access by providing alternate names for objects. Sequences generate unique numeric identifiers, supporting primary key generation in high-transaction environments.
In the domain of data loading and unloading, Informix incorporates utilities that facilitate bulk operations. The dbload and dbunload tools allow administrators to import and export data efficiently, making them essential during migrations or backup processes. Understanding the syntax, options, and best practices for using these tools is part of the practical knowledge expected in the exam. Furthermore, awareness of how these operations affect locking, logging, and transaction control is indispensable for maintaining system stability during large-scale data movement.
The syllabus also touches upon replication and high-availability mechanisms. Informix 11.70 includes features such as High-Availability Data Replication (HDR), Remote Secondary Servers, and Enterprise Replication. These technologies enable organizations to achieve redundancy and load distribution across multiple servers. Candidates should understand the conceptual framework behind replication, how data synchronization occurs, and what roles primary and secondary servers play. Although this exam focuses on fundamentals rather than advanced configuration, having a foundational comprehension of replication principles reflects a more holistic grasp of the Informix environment.
Informix’s extensibility is another theme present in the examination scope. Through the use of DataBlades, Informix allows developers to integrate custom data types, routines, and access methods into the database engine. This modularity enhances its ability to handle specialized applications such as spatial analysis or time-series processing. Candidates should be aware of how extensibility enhances flexibility without compromising stability or performance.
Finally, system maintenance and troubleshooting are integral to the exam’s syllabus. Informix administrators are often required to identify and resolve performance bottlenecks, connectivity failures, or configuration errors. Understanding how to interpret error logs, analyze core dumps, and recover from abnormal terminations ensures operational continuity. The examination evaluates a candidate’s ability to apply logical reasoning to diagnose problems and implement corrective actions.
Through this comprehensive exploration, the IBM Informix 11.70 Fundamentals (C2090-558) exam emphasizes both conceptual depth and applied understanding. It challenges candidates to demonstrate not only memory of commands or syntax but also their capacity to interpret system behavior and anticipate interactions between components. The Informix environment, with its balance of robustness and adaptability, represents a paradigm where theoretical knowledge and real-world application converge.
Enhancing System Performance and Ensuring High Availability in IBM Informix 11.70
In the realm of IBM Informix 11.70, system performance and high availability constitute critical competencies that candidates must master for the C2090-558 examination. Beyond fundamental comprehension of database structures, storage mechanisms, and SQL operations, advanced configuration entails a thorough understanding of resource allocation, server tuning, and fault-tolerant strategies. Informix provides an intricate yet coherent framework for administering high-performance environments, enabling administrators and developers to harness the platform’s capabilities to their fullest extent. The certification emphasizes not only knowledge but also practical foresight, ensuring that database professionals can anticipate system behavior under varying workloads.
One of the foremost aspects of advanced configuration is memory management. Informix allocates multiple memory pools, including the shared memory pool, sort memory, and buffer pools, each playing a specialized role in query processing and transaction management. The shared memory pool acts as the central repository for locks, caches, and system information, while buffer pools store frequently accessed data pages, enhancing retrieval speed. Sort memory is employed when complex operations, such as order-by clauses or multi-table joins, require temporary storage. Candidates must comprehend how to analyze memory usage and adjust parameters to mitigate bottlenecks and optimize throughput. Misconfigured memory can result in contention, excessive paging, or suboptimal execution plans, which directly affect transactional latency and server responsiveness.
Disk storage configuration is another domain of significance. Informix uses chunks as the fundamental unit of physical storage, which are then organized into dbspaces and blobspaces. Proper allocation and alignment of chunks influence I/O efficiency and minimize fragmentation. Administrators are expected to monitor free space, extend dbspaces proactively, and redistribute data when necessary to maintain performance consistency. The interplay between physical layout and logical schema dictates data accessibility, and understanding this relationship is crucial for sustaining large-scale operations. Informix also supports automatic storage expansion, a feature that allows the system to dynamically add chunks as the database grows, reducing the need for continuous manual intervention.
Logging and recovery mechanisms form a cornerstone of reliable operations. Informix maintains logical logs that record transactional activity, providing the ability to roll back incomplete transactions and recover committed ones. Physical logs complement this by capturing low-level page changes, ensuring durability in the event of abrupt interruptions. Candidates are expected to know how to configure log file sizes, monitor usage, and schedule routine backups. The examination evaluates awareness of checkpoints, which are synchronization points that consolidate in-memory changes with disk storage, reducing recovery time after failures. Effective use of logical and physical logs safeguards data integrity while facilitating rapid restoration in diverse operational scenarios.
High availability in Informix is reinforced through mechanisms such as High-Availability Data Replication (HDR), Remote Secondary Servers, and Enterprise Replication. HDR ensures continuous synchronization between a primary server and a standby server, providing automatic failover capabilities in case of primary system failure. Remote Secondary Servers enable replication across geographically dispersed environments, enhancing disaster recovery preparedness. Enterprise Replication allows selective data synchronization across multiple nodes, supporting distributed applications that require consistency and resilience. Understanding the nuances of each method, including their strengths and constraints, is integral for maintaining uninterrupted service. Candidates should grasp not only configuration procedures but also monitoring strategies to detect synchronization lags, network interruptions, or server discrepancies.
Performance tuning is closely associated with system monitoring. Informix provides tools that deliver insights into CPU utilization, lock contention, buffer usage, and I/O throughput. The onstat utility, for instance, presents a real-time snapshot of active processes, transaction states, and memory allocation. Administrators can use this information to identify performance bottlenecks, such as long-running queries, excessive page reads, or uneven workload distribution. Performance tuning extends to adjusting configuration parameters, including thread count, buffer size, and page size, to match the demands of concurrent users. Candidates must understand the principles behind these adjustments, recognizing that small modifications can yield significant improvements in overall efficiency.
