Certification: CISSP-ISSMP
Certification Full Name: Information Systems Security Management Professional
Certification Provider: ISC
Exam Code: CISSP-ISSMP
Exam Name: Information Systems Security Management Professional
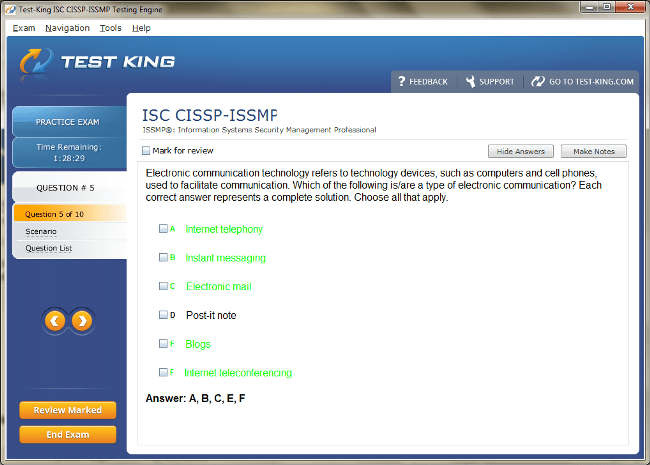
CISSP-ISSMP Exam Product Screenshots
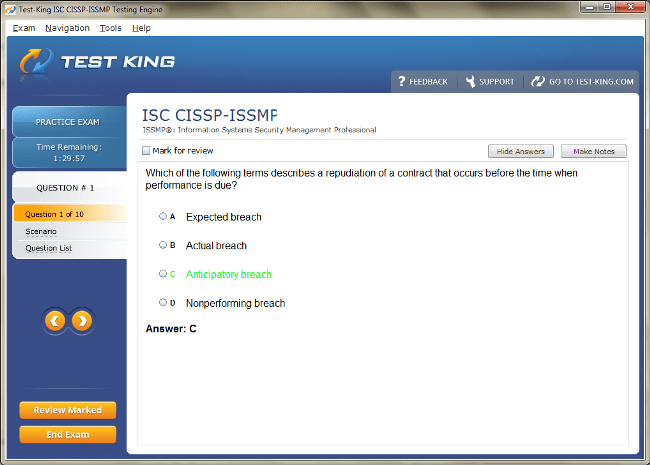
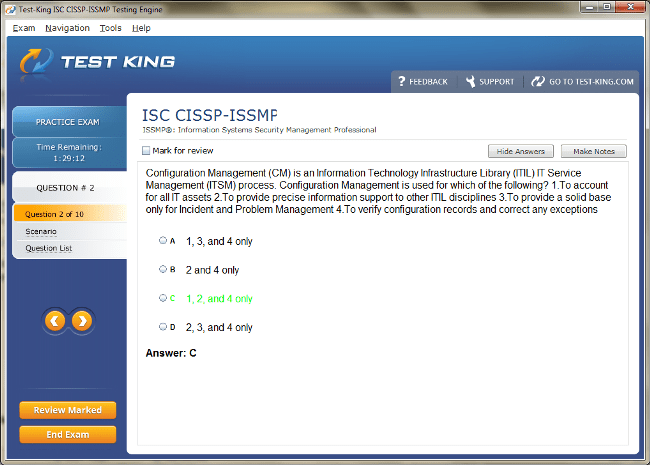
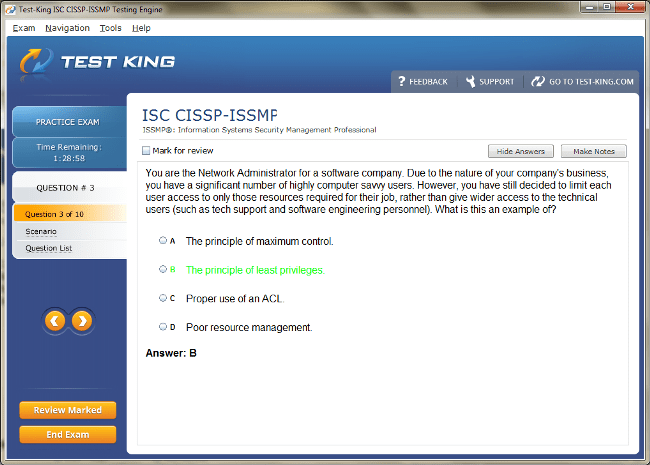
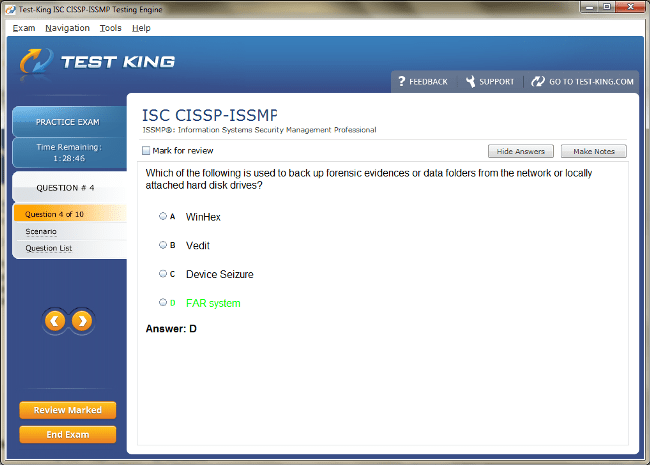
CISSP-ISSMP Certification: Elevating Security Management Expertise for Modern Professionals
In the rapidly evolving landscape of information technology, the protection of digital assets has transcended the realm of mere technical proficiency and entered the domain of strategic governance and managerial acumen. The ISC2 Information Systems Security Management Professional certification represents a pinnacle of achievement for executives who aspire to not only comprehend the intricacies of security technologies but also orchestrate comprehensive security programs that encompass organizational governance, risk mitigation, and operational continuity. This certification validates a professional's capacity to conceive, implement, and supervise information security strategies that safeguard sensitive data while aligning with the strategic objectives of an organization.
Understanding the Significance of CISSP-ISSMP in Contemporary IT Security
The realm of cybersecurity is no longer confined to firewalls, encryption protocols, or intrusion detection systems. Today, the role of a security executive encompasses a nuanced understanding of risk management frameworks, compliance regulations, and corporate governance principles. A professional equipped with this certification demonstrates mastery in devising policies that anticipate potential threats, establishing protocols for incident response, and creating resilient security architectures that endure the dynamic threats of modern cyberspace. Such expertise requires a judicious blend of technical understanding and managerial foresight, ensuring that security initiatives support organizational growth without compromising data integrity.
A certified professional is entrusted with responsibilities that range from evaluating organizational vulnerabilities to drafting comprehensive disaster recovery plans and ensuring continuous compliance with regulatory mandates. The curriculum of this certification is meticulously designed to encompass these multifaceted obligations, emphasizing strategic planning, project oversight, and operational governance. Professionals in this domain are expected to exhibit a meticulous approach toward risk assessment, develop response strategies for potential security breaches, and integrate security considerations into the broader fabric of organizational management. The synthesis of these competencies not only elevates the professional standing of the individual but also fortifies the organization’s resilience against complex cyber threats.