The SQL optimizer plays a pivotal role in query execution and performance management. Informix’s cost-based optimizer evaluates multiple access paths and selects the most efficient execution plan. Factors influencing this choice include index availability, data distribution, join strategies, and the complexity of predicates. Candidates must be able to interpret optimizer outputs and understand how table statistics, histograms, and sampling influence execution plans. For example, poorly maintained statistics can mislead the optimizer, resulting in suboptimal joins or sequential scans. Knowledge of indexing strategies, including B-tree, functional, and R-tree indexes, allows administrators to guide the optimizer toward faster query paths. Additionally, understanding when to use temporary tables or materialized views can enhance performance for complex analytical operations.
Locking and concurrency control are central themes in high-performance Informix systems. The server employs sophisticated mechanisms to ensure transactional consistency while allowing multiple users to access shared resources. Shared locks, exclusive locks, and intent locks regulate access to rows, tables, or pages, preventing conflicts and maintaining data integrity. Deadlocks, which occur when two transactions block each other indefinitely, must be detected and resolved efficiently. Candidates are expected to understand how locking strategies, isolation levels, and transaction boundaries affect system behavior. Proper management of concurrency not only prevents anomalies but also optimizes throughput in multi-user environments.
Indexing strategies are closely linked with performance optimization. Informix allows the creation of multiple index types, each suitable for different query patterns. B-tree indexes are ideal for ordered searches and equality conditions, while R-tree indexes support spatial data queries. Functional indexes accelerate operations on computed expressions. Understanding the impact of index selection, fragmentation, and maintenance on query performance is crucial. Candidates must recognize that indexing improves read efficiency but can introduce overhead during insertions, updates, or deletions, necessitating a balanced approach to schema design.
Space management remains an ongoing responsibility. Informix dbspaces can be extended by adding chunks, allowing the database to grow without disrupting operations. Administrators must monitor free space thresholds and plan expansions proactively. Blobspaces, dedicated to large objects, require similar attention to avoid fragmentation and I/O bottlenecks. Informix provides system tables and utilities to monitor space usage, track allocation trends, and generate alerts when thresholds are approached. Candidates should understand how to integrate space management with backup strategies to ensure consistency and availability.
Backup and recovery strategies form an essential component of high availability. Informix provides multiple options for safeguarding data, including full backups, incremental backups, and logical unloads. The ontape and onbar utilities facilitate both offline and online backups, allowing administrators to protect data without disrupting active transactions. Candidates must be familiar with recovery procedures, including restoring databases from backups, applying logical logs, and verifying data consistency post-restoration. The ability to orchestrate a reliable backup and recovery plan is a hallmark of proficient Informix administration.
Monitoring and alerting systems enable proactive maintenance. Informix can be configured to send alerts based on thresholds for CPU usage, disk space, transaction time, or replication lag. Tools such as onstat and onmonitor allow administrators to examine system health, detect anomalies, and anticipate potential failures. By understanding how to interpret these metrics, candidates can implement corrective actions before issues escalate, preserving both performance and availability.
Security within high-availability environments also deserves attention. Informix enforces access controls at multiple levels, ensuring that replication processes, backups, and administrative operations are performed securely. User privileges must be managed carefully to prevent unauthorized access to critical functions. Authentication mechanisms, including server-based or host-based validation, coupled with audit trails, enable administrators to maintain accountability and traceability. Candidates should comprehend the implications of security policies on replication, backups, and overall system resilience.
Replication scenarios necessitate awareness of network behavior and latency. HDR and remote replication rely on stable connections between primary and secondary nodes. Network interruptions or bandwidth limitations can introduce lag, impacting data consistency. Administrators must monitor replication queues, identify delays, and implement optimizations such as compression or batch updates. Candidates should understand the trade-offs between synchronous and asynchronous replication, balancing the need for immediacy with performance efficiency.
Informix 11.70 also offers extensibility options that intersect with optimization and availability. DataBlades, which allow integration of specialized data types, routines, and access methods, must be configured carefully to avoid performance degradation. While DataBlades enhance capabilities, they introduce additional load on memory and CPU resources. Candidates must consider the implications of custom modules in high-performance environments, ensuring that enhancements do not compromise system stability.
Automation and scheduling enhance operational efficiency. Informix supports event scheduling for routine tasks such as statistics collection, backups, and maintenance operations. By automating repetitive tasks, administrators can reduce human error and optimize resource utilization. Candidates should be familiar with how scheduled tasks integrate with performance monitoring, replication, and storage management, creating a cohesive ecosystem that sustains both availability and responsiveness.
Troubleshooting remains a continuous responsibility. Even well-tuned systems encounter unexpected behaviors, ranging from slow query execution to replication inconsistencies. Candidates must be adept at diagnosing issues using available utilities, interpreting error messages, analyzing logs, and isolating root causes. Effective troubleshooting often combines observational acuity with analytical reasoning, ensuring that corrective measures restore both performance and reliability promptly.
Data integrity under high workload conditions is another focal point. Informix ensures that transactional consistency is maintained through ACID principles, even when replication, backup, and high-concurrency operations occur simultaneously. Candidates must understand how isolation levels, lock management, and recovery procedures interact to prevent anomalies such as lost updates or dirty reads. Awareness of these interactions underpins informed decision-making regarding performance tuning and system configuration.
Finally, capacity planning ties together all aspects of advanced Informix administration. Candidates should be able to forecast storage needs, evaluate growth trends, and anticipate resource demands based on usage patterns. By aligning configuration parameters, memory allocation, indexing strategies, and replication mechanisms with projected workloads, administrators ensure that the database environment remains both performant and resilient under varying conditions.
The examination tests not only the retention of technical concepts but also the candidate’s ability to apply these principles in practical scenarios. The combination of advanced configuration, optimization, and high-availability strategies underscores the multifaceted nature of IBM Informix 11.70 Fundamentals, preparing professionals to manage enterprise-grade database systems with competence, foresight, and agility.
Safeguarding Data, Managing Access, and Ensuring Connectivity in IBM Informix 11.70
Within the IBM Informix 11.70 environment, the interplay of security management, user privileges, replication strategies, and client connectivity forms a crucial domain for candidates preparing for the C2090-558 examination. Beyond foundational knowledge of database architecture and performance optimization, a competent professional must grasp how to protect sensitive information, administer user roles, configure replication mechanisms, and establish reliable client-server communication. Informix provides an integrated ecosystem where security and accessibility coexist, supporting robust, scalable, and high-availability systems suitable for enterprise applications.
Security management in Informix is designed to enforce data confidentiality, integrity, and accountability. The system employs multiple layers of protection, encompassing authentication, authorization, and auditing. Authentication verifies the identity of users attempting to access the database. Informix supports host-based authentication, which validates users through the operating system, and server-based authentication, which relies on credentials maintained within the database. A candidate must understand the implications of each method, recognizing how they affect login procedures, password policies, and integration with external security frameworks. In addition to basic verification, Informix allows the use of complex password rules, expiration policies, and encryption mechanisms to enhance resilience against unauthorized access.
Authorization, the next tier in security, governs what users can do once authenticated. Informix employs a granular privilege system, enabling administrators to grant or revoke permissions at the database, table, column, or routine level. Users may receive roles that bundle multiple privileges, simplifying administration while maintaining control over sensitive operations. For example, a role might provide read-only access to certain financial tables while allowing full insert and update permissions in operational datasets. Candidates must understand how privilege hierarchies function, how they propagate through dependent objects, and how to avoid over-privileging, which can inadvertently compromise security.
Auditing complements authentication and authorization by providing traceability of user activity. Informix’s audit subsystem can be configured to record actions such as logins, table modifications, and administrative changes. This creates a permanent record that can be used for compliance verification, forensic investigation, or performance review. Candidates should be familiar with enabling audit trails, interpreting logs, and generating reports that highlight anomalies or unauthorized attempts. Auditing serves a dual purpose: ensuring compliance with organizational policies and providing insight into potential operational inefficiencies or security gaps.
User account management is closely tied to privilege administration. Creating, modifying, and deactivating user accounts is a fundamental responsibility of the Informix administrator. Each account must be associated with appropriate roles, group memberships, and authentication requirements. In larger environments, managing numerous accounts demands strategic planning, including the periodic review of permissions, password rotations, and role adjustments. Candidates are expected to appreciate that effective account management prevents security breaches, reduces administrative overhead, and enhances overall system integrity.
Replication in Informix 11.70 is a critical mechanism for both high availability and data protection. The system offers High-Availability Data Replication (HDR), Remote Secondary Servers, and Enterprise Replication. HDR provides real-time duplication between a primary and standby server, ensuring minimal downtime in case of failure. Remote Secondary Servers extend replication across geographically dispersed locations, enabling disaster recovery strategies that can withstand local outages. Enterprise Replication allows selective synchronization of specific tables or subsets of data, supporting distributed applications and data consolidation. Candidates must understand the operational differences between these replication modes, including their impact on performance, network bandwidth, and consistency guarantees.
Configuring replication requires meticulous attention to server settings, network reliability, and data integrity. HDR replication, for instance, relies on transaction logs to propagate committed changes from the primary to the standby server. Any lag or interruption in the replication stream can result in data discrepancies, making continuous monitoring essential. Administrators must be able to analyze replication queues, identify bottlenecks, and implement corrective actions to maintain synchronization. Understanding the nuances of synchronous versus asynchronous replication, as well as the trade-offs between immediacy and throughput, is vital for informed decision-making.
Replication also intersects with security considerations. Replication channels must be secured to prevent unauthorized interception or tampering. Informix supports encrypted replication streams and access controls for replication accounts, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected during transmission. Candidates should comprehend how to combine encryption, authentication, and role-based access control to safeguard replicated data while preserving performance efficiency.
Client connectivity represents another crucial dimension of Informix administration. Effective communication between applications and the database server is essential for operational reliability and responsiveness. Informix uses the sqlhosts file to define server names, protocols, host addresses, and service ports. Understanding the configuration of this file, including the nuances of protocol selection such as shared memory, TCP/IP, or SDP (Sockets Direct Protocol), enables administrators to optimize network interactions. Candidates must also recognize the implications of client connectivity on performance, latency, and concurrent session management.
The Informix Client Software Development Kit (CSDK) further expands connectivity options. CSDK provides APIs and libraries that allow applications to communicate with the database in various programming languages, including Java, C, and .NET environments. Awareness of CSDK capabilities, connection pooling, and transaction handling ensures that applications interact efficiently with the server while minimizing resource consumption. Candidates should appreciate how proper client configuration complements server tuning and replication strategies, contributing to a cohesive, high-performing ecosystem.
Security within client-server interactions extends beyond mere connectivity. Encryption protocols, secure sockets, and authentication mechanisms are vital to protecting data in transit. Informix supports SSL/TLS encryption for client connections, enabling the safeguarding of sensitive information across networks. Administrators must ensure that certificates are properly managed, verified, and periodically updated to maintain trustworthiness. Candidates are expected to understand the interplay between secure connections, authentication credentials, and replication integrity, recognizing that vulnerabilities in client communication can compromise the entire system.
Informix also allows fine-grained control over session management and resource allocation for connected clients. Administrators can set limits on concurrent sessions, memory usage, and query execution time, preventing individual applications from monopolizing server resources. This capacity to regulate access is essential in multi-tenant or high-concurrency environments, where performance degradation can occur rapidly. Candidates should understand how to monitor active sessions, identify long-running transactions, and implement measures to maintain balanced resource utilization.
The management of transactions within connected clients is equally important. Informix ensures that operations adhere to ACID principles, maintaining atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability. Clients must be aware of transaction boundaries, commit and rollback procedures, and isolation levels to avoid anomalies such as dirty reads or lost updates. Administrators must guide developers in implementing best practices that leverage Informix transaction management effectively. Understanding the interactions between client applications, server processes, and replication mechanisms enables candidates to ensure both data integrity and system responsiveness.
Replication, security, and client connectivity converge in high-availability and disaster recovery scenarios. Administrators must coordinate these elements to maintain uninterrupted service while protecting sensitive information. For instance, during a failover from primary to standby servers, client connections must be redirected seamlessly, replication streams must resume without loss, and user privileges must remain intact. Candidates are expected to appreciate these orchestration challenges and understand how Informix provides tools and configurations to manage such transitions gracefully.