Candidates who pursue this certification are typically those occupying or aspiring to executive positions within IT and security hierarchies. Chief technology officers, chief information security officers, and senior executives in security and information management find particular relevance in the credential. Such professionals are often responsible for aligning security initiatives with corporate objectives, ensuring that the organization's technological infrastructure is both robust and compliant with contemporary standards. The certification serves as a testament to their strategic vision, technical competence, and managerial capabilities, signaling to peers, stakeholders, and employers that they possess the requisite expertise to navigate the intricate interplay of technology, risk, and governance.
In addition to validating leadership and strategic acumen, the certification confers tangible advantages in career trajectory and remuneration. Professionals equipped with this credential frequently find themselves poised for elevated responsibilities, leading critical projects, and making strategic decisions that impact the overall cybersecurity posture of their organization. Recognition in the industry grows commensurately, as peers and decision-makers acknowledge the rigorous standards required to achieve such a distinction. Consequently, career advancement opportunities proliferate, and the potential for higher compensation becomes a natural corollary to the enhanced professional stature.
The preparation for attaining this certification is deliberate and exhaustive, requiring a thorough understanding of multiple domains that collectively define the framework of information security management. Candidates are expected to engage with extensive study resources provided by ISC2, including comprehensive guides, practice tests, and specialized training courses. These materials elucidate the core principles of security governance, risk assessment, project management, and compliance, offering a structured approach to mastering the knowledge areas tested in the examination. While theoretical understanding is indispensable, practical application remains equally critical, as the certification emphasizes the ability to implement security strategies effectively within complex organizational contexts.
Success in the examination demands not only familiarity with theoretical constructs but also the capacity to analyze scenarios, identify risks, and propose pragmatic solutions. The assessment includes a combination of multiple-choice and multi-response questions, designed to gauge the candidate's comprehension, analytical reasoning, and decision-making aptitude. Candidates are allotted a finite window to navigate the questions, necessitating disciplined time management and methodical preparation. The scoring methodology ensures that only those who demonstrate proficiency across all domains are recognized, thereby maintaining the integrity and value of the certification.
Engaging with professional cohorts and study groups can significantly enhance preparedness. Interaction with peers provides opportunities to discuss complex topics, share insights, and gain perspectives on practical challenges faced by security managers. Such collaboration often illuminates nuances that individual study may overlook, fostering a deeper understanding of strategic and operational considerations. Complementing this collaborative approach, online resources, including video tutorials, webinars, and expert-led discussions, provide additional avenues for comprehension, allowing candidates to assimilate varied viewpoints and apply them to hypothetical or real-world scenarios.
A meticulous approach to time allocation is imperative, given the breadth and depth of the curriculum. Candidates benefit from establishing a structured study schedule that harmonizes professional obligations with dedicated preparation time. Initiating the study process several months in advance allows for incremental learning, reinforcement of complex concepts, and ample practice with mock examinations. Utilizing practice tests not only familiarizes candidates with the format and nature of questions but also enables identification of areas requiring additional focus. This iterative cycle of study, practice, and review fortifies the candidate's command over the subject matter and enhances confidence in navigating the examination under time constraints.
The examination encompasses a diverse range of knowledge domains, each integral to the overarching competence of a security management professional. Governance and risk management form the foundation, elucidating principles that ensure organizational policies align with regulatory requirements and internal objectives. Security program development emphasizes the creation of structured initiatives that address both preventive and responsive measures, fostering resilience against potential threats. Project management principles are intertwined with operational oversight, requiring candidates to demonstrate proficiency in coordinating resources, timelines, and personnel to achieve defined security outcomes. Incident response and continuity planning underscore the proactive and reactive dimensions of security, necessitating strategies that minimize disruption and preserve organizational functionality.
Beyond technical and managerial proficiency, the certification instills a mindset oriented toward strategic foresight and ethical responsibility. Candidates cultivate the ability to anticipate emerging threats, evaluate the implications of technological advancements, and integrate security considerations into broader organizational strategies. Ethical considerations are paramount, as decisions made at the executive level reverberate through operational processes, affecting stakeholders, data integrity, and organizational reputation. Mastery in this arena signifies that the professional can navigate the delicate balance between technological innovation, operational efficiency, and security imperatives.
The role of a certified professional extends into advocacy and mentorship within the organization. By guiding teams, imparting best practices, and fostering a culture of security awareness, they contribute to an environment where risk-conscious decision-making becomes intrinsic to daily operations. Strategic initiatives, such as risk assessments, compliance audits, and security awareness programs, gain credibility and efficacy under the stewardship of a certified executive. The synthesis of leadership, technical acumen, and strategic insight positions such professionals as indispensable assets, capable of steering the organization through the complexities of contemporary cybersecurity challenges.
In addition to professional recognition, attaining this credential requires an investment of both effort and resources. The examination fee reflects the comprehensive nature of the certification, and candidates must commit substantial time to study and preparation. This investment is offset by the career advantages conferred, including elevated recognition, leadership opportunities, and enhanced earning potential. The process is rigorous by design, ensuring that certified individuals exemplify the highest standards of competence, judgment, and ethical responsibility in the domain of information security management.
Ultimately, the ISC2 Information Systems Security Management Professional certification transcends conventional assessments of technical ability. It embodies the integration of managerial foresight, strategic thinking, and ethical stewardship in safeguarding organizational assets. The credential signifies that an individual is equipped to navigate the complex interplay of technology, governance, and risk, demonstrating the expertise necessary to protect, manage, and advance information security initiatives at an executive level. Professionals who achieve this distinction not only enhance their own careers but also contribute meaningfully to the resilience, integrity, and strategic advantage of the organizations they serve.
How CISSP-ISSMP Shapes Career Trajectories and Executive Capabilities
In the evolving domain of information security, the ISC2 Information Systems Security Management Professional credential signifies a profound integration of strategic insight, managerial competence, and technological acumen. Professionals pursuing this certification are frequently those aiming to elevate their influence within the cybersecurity landscape, blending operational expertise with visionary leadership. The credential confers not only recognition of technical mastery but also affirmation of the ability to guide organizational security policies, manage risks, and orchestrate comprehensive security programs. As organizations increasingly grapple with sophisticated threats and complex regulatory environments, the demand for executives equipped with such certification has intensified, creating unique pathways for career advancement and professional distinction.
Individuals who obtain this certification often hold, or aspire to, senior leadership positions within their organizations. Chief technology officers, chief information security officers, chief information officers, and senior security executives find the credential particularly relevant. These roles demand the orchestration of multifaceted security initiatives, requiring proficiency in governance, risk assessment, project oversight, and incident management. A professional armed with this certification is empowered to align security strategies with organizational objectives, ensuring that the technological infrastructure supports enterprise resilience while mitigating exposure to evolving cyber threats.
Recognition in the industry is a natural consequence of achieving this credential. Peers, stakeholders, and decision-makers perceive certified professionals as authoritative figures capable of steering complex projects and influencing strategic decision-making. This recognition enhances credibility, fostering trust in the professional's judgment and reinforcing their value to the organization. Moreover, the certification communicates a commitment to excellence and continuous development, traits that are increasingly sought after in leadership roles where the stakes of operational missteps are high and organizational reputation is paramount.
In addition to recognition, the credential opens avenues for diverse career trajectories. Executives who attain this certification are often considered for positions that involve oversight of mission-critical assets, leadership of security teams, and management of enterprise-wide initiatives. Opportunities extend to roles in consultancy, risk advisory, and organizational governance, where strategic input is paramount. The credential thus functions as both a testament to professional expertise and a catalyst for mobility within the hierarchical and functional layers of an organization.