Monitoring and troubleshooting encompass all aspects of security, replication, and connectivity. Informix provides utilities and system tables that allow administrators to observe authentication attempts, replication status, session activity, and resource utilization. Candidates must develop the analytical skills to interpret logs, detect anomalies, and implement corrective actions. For example, repeated authentication failures may indicate attempted breaches, while replication lag could signal network instability or misconfiguration. The ability to correlate disparate observations into actionable insights is a hallmark of competent Informix administration.
Advanced topics within this domain include handling large-scale distributed systems and multi-node replication topologies. Enterprise Replication allows multiple servers to synchronize subsets of data asynchronously, requiring careful configuration to prevent conflicts and ensure data consistency. Conflict resolution strategies, such as last-update-wins or timestamp-based reconciliation, must be understood conceptually to maintain coherent datasets across multiple nodes. Candidates should be familiar with the principles underlying replication conflict detection, resolution policies, and their impact on performance and data integrity.
Security policies must also account for evolving compliance requirements. Regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA impose strict guidelines on data handling, retention, and access control. Informix administrators must ensure that authentication, authorization, and auditing procedures align with these mandates. Candidates should be aware of how role-based access control, encryption, and audit logging can facilitate compliance, providing both operational security and regulatory assurance.
In distributed environments, network latency, bandwidth limitations, and failover behavior must be factored into both replication and client connectivity planning. Administrators need to balance the desire for real-time replication with the practical constraints of network infrastructure. Understanding how Informix manages replication queues, transaction batching, and error recovery is essential for maintaining high availability without sacrificing performance. Candidates are expected to conceptualize these dynamics and anticipate potential issues before they affect operational continuity.
Session security and isolation play a vital role in multi-user systems. Informix ensures that concurrent sessions operate independently, respecting user privileges and maintaining transactional boundaries. Candidates must understand how to configure session parameters, monitor active users, and enforce limits to prevent resource contention or inadvertent privilege escalation. Maintaining session integrity is fundamental to both performance and security, ensuring that users can operate efficiently without compromising the broader environment.
Finally, the integration of security, replication, and connectivity into a cohesive operational strategy reflects the holistic approach promoted by the IBM Informix 11.70 Fundamentals exam. Candidates must appreciate the interdependencies between these domains, recognizing that changes in one area can influence performance, availability, and reliability in another. By mastering these concepts, administrators and developers are equipped to design, implement, and maintain Informix environments that are resilient, secure, and optimized for enterprise workloads.
Mastering Data Interaction and Performance in IBM Informix 11.70
In the IBM Informix 11.70 environment, the manipulation of data, execution of SQL operations, strategic indexing, application of constraints, and query optimization constitute indispensable knowledge for candidates preparing for the C2090-558 examination. Mastery of these components ensures that database professionals can efficiently manage, retrieve, and safeguard information while sustaining system performance and integrity. The database engine provides a sophisticated framework where logical structure, physical storage, and transactional operations intersect, requiring both conceptual understanding and practical skill.
Data manipulation forms the foundational pillar for working effectively within Informix. The core operations, including inserting, updating, deleting, and retrieving data, are executed through structured query language commands that the database engine interprets and processes. While the syntax may appear straightforward, the underlying execution involves intricate mechanisms such as lock acquisition, transaction logging, buffer management, and index utilization. Candidates must comprehend not only the commands themselves but also the system processes they trigger, as these interactions affect performance, concurrency, and recovery.
The insert operation allows new records to be added to a table while maintaining data integrity. Informix enforces constraints during insertion, ensuring that primary keys, unique constraints, and foreign key relationships are honored. The update operation modifies existing data, often necessitating careful consideration of indexes and triggers to prevent unintended side effects. Deleting data requires similar attention, as cascading deletions, referential integrity checks, and trigger executions can propagate changes across multiple tables. Understanding these operations in the context of transactional boundaries and recovery mechanisms is essential for accurate and efficient data management.
Retrieving data is achieved primarily through the select command, which can range from simple queries to complex joins, subqueries, and aggregations. Informix supports multiple join types, including inner joins, outer joins, and self-joins, enabling the combination of data from related tables. Subqueries allow nested operations that provide intermediate results for filtering or computation. Aggregation functions, including sum, average, minimum, maximum, and count, permit analytical operations on grouped data. Candidates must understand how query structure, indexing, and join strategies influence execution plans and performance.
Indexing is integral to efficient data retrieval and query optimization. Informix allows various types of indexes, such as B-tree, functional, and R-tree, each suited to specific data and query patterns. B-tree indexes facilitate ordered access and equality comparisons, functional indexes accelerate computed expressions, and R-tree indexes support spatial data queries. Candidates should comprehend the implications of index selection on query performance, the impact of index maintenance during insertions, updates, and deletions, and the trade-offs between storage consumption and retrieval speed. Strategic indexing enhances performance while balancing resource utilization across the system.
Constraints play a pivotal role in enforcing data integrity within Informix databases. Primary keys uniquely identify records within a table, ensuring that no duplicates exist. Foreign keys maintain referential integrity between related tables, preventing orphaned records. Unique constraints guarantee that specific columns contain distinct values, while check constraints impose conditions on column values, enforcing business rules. Informix evaluates constraints during data manipulation operations, integrating enforcement with transaction management to ensure consistency. Candidates are expected to understand the purpose and implementation of constraints, as well as how they interact with transactional behavior, indexing, and query optimization.
Query optimization represents a sophisticated domain where Informix demonstrates its intelligence. The cost-based optimizer evaluates multiple access paths for executing a query, considering factors such as available indexes, data distribution, join strategies, and predicate complexity. Candidates must be able to interpret optimizer outputs, recognize inefficient plans, and understand how schema design, statistics, and indexing influence execution. Proper query design, combined with an understanding of how the optimizer selects paths, ensures both rapid data retrieval and minimal resource consumption. For example, appropriate indexing can transform a full table scan into a targeted index lookup, dramatically reducing I/O operations.