Financial prospects are also positively influenced by certification. Executives equipped with this credential frequently encounter increased earning potential due to the specialized knowledge and leadership capabilities they bring to the table. Organizations are willing to invest in professionals who can safeguard critical information, ensure compliance, and mitigate risks that could result in operational or financial detriment. Compensation growth reflects both the technical acumen and strategic foresight that certified professionals embody, positioning them advantageously in a competitive job market where the scarcity of qualified security leaders amplifies their value.
The preparation and attainment of this certification require a deliberate and rigorous approach. Candidates engage with a comprehensive array of study resources, including ISC2-authorized guides, practice tests, and structured training courses. These resources facilitate mastery of key domains such as security governance, program development, risk assessment, incident response, and business continuity planning. Through disciplined study and iterative practice, professionals cultivate a nuanced understanding of organizational security imperatives, learning to translate theoretical concepts into actionable strategies that align with corporate objectives.
Time management emerges as a critical component of successful preparation. Candidates must harmonize professional responsibilities with sustained study efforts, allocating sufficient time to internalize complex concepts and reinforce practical application. Initiating preparation well in advance of examination schedules allows for incremental learning, comprehensive review, and repeated engagement with practice scenarios. Practice tests play a central role in this preparation, providing familiarity with question formats, revealing gaps in knowledge, and honing decision-making skills under timed conditions. Engagement with these evaluative exercises enhances confidence and ensures a methodical approach to tackling the examination.
The professional impact of the certification extends beyond immediate career advancement. Certified executives often assume roles that require mentorship and guidance, shaping the capabilities and awareness of teams responsible for operational security. They influence organizational culture by embedding risk-conscious practices, advocating for policy adherence, and fostering an environment where strategic security considerations are integrated into routine business decisions. Through this stewardship, the certified professional contributes to a sustainable security posture that balances technological innovation with prudent risk management, establishing a legacy of resilience within the enterprise.
Moreover, the credential underscores ethical stewardship and strategic foresight, integral qualities for leadership in information security. Executives must navigate intricate scenarios where technical, regulatory, and business objectives intersect, requiring judicious decision-making that prioritizes both organizational goals and stakeholder interests. Ethical considerations are pervasive, encompassing data privacy, compliance adherence, and responsible management of information resources. Professionals who demonstrate competency in these areas command respect and trust, further enhancing their influence within and beyond their organizations.
The certification also facilitates engagement with a broader professional ecosystem. ISC2-certified executives often participate in specialized forums, professional groups, and networks of like-minded peers. Such interactions provide opportunities to exchange insights, discuss emerging threats, and explore innovative approaches to security management. Exposure to diverse perspectives enriches strategic thinking, encourages continuous learning, and reinforces the applicability of theoretical knowledge in practical contexts. Networking within these circles fosters recognition at an industry level, connecting professionals to opportunities that extend beyond organizational boundaries and enhancing visibility within global cybersecurity communities.
From a practical perspective, the credential equips professionals to manage high-stakes projects with confidence. The responsibilities entrusted to certified executives often encompass oversight of enterprise-wide security programs, including the implementation of advanced technologies, coordination of multidisciplinary teams, and alignment of initiatives with regulatory frameworks. The capacity to assess organizational vulnerabilities, prioritize mitigation strategies, and orchestrate coordinated responses to incidents positions certified professionals as indispensable architects of secure and resilient operational environments. The synthesis of strategic vision, managerial oversight, and technical expertise enables these executives to anticipate challenges, implement solutions, and sustain operational continuity under complex conditions.
Candidates preparing for the certification are encouraged to integrate both formal and informal learning approaches. Authorized study materials, structured courses, and practice tests provide the foundational knowledge necessary for examination success, while collaborative engagement with peers and mentors offers contextual insights and practical strategies. Immersion in real-world scenarios, analysis of case studies, and application of risk management frameworks further consolidate learning, bridging the gap between theoretical constructs and operational execution. This blended approach nurtures the analytical acumen, decision-making capacity, and leadership qualities that distinguish certified professionals in high-stakes environments.
The examination itself is designed to evaluate holistic competence across multiple knowledge domains. Candidates encounter a variety of question types that assess analytical reasoning, scenario evaluation, and the application of security principles to organizational challenges. Mastery of the curriculum requires more than rote memorization; it demands critical thinking, strategic synthesis, and the ability to contextualize principles within diverse operational frameworks. Success in this rigorous assessment attests to the professional’s capacity to manage, lead, and influence organizational security initiatives at an executive level.
Furthermore, the certification reinforces the integration of risk management into broader organizational strategy. Certified executives are adept at identifying vulnerabilities, evaluating potential threats, and implementing mitigative measures that support enterprise objectives. The credential emphasizes the proactive development of security programs, alignment with governance structures, and anticipation of emergent risks. Professionals are trained to view security not merely as a technical challenge but as a strategic imperative, ensuring that risk management, compliance, and operational resilience are embedded within the organizational ethos.
The long-term professional impact of this credential is multidimensional. It enhances the ability to lead cross-functional teams, influence strategic planning, and advocate for policies that safeguard organizational integrity. Certified executives are recognized for their capacity to harmonize technological initiatives with regulatory compliance and corporate objectives, translating complex security concepts into actionable strategies that resonate with stakeholders. The certification thus becomes a conduit for professional distinction, career mobility, and industry recognition, positioning holders as authoritative figures in the domain of information security management.
In addition to career and professional benefits, the credential cultivates a mindset oriented toward continuous improvement and lifelong learning. Executives must remain attuned to emerging threats, evolving technologies, and regulatory changes, ensuring that their knowledge remains current and applicable. The ISC2 framework encourages ongoing engagement with professional development resources, practice tests, and collaborative forums, reinforcing the habit of reflective learning and adaptive strategy formulation. This commitment to growth ensures that certified professionals remain agile, informed, and effective in navigating the shifting landscape of cybersecurity challenges.
The practical application of knowledge acquired through the certification spans diverse organizational contexts. Executives are positioned to lead initiatives such as comprehensive risk assessments, security audits, incident response planning, and continuity of operations exercises. They are also responsible for guiding policy development, enforcing compliance with standards, and ensuring that security considerations are integrated into broader business processes. The holistic skill set developed through preparation and certification equips professionals to anticipate threats, implement mitigative measures, and sustain operational resilience, all while maintaining alignment with organizational objectives and stakeholder expectations.
Comprehensive Overview of the Examination and Its Core Competencies
The ISC2 Information Systems Security Management Professional credential is distinguished not only by its strategic significance but also by the rigorous standards established for its assessment. Professionals pursuing this certification encounter a meticulously designed evaluation that measures proficiency across a spectrum of knowledge domains critical for executive-level security management. The examination evaluates both theoretical understanding and practical application, ensuring that candidates possess the analytical, managerial, and technical skills necessary to navigate complex organizational environments while safeguarding digital assets and ensuring operational resilience.
The examination consists of a total of 125 questions, which encompass a combination of multiple-choice and multi-response formats. Candidates are provided 180 minutes to complete the test, requiring a blend of speed, accuracy, and strategic time management. Success is measured on a scale of 1000 points, with a minimum of 700 required to attain certification. The structure of the examination ensures comprehensive coverage of all domains, from governance and risk management to business continuity and program oversight, thereby affirming that certified professionals possess a balanced and holistic mastery of information security management principles. The examination fee reflects the intensive preparation required, representing both a commitment of resources and the professional value attributed to achieving this credential.
At the core of the credential’s curriculum are several interrelated domains, each addressing a distinct facet of security management while collectively forming an integrated framework. Governance and risk management constitute the foundational domain, emphasizing the establishment of policies, procedures, and strategic oversight mechanisms. Professionals are trained to evaluate organizational vulnerabilities, implement mitigation strategies, and ensure adherence to regulatory mandates, creating a secure and compliant operational environment. The domain also highlights the importance of aligning security initiatives with organizational objectives, fostering a culture where risk management is not merely reactive but anticipatory and integrated into the strategic planning process.
The domain of security program development is concerned with the orchestration of comprehensive initiatives that encompass preventive, detective, and corrective measures. Candidates learn to design and implement programs that mitigate potential threats while promoting operational efficiency. The curriculum emphasizes the evaluation of organizational needs, allocation of resources, and coordination of cross-functional teams, highlighting the executive’s role in translating policy frameworks into actionable and measurable outcomes. This domain requires not only technical acumen but also the capacity for strategic vision, as professionals must anticipate emerging threats and develop programs that remain adaptive and effective in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
Project management principles are interwoven throughout the curriculum, reflecting the necessity of overseeing initiatives that require coordinated effort across multiple stakeholders. Professionals are expected to demonstrate proficiency in defining objectives, establishing timelines, allocating resources, and monitoring progress to achieve desired security outcomes. The integration of project management into the credential underscores the executive’s responsibility for ensuring that security initiatives are executed efficiently, within budgetary constraints, and in alignment with organizational priorities. This competency requires a combination of analytical thinking, organizational foresight, and communication skills, enabling leaders to navigate complex projects while maintaining focus on strategic goals.
Incident response and continuity planning constitute another critical domain, highlighting the need for preparedness and resilience in the face of disruptive events. Professionals are trained to develop comprehensive response strategies, including identification, containment, eradication, and recovery procedures. The domain emphasizes proactive measures to minimize the impact of incidents, as well as post-incident analysis to strengthen future resilience. By mastering these competencies, executives ensure that organizations can maintain continuity of operations, protect critical assets, and preserve stakeholder confidence even under adverse conditions. This domain integrates technical problem-solving with strategic foresight, requiring professionals to anticipate contingencies and implement robust mitigation plans.
Ethics, legal considerations, and regulatory compliance form an overarching theme that permeates the curriculum, reinforcing the executive’s obligation to act responsibly and with integrity. Certified professionals are expected to understand applicable laws, standards, and industry best practices, ensuring that security decisions are both lawful and ethically sound. The emphasis on compliance highlights the interconnectedness of technology, governance, and organizational policy, underscoring the executive’s role in safeguarding not only information assets but also organizational reputation and legal standing. This knowledge equips professionals to navigate the intricate balance between operational efficiency, technological advancement, and regulatory adherence.
Preparation for the examination demands a multifaceted approach that encompasses theoretical study, practical application, and iterative assessment. Authorized study guides provide structured coverage of all knowledge domains, offering explanations, case studies, and scenario-based exercises that facilitate understanding. Candidates benefit from immersive engagement with practice tests, which simulate the examination environment, expose gaps in knowledge, and refine decision-making under time constraints. Such exercises are invaluable in cultivating both proficiency and confidence, enabling candidates to approach the examination with a comprehensive and methodical strategy.
Collaborative learning serves as an additional instrument for preparation. Study groups, professional forums, and peer discussions allow candidates to explore complex concepts, debate alternative approaches, and assimilate diverse perspectives. Interaction with professionals who have previously attained the credential offers insights into effective study methodologies, practical applications of knowledge, and strategies for addressing challenging scenarios. This collaborative dynamic enhances comprehension, reinforces learning, and fosters a deeper appreciation for the strategic and operational dimensions of information security management.
Time management remains a critical factor throughout the preparation process. Candidates must balance professional obligations, personal commitments, and dedicated study periods, creating a disciplined schedule that supports sustained engagement with the curriculum. Incremental learning, coupled with regular revision and practice assessments, ensures that candidates internalize complex concepts, develop analytical acumen, and cultivate the ability to apply knowledge in varied contexts. The combination of structured preparation, iterative practice, and reflective learning establishes a robust foundation for examination success.
The examination’s multi-response questions demand analytical reasoning and scenario evaluation, requiring candidates to consider multiple facets of a given problem before selecting the most appropriate responses. Mastery of these question types entails both content knowledge and critical thinking, as well as the ability to synthesize information from different domains to arrive at coherent solutions. The emphasis on scenario-based assessment underscores the credential’s focus on practical applicability, ensuring that certified professionals can translate theoretical principles into actionable strategies within organizational settings.
In addition to evaluating knowledge and analytical skills, the examination assesses the executive’s capacity for strategic decision-making. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to prioritize initiatives, allocate resources effectively, and evaluate the consequences of decisions within complex organizational environments. This evaluative approach mirrors real-world challenges, where executives navigate competing priorities, emerging threats, and resource constraints while maintaining alignment with corporate objectives. Success in the examination signals not only proficiency in security principles but also the capacity to lead, influence, and innovate within the enterprise.
The examination also encompasses content related to program evaluation and performance measurement. Professionals are trained to establish metrics, monitor progress, and assess the effectiveness of security initiatives, ensuring that programs deliver intended outcomes and support organizational objectives. This competency emphasizes the iterative nature of security management, where continuous assessment and refinement are essential for sustaining operational resilience and strategic alignment. By mastering program evaluation, executives demonstrate the ability to drive improvement, optimize resource utilization, and enhance organizational security posture over time.
Ethical considerations are integrated into every domain, highlighting the imperative for responsible stewardship of information assets. Executives are expected to model ethical behavior, advocate for transparency, and foster a culture of accountability within their organizations. This ethical orientation complements technical and managerial competencies, ensuring that decisions are guided by both legal standards and moral principles. Professionals who internalize these values are better equipped to navigate complex scenarios, mitigate risks, and maintain stakeholder trust in high-stakes environments.
Finally, the preparation journey is enriched by engagement with multimedia resources, including instructional videos, webinars, and interactive simulations. These resources provide alternative perspectives, contextual explanations, and practical demonstrations that reinforce conceptual understanding. Coupled with structured study guides, practice tests, and peer collaboration, such resources contribute to a comprehensive, multifaceted preparation strategy that equips candidates to approach the examination with confidence and competence.
Through mastery of the curriculum and successful completion of the examination, professionals attain a credential that signifies comprehensive expertise in information security management. Certified individuals are recognized for their ability to integrate governance, risk management, program oversight, incident response, compliance, and ethical stewardship into coherent strategies that protect organizational assets. The credential serves as both a testament to professional competence and a catalyst for career advancement, positioning holders to lead initiatives, influence organizational strategy, and contribute to the resilience and security of enterprise operations.
Best Approaches to Mastering the ISC2 Examination
Preparation for the ISC2 Information Systems Security Management Professional credential requires a methodical and comprehensive approach that combines theoretical study, practical application, and disciplined practice. The rigorous nature of the examination necessitates that candidates develop not only an understanding of technical concepts but also the capacity to integrate strategic and managerial principles into coherent security frameworks. Mastery of these competencies ensures that professionals are capable of overseeing organizational security programs, guiding risk management initiatives, and maintaining compliance with complex regulatory standards.