Statistics play a vital role in guiding the optimizer. Informix collects data distribution information, histograms, and table cardinality metrics to estimate costs associated with various execution strategies. Candidates must understand how maintaining up-to-date statistics improves optimizer accuracy and leads to better query performance. Ignoring statistics can result in suboptimal execution plans, excessive resource usage, and longer query times. Regularly updating statistics as part of database maintenance is a best practice that integrates closely with performance optimization efforts.
The execution of complex SQL operations, including joins, subqueries, unions, and set operations, requires a nuanced understanding of how Informix manages memory, locks, and temporary storage. Join operations, for instance, involve combining data from multiple tables based on specified conditions. The choice of join strategy, whether nested-loop, merge, or hash join, is determined by the optimizer and influenced by indexes, table size, and data distribution. Subqueries provide intermediate results that can be used in filtering, aggregation, or computation. Candidates must recognize how execution strategies, resource allocation, and query complexity impact performance and concurrency.
Aggregation and grouping operations are essential for analytical tasks within Informix. The group by clause allows data to be categorized into meaningful subsets, enabling aggregation functions to compute summaries for each group. Having clause conditions further refine these subsets, filtering aggregated results based on specified criteria. Candidates should understand the impact of grouping and aggregation on memory usage, temporary storage, and query optimization, particularly in large datasets or high-concurrency environments.
Advanced indexing techniques support complex queries and specialized data types. Functional indexes, for example, precompute expressions or transformations on column data, accelerating queries that involve computations. R-tree indexes facilitate spatial operations, such as proximity searches or geometric intersections, crucial for applications in geospatial analysis or scientific research. Candidates must appreciate how these specialized indexes interact with the optimizer, affecting execution plans and resource allocation. The careful application of indexing strategies ensures that queries remain performant even under demanding workloads.
Constraints interact closely with data manipulation and indexing. The enforcement of primary keys and unique constraints may necessitate index maintenance, while foreign key constraints can trigger cascading operations across related tables. Check constraints provide a mechanism to enforce domain-specific rules, ensuring that business logic is preserved at the database level. Candidates should recognize how constraints influence query execution, impact performance, and contribute to overall data integrity, integrating this understanding into both schema design and operational practices.
Transactions encompass the coordination of multiple data manipulation operations into a single atomic unit. Informix ensures that transactions adhere to ACID principles, maintaining consistency, isolation, and durability even in the presence of concurrent operations or system failures. Candidates must comprehend how transaction boundaries, isolation levels, and locking mechanisms influence query execution, concurrency control, and performance. Proper transaction management prevents anomalies such as dirty reads, phantom reads, or lost updates, ensuring that database operations remain reliable and predictable.
Optimization extends beyond query design to include physical schema considerations. The distribution of tables across dbspaces, the placement of indexes, and the organization of large objects influence I/O patterns, memory usage, and transaction throughput. Candidates should understand how physical design decisions impact execution strategies, particularly in environments with high transaction volumes or complex analytical workloads. Effective schema design, informed by both logical and physical considerations, enhances system efficiency and maintains responsiveness under varied conditions.
Data retrieval strategies incorporate considerations of caching, temporary storage, and execution plan reuse. Informix may utilize memory buffers, temporary tables, or in-memory sorting to accelerate query execution. Candidates must understand how these mechanisms operate, how to monitor their impact on performance, and how to adjust configurations to optimize resource utilization. Knowledge of these subtleties ensures that queries execute efficiently while maintaining the integrity and stability of the database system.
Complex operations such as nested subqueries, correlated subqueries, and set-based transformations highlight the sophistication of Informix query processing. Nested subqueries provide intermediate results that feed into outer queries, while correlated subqueries reference columns from enclosing queries, introducing dependencies that affect execution order. Set-based operations, including union, intersect, and minus, enable the combination or comparison of multiple datasets. Candidates must appreciate how these constructs influence execution plans, memory consumption, and performance optimization.
Informix also supports stored procedures, triggers, and user-defined functions, which integrate with data manipulation and optimization strategies. Stored procedures allow precompiled, reusable logic to be executed on the server, reducing network traffic and improving execution speed. Triggers automatically respond to data changes, enforcing business rules or maintaining derived data. User-defined functions extend the capabilities of SQL, allowing custom computations and transformations. Candidates should understand how these programmable objects interact with queries, constraints, transactions, and indexes, and how they can enhance both efficiency and maintainability.
Monitoring query performance involves interpreting execution plans, analyzing I/O patterns, and assessing resource consumption. Informix provides utilities that reveal the steps taken to execute a query, the cost associated with each operation, and the estimated versus actual performance metrics. Candidates must develop the ability to read and interpret these outputs, identify inefficiencies, and implement corrective measures. Optimization is an iterative process, balancing query complexity, indexing strategies, and system resources to achieve consistent and predictable performance.
Data manipulation, SQL operations, indexing, constraints, and optimization collectively define the operational competence expected for the IBM Informix 11.70 Fundamentals examination. Candidates must integrate these concepts, understanding how they interrelate and influence the overall behavior of the database system. Mastery of these areas ensures that administrators and developers can manage complex datasets efficiently, enforce data integrity, and maintain high-performance operations even under demanding workloads.
Managing Database Objects, Storage, and System Reliability in IBM Informix 11.70
The IBM Informix 11.70 environment provides a comprehensive ecosystem for managing database objects, overseeing storage allocation, executing backup and recovery strategies, and monitoring performance for optimal efficiency. Candidates preparing for the C2090-558 examination are expected to understand the intricate interplay between logical schema design, physical storage management, and operational continuity. Mastery of these domains enables administrators and developers to ensure reliability, scalability, and responsiveness in complex enterprise systems, while sustaining data integrity and availability.
Database objects constitute the fundamental units of logical organization within Informix. Tables, which store structured data, are central to all operations. Each table is defined by columns, data types, and constraints that enforce business rules and maintain integrity. Views provide virtual representations of data, allowing users to simplify query operations and encapsulate complex logic. Synonyms serve as alternate names for existing objects, facilitating easier access or abstraction for applications. Sequences generate unique numeric identifiers, commonly used for primary keys, ensuring that inserted records maintain distinct identities. Understanding the creation, management, and interrelationships of these objects is essential for efficient database design and administration.