Candidates embarking on the preparation journey typically begin with an assessment of available study resources. ISC2 provides a variety of authorized materials, including detailed study guides, practice tests, and training courses, each designed to reinforce understanding of the key domains tested in the examination. The study guides offer structured coverage of governance, risk assessment, security program development, incident response, business continuity, and ethical considerations, while the practice tests simulate the exam environment, helping candidates gauge their readiness and identify areas for further study. Utilizing these resources in combination allows for a layered and immersive approach to learning, ensuring that candidates internalize both foundational and advanced concepts.
In addition to formal study materials, engagement with collaborative learning environments significantly enhances preparation. Candidates benefit from participation in study groups, professional forums, and networks of peers pursuing similar objectives. Interaction with colleagues facilitates discussion of complex topics, provides opportunities to explore alternative approaches to problem-solving, and allows for sharing of insights derived from practical experience. These collaborative engagements reinforce learning, expose candidates to a broader range of perspectives, and promote critical thinking, which is essential for analyzing scenario-based questions that often appear on the examination.
Time management emerges as a pivotal element in effective preparation. Candidates must balance professional responsibilities, personal obligations, and the substantial effort required to master the examination content. Developing a structured study schedule that allocates dedicated time for each knowledge domain, interspersed with regular review and practice testing, ensures consistent progress and minimizes the risk of last-minute cramming. Beginning preparation several months in advance allows for incremental learning, reflection, and repeated engagement with complex concepts, thereby solidifying comprehension and enhancing retention.
Practice tests serve as a cornerstone of examination readiness, providing candidates with insights into question formats, difficulty levels, and time management requirements. Engaging repeatedly with these evaluative exercises fosters familiarity with both multiple-choice and multi-response questions, hones analytical reasoning skills, and enhances decision-making under timed conditions. Practice tests also illuminate areas requiring further study, enabling candidates to focus their efforts strategically and efficiently. Through iterative cycles of study and assessment, candidates gradually cultivate the confidence and proficiency necessary to approach the examination with composure and competence.
A multifaceted preparation approach is strengthened through immersion in real-world scenarios and practical applications. Case studies, incident simulations, and hypothetical organizational challenges provide opportunities to apply theoretical knowledge in contexts that mirror actual executive responsibilities. This practical dimension reinforces understanding of governance, risk management, program development, and incident response, while also cultivating the ability to make informed strategic decisions. By translating conceptual learning into actionable strategies, candidates develop the analytical and managerial acumen required to succeed not only on the examination but also in professional practice.
Integration of multimedia learning resources further enhances the preparation experience. Video tutorials, webinars, and interactive modules offer alternative perspectives, illustrative examples, and detailed explanations that reinforce comprehension of complex subjects. Such resources allow candidates to revisit challenging concepts, explore nuanced scenarios, and gain exposure to diverse methodologies and problem-solving approaches. Combined with formal study materials and collaborative engagement, multimedia resources contribute to a rich and holistic learning environment that supports mastery of the curriculum.
Time allocation during study is critical, particularly for balancing the depth of content coverage with the need for review and reinforcement. Candidates benefit from segmenting study sessions to focus intensively on individual domains, followed by periods of synthesis that integrate knowledge across multiple areas. This approach not only strengthens retention but also fosters the ability to analyze interdependencies between governance, risk assessment, program management, and operational continuity. The iterative process of focused study, review, and practice consolidates learning, preparing candidates to tackle the examination confidently.
Developing a comprehensive understanding of scenario-based questions is another essential preparation strategy. The examination frequently presents candidates with complex situations requiring analysis of multiple factors and identification of optimal responses. Mastery of these questions necessitates both content knowledge and critical thinking, as well as the ability to evaluate the implications of different approaches. By engaging with practice scenarios and discussing solutions with peers or mentors, candidates cultivate the analytical reasoning and decision-making skills that are central to executive-level information security management.
Mentorship and guidance from professionals who have previously attained the certification provide additional advantages. Experienced mentors offer insights into effective study techniques, common pitfalls, and practical applications of knowledge in organizational contexts. Their guidance illuminates nuances that may not be immediately apparent from study materials alone, enriching the preparation process and enhancing the candidate’s ability to approach complex problems strategically. Mentorship also fosters motivation and accountability, supporting sustained engagement with the rigorous preparation requirements.
Preparation strategies are further enhanced by continuous evaluation of progress. Regular self-assessment through practice tests, quizzes, and scenario exercises allows candidates to identify strengths and weaknesses, monitor improvements, and adjust study plans accordingly. This reflective approach promotes efficiency in learning, ensures comprehensive coverage of all domains, and instills the confidence required to perform effectively during the examination. By incorporating systematic evaluation into their preparation regimen, candidates maximize their readiness and optimize the probability of success.
A disciplined approach to integrating theoretical and practical learning is essential for developing the competencies required by the credential. Governance and risk management principles must be understood not only conceptually but also in terms of their application to organizational decision-making. Security program development, incident response, and business continuity planning similarly require the ability to design, implement, and monitor initiatives that protect assets, mitigate risks, and ensure operational resilience. By synthesizing theoretical knowledge with applied practice, candidates cultivate the holistic understanding necessary for both examination success and professional efficacy.
The integration of ethical considerations, legal frameworks, and regulatory compliance into preparation is paramount. Candidates must develop an awareness of relevant laws, industry standards, and professional codes of conduct, and understand how these elements influence security policies and executive decision-making. Ethical decision-making is woven into each domain, reinforcing the importance of integrity, accountability, and responsible stewardship in executive roles. This focus ensures that candidates are equipped to navigate complex organizational landscapes while maintaining both legal compliance and moral responsibility.
Collaborative study and discussion enhance comprehension of these ethical and regulatory dimensions. Engaging with peers or mentors in evaluating scenarios that involve ethical dilemmas, compliance challenges, or regulatory ambiguities fosters critical thinking and encourages the application of principles to practical situations. Such interactions strengthen analytical reasoning, broaden perspectives, and prepare candidates to address real-world challenges with confidence and discernment. By blending individual study with collaborative exploration, candidates achieve a richer and more nuanced understanding of professional responsibilities.
Time management during the examination itself is also a key competency cultivated through preparation. Candidates must allocate attention effectively across all questions, balancing the need for careful analysis with the constraints of the testing period. Practice tests, timed exercises, and simulated examination environments enable candidates to refine pacing strategies, prioritize questions according to complexity, and develop the stamina required to sustain focus throughout the assessment. Mastery of these techniques reduces anxiety, enhances accuracy, and ensures that candidates can demonstrate their competencies comprehensively.
The use of case studies and real-world examples further reinforces preparation. By examining historical security incidents, organizational responses, and lessons learned, candidates gain insights into the practical challenges faced by executives. This contextual understanding bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and applied decision-making, equipping candidates to address similar scenarios effectively in both examination and professional contexts. The synthesis of these lessons into preparation activities enhances both analytical capacity and strategic foresight, ensuring readiness for the multifaceted demands of the certification.
Finally, preparation is enriched by engagement with ongoing professional development and continuous learning resources. Webinars, industry publications, and professional forums provide insights into emerging threats, technological advancements, and evolving best practices. Integration of these resources into study plans ensures that candidates remain current with the dynamic landscape of information security management, reinforcing the relevance and applicability of knowledge acquired during preparation. This holistic approach cultivates not only examination readiness but also enduring professional competence, preparing executives to lead, innovate, and safeguard organizational assets effectively.
Advanced Insights for Achieving Excellence in ISC2 Certification
Attaining mastery in the ISC2 Information Systems Security Management Professional examination requires not merely memorization of theoretical concepts but the cultivation of analytical precision, strategic foresight, and comprehensive understanding of managerial and technical principles. The pathway to success is shaped by the candidate’s ability to synthesize knowledge from diverse domains, interpret complex security situations, and apply disciplined reasoning under time constraints. The examination, while assessing cognitive ability, also evaluates how adeptly a professional can transform conceptual knowledge into pragmatic judgment in alignment with organizational imperatives.
The most effective strategy begins with an appreciation of the scope and structure of the examination. Candidates must recognize that the test is designed to assess their capacity for synthesis rather than recollection, challenging them to navigate multifaceted scenarios where governance, compliance, risk, and leadership converge. Understanding this orientation allows aspirants to approach preparation with a more holistic mindset, focusing not on rote learning but on comprehension and contextual application. The examination includes a diverse set of question types, from straightforward knowledge-based queries to those requiring multi-response analysis. This variety demands adaptability and a capacity for agile thought, as each question may test not only one’s grasp of principles but also their ability to integrate them dynamically.
Preparation, therefore, should not be confined to reading study guides in isolation. Instead, candidates must engage in intellectual immersion, drawing connections between theoretical frameworks and real-world challenges. For example, understanding risk management extends beyond recognizing definitions; it involves the capacity to evaluate potential threats, assess mitigation options, and justify choices from a leadership perspective. Similarly, knowledge of compliance and governance must evolve into the ability to interpret regulatory demands, align them with corporate policies, and make decisions that preserve both security integrity and operational efficiency.
The process of deep learning can be facilitated through diversified study materials. ISC2 provides extensive resources, including official study guides and online modules, but true mastery often requires supplementing these with external perspectives such as professional articles, academic publications, and analytical case studies. Reading about historical incidents of security breaches or governance failures helps candidates internalize the real-world implications of theoretical principles. These examples bring abstract concepts to life and demonstrate how executive decision-making influences organizational resilience. By internalizing the reasoning behind successful security leadership, candidates develop an instinctive understanding of the complexities the examination seeks to measure.
Beyond self-study, engagement in professional communities contributes significantly to preparedness. Discussion forums, cybersecurity conferences, and virtual study groups expose candidates to a wealth of insights from practitioners across industries. These environments encourage debate, questioning, and reflection, all of which refine critical thinking and broaden interpretive capacity. In particular, dialogue with individuals who have already earned the credential provides valuable firsthand perspectives about common pitfalls, time management strategies, and effective ways to deconstruct intricate exam questions.
A pivotal component of performance optimization lies in time management. Many candidates falter not because of insufficient knowledge but due to misallocation of time during the examination. Developing a disciplined pacing strategy is essential. Candidates should begin by analyzing their average response time during practice tests and adjusting their rhythm to ensure that they can navigate through all 125 questions without exhaustion or panic. Prioritization is vital: questions that appear straightforward should be answered promptly, reserving additional time for those requiring deeper contemplation. The skill of swift comprehension and deliberate pacing can only be cultivated through persistent simulation of exam conditions. Regularly practicing under timed constraints trains the mind to operate efficiently while sustaining focus and precision.
Mock examinations serve as the crucible in which knowledge and skill are refined. Each practice test is an opportunity to identify weaknesses, recalibrate study focus, and build confidence. The most effective use of mock exams involves reviewing every question thoroughly, analyzing both correct and incorrect answers, and understanding the rationale behind them. This introspective review deepens understanding, highlights cognitive patterns, and helps candidates avoid repetitive mistakes. When candidates confront a particular concept repeatedly across multiple tests, they begin to discern its nuanced applications, reinforcing memory retention and conceptual clarity.
The cultivation of analytical reasoning is indispensable. Many questions in the CISSP-ISSMP exam present layered scenarios demanding nuanced judgment. Candidates must be able to dissect complex situations, identify interdependencies, and determine optimal courses of action that balance security needs, operational priorities, and compliance obligations. Analytical reasoning extends beyond technical knowledge; it encompasses emotional intelligence, risk perception, and ethical discernment. These dimensions are particularly vital for professionals at the executive level, where decisions affect not just systems but people, reputation, and organizational trust.
Ethical and governance-oriented judgment also plays a central role. ISC2 emphasizes adherence to professional ethics as a cornerstone of the certification. Candidates should approach preparation with an understanding of ethical frameworks, legal responsibilities, and the broader implications of executive decisions. This involves examining scenarios where moral reasoning must guide security policy — for instance, balancing transparency with confidentiality or determining appropriate responses to insider threats. The ability to navigate these dilemmas with integrity and accountability enhances both examination performance and professional authenticity.
Another critical strategy involves cognitive endurance training. The duration of the exam, typically spanning three hours, demands sustained concentration. Candidates must prepare mentally for prolonged analytical exertion, ensuring that fatigue does not compromise accuracy. Techniques such as interval studying, mindfulness exercises, and short mental breaks during preparation can improve attention span and cognitive resilience. In practice sessions, replicating real exam conditions — including the duration and environment — helps condition the mind for the pressures of the actual test. This psychological readiness is often the defining factor distinguishing successful candidates from those who struggle despite sound knowledge.
Comprehensive understanding of each domain is essential, yet true mastery arises from integration rather than isolation. Candidates must learn to view the six major domains of the certification as interconnected elements of a cohesive security management ecosystem. Governance and risk management form the strategic foundation upon which program development, incident response, and continuity planning are constructed. By studying these relationships, candidates cultivate a systems-oriented perspective that enhances their ability to analyze holistic scenarios. This interconnected mindset aligns closely with the evaluation approach of the examination, which rewards the ability to perceive the big picture.
Language proficiency and comprehension skills should not be underestimated. Many candidates overlook the subtlety of question phrasing, leading to misinterpretation. Questions may be designed to test precision of understanding, and a single misread phrase can alter the intended meaning entirely. Reading practice materials critically and developing familiarity with the linguistic style used in ISC2 assessments ensures that candidates are not misled by intricate wording. When confronted with complex scenarios, rephrasing the question mentally and identifying the central issue helps to anchor understanding and guide reasoning toward the correct response.
Regular review sessions, interspersed throughout the preparation period, consolidate learning. Revisiting earlier topics reinforces long-term memory and prevents the decay of knowledge acquired in earlier stages of study. Active recall techniques, such as summarizing domains in one’s own words or explaining concepts to peers, have proven to be powerful methods for deepening comprehension. This dynamic approach transforms passive reading into interactive learning, ensuring that the candidate’s understanding is both flexible and durable.
Candidates should also cultivate adaptability. The evolving nature of information security demands awareness of emerging technologies, regulatory developments, and threat landscapes. Staying updated with current industry news, white papers, and research publications allows aspirants to contextualize exam content within real-world trends. This habit of continuous learning not only prepares candidates for the examination but also instills the professional mindset expected of a certified executive. The ability to connect current cybersecurity developments with theoretical frameworks enhances both understanding and relevance.
Mental composure during the examination cannot be overstated. Anxiety can impair recall, distort reasoning, and lead to careless errors. Developing strategies to maintain calm, such as controlled breathing, positive visualization, and cognitive reframing, contributes to sustained clarity and focus. Candidates should enter the exam room with a mindset of confidence tempered by vigilance, ready to approach each question methodically. Viewing the examination as an opportunity to demonstrate competence rather than as a threat to be feared can transform pressure into productive energy.