Indexes support the accessibility and performance of database objects. By creating B-tree, functional, or R-tree indexes on tables, administrators can optimize data retrieval operations. B-tree indexes enhance ordered access and equality searches, functional indexes accelerate queries based on computed expressions, and R-tree indexes support multidimensional or spatial data queries. Indexes must be maintained carefully, as insertions, updates, and deletions can fragment or degrade their efficiency over time. Candidates must appreciate how indexing influences query execution plans, resource utilization, and transaction performance, balancing read efficiency with the cost of maintaining index structures.
Storage management is critical for sustaining performance and accommodating growth. Informix organizes storage through dbspaces, which consist of chunks that represent contiguous disk regions allocated to the database. Blobspaces handle large objects, separating them from standard tables to optimize I/O performance. The allocation, extension, and monitoring of dbspaces are vital tasks for maintaining system stability. Administrators must anticipate growth, redistribute chunks when necessary, and ensure that storage resources are not overcommitted. Informix’s automatic space expansion feature enables dynamic addition of chunks, reducing manual intervention while preserving continuity of operations.
Proper storage management also requires attention to fragmentation, free space, and distribution of objects. Informix maintains metadata about allocated and free space, allowing administrators to monitor usage trends and forecast capacity requirements. Candidates should understand how the physical layout of tables and indexes affects disk I/O patterns, memory usage, and query performance. Strategic placement of objects and periodic maintenance, such as reorganizing tables or rebuilding indexes, ensures consistent performance and minimizes resource contention.
Backup and recovery mechanisms are integral to maintaining data integrity and operational continuity. Informix provides utilities such as ontape and onbar, supporting both online and offline backup operations. Full backups capture the entire database, while incremental backups record only changes since the last backup, optimizing storage and reducing downtime. Logical unloads allow data to be exported in a portable format, facilitating migrations or archiving. Candidates must understand how to design backup schedules, select appropriate backup types, and verify backup integrity to safeguard against data loss or corruption.
Recovery procedures leverage backup sets, logical logs, and physical logs to restore the database to a consistent state following failures. Logical logs record transactional changes, enabling roll-forward or roll-back operations, while physical logs capture page-level modifications. Checkpoints ensure that in-memory data is periodically synchronized with disk storage, reducing recovery times. Candidates must be adept at coordinating these mechanisms, interpreting recovery scenarios, and applying appropriate restoration steps based on the type of failure or disaster.
Performance monitoring provides continuous insight into system health, workload distribution, and resource utilization. Informix supplies utilities such as onstat and onmonitor to observe active transactions, session activity, lock contention, memory usage, and buffer pool efficiency. Understanding how to interpret these metrics enables administrators to identify bottlenecks, assess capacity, and implement proactive optimizations. For instance, excessive lock contention may indicate poorly designed queries or transactional conflicts, while high buffer pool miss ratios suggest insufficient memory allocation. Candidates should develop the analytical skills to translate performance data into practical tuning actions.
Transaction management intersects with performance monitoring, ensuring that operations maintain ACID principles while optimizing resource consumption. Informix provides isolation levels and locking mechanisms that regulate concurrency, preventing anomalies such as lost updates or dirty reads. Candidates must understand how these mechanisms interact with storage layouts, buffer usage, and index structures to preserve data integrity while minimizing contention. Balancing transaction isolation with performance efficiency is a key aspect of advanced administration.
Monitoring I/O patterns is essential for understanding system behavior under varying workloads. Informix tracks reads, writes, and page activity, allowing administrators to identify hotspots, uneven distribution, or potential storage bottlenecks. Candidates should recognize how query patterns, indexing, and physical schema design influence I/O, and how to implement adjustments such as relocating tables, reorganizing dbspaces, or tuning buffer pools to improve throughput. Effective monitoring ensures that the system remains responsive even under high transactional loads.
Capacity planning is another critical responsibility. Informix administrators must anticipate growth in data volume, concurrent users, and transaction rates. By analyzing historical usage patterns, storage consumption, and query performance, candidates can forecast resource requirements and adjust configurations accordingly. This includes adding dbspaces, resizing logs, tuning memory pools, and balancing workloads across servers or replication nodes. Proper planning prevents unexpected performance degradation, downtime, or resource exhaustion.
Monitoring replication in conjunction with performance metrics ensures that high-availability configurations function as intended. HDR, Remote Secondary Servers, and Enterprise Replication require careful observation of transaction propagation, queue sizes, and latency. Candidates should understand how replication impacts I/O, memory, and CPU resources, and how to identify and address bottlenecks or inconsistencies. Maintaining replication health is critical for operational continuity, disaster recovery, and data integrity.
Maintenance operations such as updating statistics, reorganizing tables, and rebuilding indexes play a pivotal role in sustaining performance. Informix relies on up-to-date statistics to guide the optimizer, influencing query plans and execution efficiency. Reorganization of tables can defragment storage, reclaim space, and improve I/O performance. Index maintenance ensures that retrieval operations remain efficient and that additional overhead from fragmented or outdated structures is minimized. Candidates must understand the timing, frequency, and impact of these maintenance tasks to integrate them effectively into operational routines.
Monitoring server parameters and configuration settings is essential for maintaining stability and responsiveness. Informix uses configuration files to define parameters such as buffer sizes, thread allocation, and memory distribution. Adjusting these parameters based on workload patterns, transaction volume, and system capacity directly affects performance and availability. Candidates should be familiar with how to observe server behavior, interpret performance metrics, and implement configuration changes without disrupting active operations.
Security monitoring complements performance oversight by ensuring that data access, replication, and backup operations adhere to organizational policies. Tracking authentication attempts, role assignments, privilege usage, and audit logs provides visibility into potential vulnerabilities. Candidates must understand how security considerations intersect with operational efficiency, balancing protective measures with the need for performance and availability.