The discipline of self-assessment should continue throughout preparation. By maintaining a log of study sessions, practice test scores, and progress reflections, candidates can track their improvement objectively. This data-driven self-evaluation identifies patterns, such as which domains consistently yield lower performance, and allows for targeted remediation. Furthermore, documenting reflections after each mock test provides insights into cognitive tendencies, such as rushing through certain question types or overanalyzing others. Awareness of these patterns empowers candidates to refine their strategy with surgical precision.
Mentorship, when accessible, remains one of the most valuable assets. Professionals who have already earned the credential can provide nuanced insights that transcend textbook explanations. They can illustrate how to interpret ambiguous questions, explain the reasoning behind particular exam answers, and share experiences that shape realistic expectations. Such mentorship cultivates both intellectual and emotional preparation, reminding candidates that success in this pursuit is not solely an academic achievement but a professional transformation.
Collaboration with peers pursuing the same goal can further strengthen preparation. Shared study sessions, discussion of case studies, and group problem-solving exercises stimulate cognitive engagement. Diverse interpretations of the same topic reveal new dimensions of understanding and challenge assumptions, thereby refining analytical agility. This communal learning dynamic mirrors the collaborative nature of executive leadership, reinforcing skills that will remain valuable long after the examination has concluded.
Preparation for this certification is ultimately a discipline of balance — balancing theory with practice, speed with accuracy, and confidence with caution. Candidates must cultivate a rhythm that allows for steady progress without burnout. The most successful aspirants are those who approach the process as a professional development journey rather than a mere academic hurdle. Through consistency, adaptability, and introspection, they evolve into leaders capable of translating knowledge into strategy and foresight into action.
When the day of examination arrives, every aspect of preparation converges into performance. Each studied concept, practiced scenario, and refined technique coalesces into a state of readiness that allows candidates to engage the test with poise and discernment. Those who have approached their preparation holistically will find that the questions, while challenging, resonate with familiarity and logic. They will recognize patterns, identify principles, and respond with clarity derived from deep understanding rather than guesswork. This is the true essence of mastery in the CISSP-ISSMP certification journey — not the accumulation of facts, but the internalization of wisdom that empowers decisive, ethical, and effective leadership in the realm of information security management.
Advancing Career Pathways and Organizational Influence in Information Security Management
Earning the ISC2 Information Systems Security Management Professional certification signifies more than the culmination of rigorous study and examination success. It marks the transformation of an individual into a strategic architect of cybersecurity management and governance. Professionals who achieve this certification possess an elevated understanding of how to integrate technical controls with leadership decisions, aligning information security with organizational missions. The post-certification journey involves a dynamic evolution in both professional capability and career trajectory, as certified individuals assume greater responsibility in steering enterprises through the intricate landscapes of risk, compliance, and technological advancement.
After obtaining the credential, professionals often discover that their roles shift from operational execution to strategic orchestration. This evolution stems from the recognition that certified individuals have demonstrated the ability to synthesize diverse domains of knowledge—risk management, governance, business continuity, and incident response—into cohesive frameworks. They are no longer merely executors of predefined policies but become designers of the very policies that safeguard the integrity of organizations. The transition demands continuous intellectual agility, as cybersecurity threats and regulatory expectations evolve at an unprecedented pace. Hence, maintaining relevance through ongoing education, industry engagement, and professional networking becomes essential to preserving the value of the credential.
The career prospects following certification are expansive. Professionals often ascend to executive leadership positions such as Chief Information Security Officer, Chief Technology Officer, or senior risk management executive. These roles involve shaping enterprise-wide strategies, determining budget allocations for security initiatives, and ensuring that every department operates under unified governance standards. The recognition associated with this certification signals to employers and stakeholders that the individual possesses the discernment required to harmonize security with innovation. As organizations increasingly prioritize resilience and trust, such leadership capabilities become indispensable.
One of the most tangible benefits of post-certification advancement lies in enhanced credibility. The certification serves as an independent validation of expertise, fostering trust among colleagues, clients, and regulatory bodies. This credibility enables professionals to influence decision-making at the board level, where cybersecurity is no longer a technical issue but a central component of organizational sustainability. The ability to articulate complex security challenges in the language of business risk positions certified professionals as indispensable advisors. In boardroom discussions, their voices carry weight because their credentials symbolize mastery of both technical competence and strategic foresight.
Beyond internal recognition, the certification also opens international avenues for collaboration and employment. The global nature of ISC2’s framework ensures that the credential is respected across industries and geographies. Certified professionals often find themselves participating in multinational projects, consulting engagements, and policy advisory roles where their insights shape the direction of digital governance. The universality of the certification’s principles facilitates cross-border understanding of compliance regimes, allowing holders to contribute meaningfully to organizations operating in multiple jurisdictions.
However, professional development does not cease once the credential is obtained. The ever-changing cybersecurity ecosystem necessitates ongoing engagement with learning opportunities, from advanced workshops and specialized certifications to participation in professional forums. Continuous professional education ensures that knowledge remains current, practical, and adaptable. Certified professionals must allocate time to explore developments in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, quantum encryption, and emerging risk models. Such intellectual curiosity not only sustains expertise but also demonstrates commitment to excellence, reinforcing the ethos that underpins the ISC2 certification framework.
Another significant aspect of post-certification evolution involves the mentoring of emerging professionals. Experienced holders of the certification often assume the role of mentors, sharing their wisdom with those aspiring to enter the field. This mentorship creates a self-sustaining ecosystem of knowledge dissemination, ensuring that organizational expertise continues to grow across generations. Mentoring enhances the mentor’s own understanding, as teaching and guiding others demand reflection, articulation, and synthesis of acquired knowledge. It transforms experienced professionals into thought leaders who shape both individual careers and the broader discipline of information security management.
The financial benefits associated with certification are equally noteworthy. Professionals often observe a significant elevation in compensation, reflecting the premium that organizations place on specialized leadership capabilities. This increase is not merely a reward for passing an examination but recognition of the enhanced strategic value that certified professionals bring to enterprises. The ability to prevent security breaches, manage compliance efficiently, and align technological investments with organizational goals translates directly into financial advantage for the employer. Consequently, certified individuals are positioned not as cost centers but as value creators.
Professional visibility within the industry also expands substantially after certification. Opportunities to publish research, deliver keynote speeches, and contribute to professional associations become more accessible. These activities amplify one’s professional stature, foster networking, and facilitate collaboration with peers tackling complex security challenges. Through active participation in such endeavors, certified professionals can influence industry standards, shape policy recommendations, and advocate for responsible security practices that balance technological advancement with ethical stewardship.
Maintaining the certification requires adherence to continuing professional education requirements. This ongoing commitment reflects the ethos of perpetual improvement that defines ISC2’s philosophy. The accumulation of continuing education credits encourages professionals to engage consistently with new developments, attend workshops, contribute to community initiatives, and explore interdisciplinary connections. This continuous evolution ensures that the certification remains not just a credential earned once but a living testament to sustained excellence.
An equally important dimension of post-certification growth involves the cultivation of leadership presence. As professionals advance into senior roles, the ability to inspire, persuade, and unify teams becomes as critical as technical mastery. Effective leaders foster environments where security is perceived not as a constraint but as an enabler of innovation. By promoting a culture of awareness, accountability, and collaboration, they embed information security into the fabric of organizational identity. Their influence extends beyond policies and procedures, shaping the collective mindset that determines how individuals across departments perceive and engage with security responsibilities.