The interplay between database objects, storage management, and performance monitoring is complex and interdependent. Efficiently designed tables, strategically placed indexes, and appropriately sized dbspaces enhance I/O performance, reduce contention, and facilitate fast query execution. Backup and recovery strategies preserve data integrity and operational continuity, while monitoring tools provide actionable insights for ongoing optimization. Candidates must integrate these components holistically, recognizing that decisions in one area impact behavior and performance across the entire environment.
Informix supports advanced storage techniques, including the separation of large objects into blobspaces, allocation of multiple chunks to dbspaces, and the use of sbspaces for specialized tables. These mechanisms allow administrators to tailor storage layouts according to data types, access patterns, and performance requirements. Understanding the implications of these strategies on I/O distribution, buffer utilization, and query performance is essential for effective administration. Candidates should appreciate how physical storage design influences the efficiency of both routine operations and complex analytical queries.
Recovery planning must account for various failure scenarios, including hardware crashes, software errors, network interruptions, or human errors. Informix provides multiple recovery strategies, combining full and incremental backups with logical and physical logs to restore the database to a consistent state. Candidates must understand how to select appropriate strategies, sequence recovery operations, and verify data integrity post-restoration. This knowledge ensures resilience and continuity in enterprise-grade deployments.
Performance monitoring is not limited to reactive observation but extends to proactive tuning. By analyzing metrics, identifying patterns, and predicting resource needs, administrators can implement preventive measures to avoid degradation. For instance, monitoring transaction rates and buffer pool usage may reveal impending bottlenecks, allowing for preemptive expansion of memory allocation or redistribution of dbspaces. Candidates should develop an anticipatory mindset, integrating monitoring into daily operational practices.
Monitoring also includes evaluation of concurrency and lock management. Informix provides visibility into active locks, waiting transactions, and potential deadlocks. Candidates must understand how to interpret lock-related metrics, adjust transaction boundaries, and optimize query execution to reduce contention. Effective management of concurrency ensures that high transaction volumes do not compromise system responsiveness or data integrity.
Integration of backup, recovery, and performance monitoring with security measures ensures a cohesive administrative strategy. Auditing, role-based access, and secure replication must be considered alongside operational procedures to maintain both integrity and availability. Candidates should appreciate that Informix’s design encourages a holistic view, where logical schema, physical storage, operational routines, and security policies interconnect to support robust and efficient database environments.
Finally, maintaining a comprehensive view of database operations requires combining insights from multiple monitoring tools, performance metrics, and maintenance activities. Candidates must develop the ability to synthesize information, identify trends, and implement corrective or optimization measures that sustain reliability, efficiency, and responsiveness. Mastery of these domains demonstrates a high level of operational competence in IBM Informix 11.70 and aligns with the expectations of the C2090-558 examination.
Ensuring Stability, Performance, and Reliability in IBM Informix 11.70
The IBM Informix 11.70 environment presents a sophisticated platform for database administration, designed to support enterprise-grade applications with high availability, resilience, and efficient resource utilization. Candidates preparing for the C2090-558 examination are expected to demonstrate advanced knowledge of administrative procedures, monitoring utilities, high-concurrency management, and troubleshooting techniques. Mastery of these domains ensures that database professionals can maintain a stable environment, anticipate potential issues, and respond effectively to operational challenges.
Advanced administrative tasks encompass a broad array of responsibilities, from system configuration to proactive optimization. Informix administration begins with understanding configuration parameters that influence memory allocation, CPU utilization, and I/O behavior. Administrators must adjust settings for buffer pools, shared memory, and thread counts to align with expected workloads. For instance, larger buffer pools can reduce disk I/O by storing frequently accessed data in memory, while properly configured thread counts optimize concurrent processing. Candidates must recognize how these parameters interact and the potential impact of changes on both performance and stability.
User and role management is a critical component of administration. Informix supports granular privilege assignments, allowing administrators to grant permissions at multiple levels, including databases, tables, columns, and routines. Roles aggregate privileges to simplify management, and audit trails track changes in user activity. Proper configuration of roles and privileges ensures secure operations while minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. Candidates should understand best practices for creating, modifying, and deactivating accounts, as well as strategies for maintaining an organized and secure user structure in complex environments.
Monitoring utilities provide real-time insights into the system’s health and performance. Tools such as onstat, onmonitor, and system tables allow administrators to observe active sessions, lock activity, memory usage, buffer pool efficiency, and I/O patterns. These utilities are indispensable for identifying bottlenecks, tracking resource consumption, and making informed tuning decisions. For example, onstat can reveal long-running transactions, lock contention, and page reads, enabling administrators to address issues proactively. Candidates must develop the skills to interpret these metrics and implement corrective measures that enhance system responsiveness.
High-concurrency handling is essential in environments where numerous users or applications access the database simultaneously. Informix employs sophisticated locking and isolation mechanisms to maintain data consistency without compromising throughput. Shared, exclusive, and intent locks govern access to rows, tables, and pages, while transaction isolation levels control the visibility of changes between concurrent operations. Administrators must balance concurrency with performance, adjusting parameters and optimizing queries to prevent deadlocks, reduce contention, and ensure smooth operation. Candidates should understand how to monitor concurrency, detect conflicts, and apply strategies that maintain both efficiency and integrity.
Locking and transactional behavior interact closely with performance optimization. Informix uses a combination of logical logging, buffer management, and checkpoints to ensure ACID compliance. Administrators must monitor transaction activity, identify sources of contention, and implement measures such as query optimization, index maintenance, or adjusted isolation levels to maintain throughput. Candidates must appreciate that efficient transaction management requires both strategic planning and responsive adjustments based on observed system behavior.
Troubleshooting is a continuous aspect of advanced administration. Informix administrators must diagnose and resolve issues ranging from connectivity failures and query performance degradation to replication inconsistencies and system crashes. Effective troubleshooting requires a methodical approach, combining observation, analysis, and corrective action. Candidates are expected to utilize utilities, interpret logs, examine configuration parameters, and apply knowledge of system architecture to restore stability. For instance, identifying the cause of replication lag may involve analyzing transaction queues, network performance, and server configuration, then implementing adjustments to realign synchronization.