The acquisition of the credential also enhances an individual’s ability to navigate the intricate interplay between technology and regulation. With global data protection laws evolving and geopolitical tensions influencing digital governance, certified professionals are uniquely positioned to interpret complex compliance requirements. They understand how to align regulatory obligations with corporate objectives without impeding operational agility. Their expertise ensures that organizations remain both secure and competitive, adapting rapidly to legislative transformations while maintaining ethical and transparent data practices.
In addition to organizational leadership, many certified professionals choose to leverage their expertise in entrepreneurial or consulting capacities. The credibility associated with the certification provides a robust foundation for establishing independent consultancies or advisory practices. These professionals guide organizations through security audits, risk assessments, and strategy development, often serving as trusted partners in high-stakes decision-making. The entrepreneurial path allows for the translation of knowledge into tangible impact, enabling certified individuals to contribute directly to the strengthening of global cybersecurity resilience.
The value of the certification also manifests in enhanced adaptability. In an era defined by volatility and rapid technological change, adaptability becomes the hallmark of enduring success. Certified professionals learn to anticipate rather than merely respond to emerging threats. They integrate foresight into planning, develop predictive risk models, and align their teams with long-term strategic objectives. This proactive approach transforms cybersecurity from a defensive necessity into a strategic advantage that propels organizational growth.
Networking remains an invaluable aspect of post-certification success. Engagement with peers through professional associations, conferences, and collaborative initiatives fosters knowledge exchange and exposes individuals to innovative practices. These networks serve as reservoirs of collective intelligence, where professionals share insights on evolving threats, advanced methodologies, and regulatory developments. Active participation in these communities enhances visibility, strengthens professional bonds, and ensures that certified individuals remain at the forefront of thought leadership in the field.
Balancing technical depth with executive perspective becomes a defining characteristic of certified professionals. They are expected to communicate seamlessly with both technical teams and senior management, translating intricate security concepts into strategic language that informs business decisions. This ability to bridge disciplines distinguishes them as indispensable mediators between innovation and governance. Their skill in articulating risk in terms of financial and reputational impact transforms security discussions from technical debates into strategic dialogues that influence the direction of the enterprise.
The post-certification journey also involves personal growth. The rigorous preparation process fosters discipline, analytical acumen, and resilience—qualities that continue to serve professionals well beyond the exam. These attributes, combined with the recognition earned through certification, often lead to increased confidence and assertiveness in professional interactions. Certified individuals develop a heightened sense of purpose, recognizing their role not merely as defenders of systems but as guardians of trust and integrity in the digital realm. This awareness deepens their commitment to ethical leadership, transparency, and responsible innovation.
While the certification enhances professional stature, its true significance lies in its capacity to instill a lifelong learning mindset. The field of cybersecurity evolves daily, with emerging threats challenging established paradigms. Certified professionals embrace this fluidity, understanding that mastery is not static but continuous. They remain vigilant observers of global trends, technological shifts, and policy reforms, ensuring that their decisions remain informed and relevant. This perpetual curiosity not only sustains expertise but also inspires others within their organizations to pursue excellence and innovation.
Engagement with academic and research institutions provides additional pathways for post-certification enrichment. Many certified professionals collaborate on scholarly projects, contribute to academic journals, or mentor students pursuing careers in cybersecurity management. This symbiosis between academia and industry fosters innovation and ensures that future generations inherit both practical wisdom and theoretical rigor. Through such collaboration, certified individuals help shape the intellectual foundations of the discipline, leaving a lasting imprint on the profession.
The influence of certified professionals extends beyond corporate boundaries. Their expertise is often sought in public policy development, governmental advisory boards, and nonprofit initiatives aimed at enhancing global digital resilience. Their contributions shape national cybersecurity strategies, influence legislative frameworks, and support initiatives promoting digital literacy and ethical technology use. This societal impact underscores the broader purpose of certification—to empower individuals to safeguard not only organizational assets but the collective digital ecosystem upon which modern life depends.
Through all these developments, the ISC2 certification acts as both a catalyst and a compass. It propels individuals toward higher achievements while guiding their professional evolution within a framework of integrity, accountability, and excellence. It is a testament to the enduring value of disciplined learning, ethical leadership, and visionary thinking. The journey that begins with examination preparation ultimately transforms into a lifelong commitment to advancing security governance and fortifying the digital foundations of contemporary civilization.
Conclusion
The attainment of the ISC2 Information Systems Security Management Professional certification represents not an endpoint but a transformative beginning. It ushers certified individuals into a realm of perpetual growth, where learning, leadership, and integrity intertwine. The professional landscape that unfolds after certification is vast, encompassing executive leadership, consulting, mentorship, and policy influence. Each role offers an opportunity to apply the principles embedded in the certification—governance, risk management, ethical conduct, and strategic foresight—in ways that shape organizations and societies alike. The true measure of success lies not merely in the credential itself but in how it empowers professionals to lead with vision, safeguard with wisdom, and inspire with purpose. In this sense, the certification is more than an achievement; it is a lifelong pledge to uphold the security, stability, and trust upon which the digital future depends.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get the products after purchase?
All products are available for download immediately from your Member's Area. Once you have made the payment, you will be transferred to Member's Area where you can login and download the products you have purchased to your computer.
How long can I use my product? Will it be valid forever?
Test-King products have a validity of 90 days from the date of purchase. This means that any updates to the products, including but not limited to new questions, or updates and changes by our editing team, will be automatically downloaded on to computer to make sure that you get latest exam prep materials during those 90 days.
Can I renew my product if when it's expired?
Yes, when the 90 days of your product validity are over, you have the option of renewing your expired products with a 30% discount. This can be done in your Member's Area.
Please note that you will not be able to use the product after it has expired if you don't renew it.
How often are the questions updated?
We always try to provide the latest pool of questions, Updates in the questions depend on the changes in actual pool of questions by different vendors. As soon as we know about the change in the exam question pool we try our best to update the products as fast as possible.
How many computers I can download Test-King software on?
You can download the Test-King products on the maximum number of 2 (two) computers or devices. If you need to use the software on more than two machines, you can purchase this option separately. Please email support@test-king.com if you need to use more than 5 (five) computers.
What is a PDF Version?
PDF Version is a pdf document of Questions & Answers product. The document file has standart .pdf format, which can be easily read by any pdf reader application like Adobe Acrobat Reader, Foxit Reader, OpenOffice, Google Docs and many others.
Can I purchase PDF Version without the Testing Engine?
PDF Version cannot be purchased separately. It is only available as an add-on to main Question & Answer Testing Engine product.
What operating systems are supported by your Testing Engine software?
Our testing engine is supported by Windows. Andriod and IOS software is currently under development.
Top ISC Exams
- CISSP - Certified Information Systems Security Professional
- CCSP - Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP)
- SSCP - System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP)
- CISSP-ISSAP - Information Systems Security Architecture Professional
- CISSP-ISSEP - Information Systems Security Engineering Professional
- CSSLP - Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional
- CISSP-ISSMP - Information Systems Security Management Professional
ISC Certifications
- CAP - Certified Authorization Professional
- CISSP - Certified Information Systems Security Professional
- CISSP Concentrations
- CISSP-ISSAP - Information Systems Security Architecture Professional
- CISSP-ISSEP - Information Systems Security Engineering Professional
- CISSP-ISSMP - Information Systems Security Management Professional
- CSSLP - Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional
- ISC-CCSP - Certified Cloud Security Professional
- SSCP - Systems Security Certified Practitioner