Replication monitoring and management are integral to high-availability environments. HDR, Remote Secondary Servers, and Enterprise Replication provide mechanisms for continuous data duplication, failover, and distributed consistency. Administrators must observe replication queues, detect delays, and ensure data consistency across nodes. Understanding the distinctions between synchronous and asynchronous replication, the impact on performance, and the recovery procedures in case of failure is crucial. Candidates should appreciate how replication integrates with transactional logging, backup strategies, and concurrency control to provide a resilient operational framework.
Backup and recovery planning is an ongoing administrative responsibility. Informix offers ontape and onbar utilities for full and incremental backups, complemented by logical unload operations. Administrators must schedule regular backups, verify integrity, and understand restoration procedures, including roll-forward and roll-back using logical logs. Candidates must also account for high-availability scenarios, ensuring that backups and recovery operations do not disrupt replication, client connectivity, or ongoing transactions. Effective planning minimizes downtime and preserves both data integrity and system reliability.
Performance tuning extends beyond configuration parameters to include query optimization, index maintenance, and schema adjustments. Informix’s cost-based optimizer evaluates query execution plans using statistics, indexes, and data distribution. Administrators must monitor execution patterns, detect suboptimal plans, and implement changes such as updating statistics, restructuring queries, or adding indexes to improve efficiency. Index maintenance involves rebuilding or reorganizing structures to reduce fragmentation and maintain retrieval speed. Candidates should understand the cumulative impact of these tuning efforts on system responsiveness, concurrency, and resource utilization.
Monitoring memory, buffer pools, and I/O activity is crucial for sustaining performance under heavy workloads. Buffer pool hit ratios, page reads, and memory allocation patterns provide insights into efficiency and potential bottlenecks. Administrators can adjust buffer pool sizes, page sizes, and memory allocation to align with workload demands. Candidates should be adept at interpreting these metrics and making informed adjustments that enhance performance without compromising stability or reliability.
Client connectivity monitoring ensures that applications maintain stable communication with the database server. Informix provides detailed metrics on active sessions, connection status, and resource utilization per client. Administrators must detect and resolve issues such as slow connections, failed authentications, or resource contention caused by misconfigured applications. Proper management of client connectivity contributes to both performance and security, ensuring that users can access data reliably while maintaining system integrity.
Alerting and proactive monitoring are essential for preemptive issue resolution. Informix can generate alerts for thresholds on CPU utilization, disk space, transaction duration, replication lag, and other critical metrics. Administrators must configure alert parameters, respond to notifications, and implement corrective actions to prevent escalation. Candidates should understand how proactive monitoring integrates with routine maintenance, performance tuning, and high-concurrency management to maintain a resilient environment.
Troubleshooting also involves analyzing error messages, system logs, and diagnostic outputs. Informix provides extensive logs capturing transaction activity, replication events, memory usage, and system errors. Candidates must interpret these records to identify root causes, implement fixes, and verify resolution. Troubleshooting scenarios often require combining knowledge of system architecture, transaction behavior, query execution, and replication mechanics to restore optimal operation.
Capacity planning and workload forecasting complement monitoring and tuning. Administrators must anticipate growth in data volume, user connections, and transaction complexity. By analyzing historical trends and system metrics, candidates can recommend expansions to storage, memory, and processing capacity, as well as adjustments to configuration parameters to sustain performance. Effective planning ensures that the Informix environment remains scalable, efficient, and resilient under varying operational conditions.
Integrating high-concurrency handling, monitoring, backup strategies, replication, and troubleshooting establishes a comprehensive administration framework. Each aspect reinforces the others: performance tuning enhances throughput for concurrent users, monitoring provides early detection of issues, replication and backups ensure continuity, and troubleshooting restores stability when unexpected events occur. Candidates must appreciate the interdependencies between these domains and apply holistic strategies to maintain a robust Informix environment.
Training and documentation complement technical administration. Informix administrators should maintain records of configuration changes, monitoring outputs, troubleshooting actions, and performance adjustments. Documenting procedures, schedules, and best practices enhances operational consistency, facilitates knowledge transfer, and supports audit and compliance requirements. Candidates should understand the value of documentation as part of a disciplined approach to advanced administration.
The examination also emphasizes the ability to synthesize concepts into practical application. Candidates are expected to demonstrate not only theoretical knowledge but also the ability to manage complex operational scenarios, optimize system performance, secure data, handle high-concurrency environments, and respond effectively to failures. Integrating these skills ensures that Informix administrators can provide reliable, high-performance solutions in enterprise contexts.
Continuous learning is inherent to advanced administration. The Informix environment evolves with new features, patches, and enhancements. Administrators must stay informed about updates, best practices, and emerging techniques to sustain efficiency and reliability. Candidates preparing for certification must adopt a mindset of ongoing skill development, ensuring that they can apply their knowledge effectively in dynamic operational environments.
Effective communication and collaboration are also part of advanced administrative competence. Administrators interact with application developers, network engineers, security teams, and management personnel to align database operations with organizational goals. Candidates should appreciate the importance of clear reporting, cross-team coordination, and proactive engagement in planning, troubleshooting, and optimization initiatives.
In summary, IBM Informix 11.70 administration encompasses advanced configuration, monitoring, high-concurrency handling, replication management, backup and recovery, performance tuning, and troubleshooting. These domains collectively equip database professionals to maintain stable, secure, and high-performing environments, while ensuring data integrity, scalability, and resilience under varied operational conditions. Mastery of these skills aligns with the objectives of the C2090-558 examination, demonstrating a comprehensive understanding of both theoretical principles and practical applications within Informix systems.
Conclusion
Achieving proficiency in IBM Informix 11.70 Fundamentals requires integrating knowledge across architecture, data management, performance optimization, security, replication, and administrative operations. Advanced administration, monitoring, and troubleshooting skills ensure that database environments remain resilient, efficient, and secure, even under complex workloads or unexpected events. By synthesizing these competencies, professionals are prepared not only to excel in the C2090-558 examination but also to manage enterprise-grade Informix systems with confidence and expertise. Mastery of these domains empowers administrators to anticipate challenges, implement effective solutions, and maintain the integrity and performance of critical data infrastructures, establishing themselves as capable custodians of information in demanding environments.