Certification: SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9
Certification Full Name: SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9
Certification Provider: SAS Institute
Exam Code: A00-211
Exam Name: SAS Base Programming for SAS 9
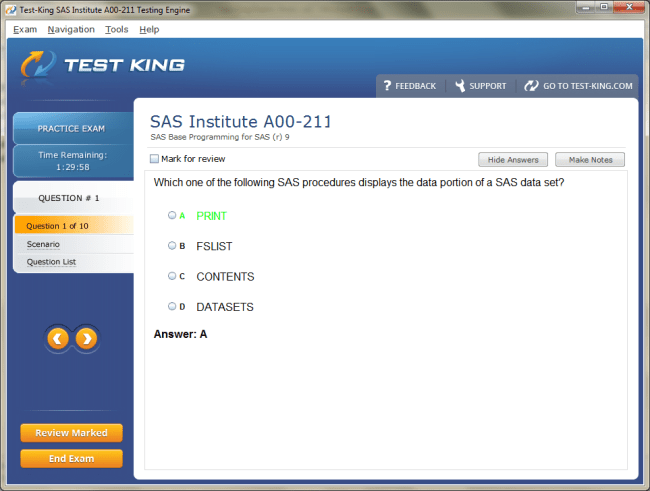
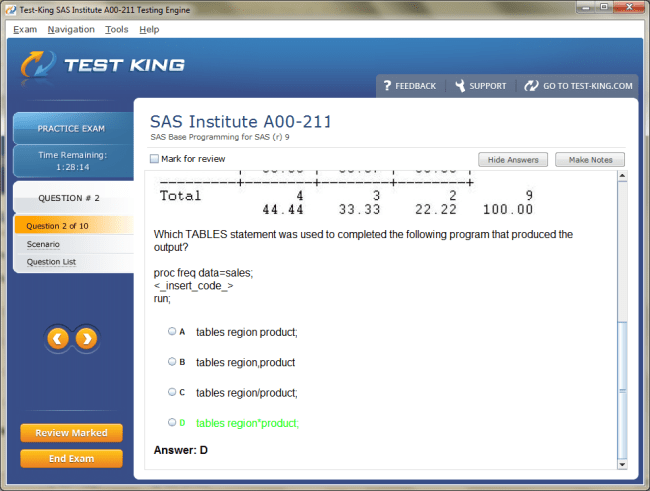
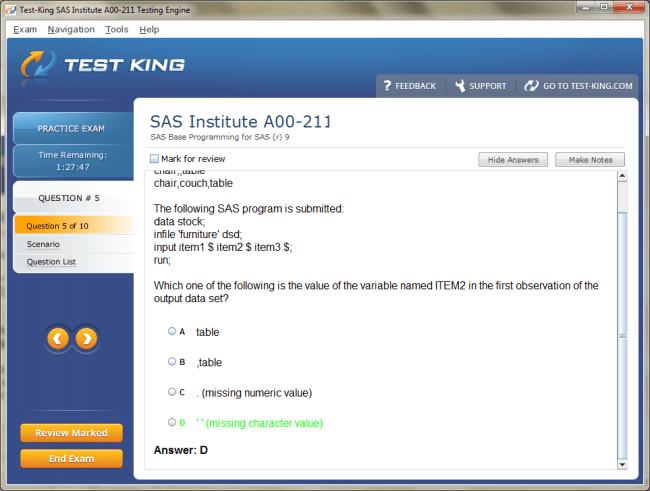
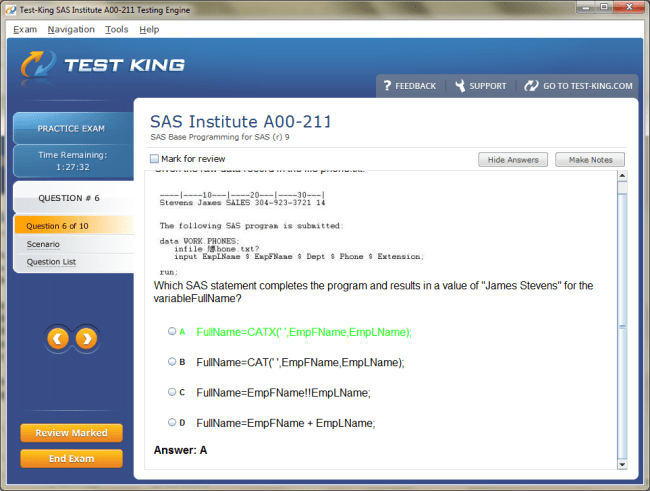
A00-211 Exam Product Screenshots
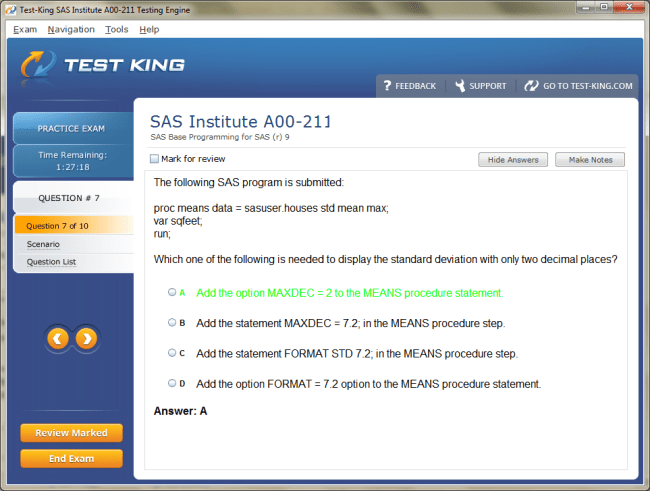
Career Opportunities After Certification of SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9
SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 opens doors to a vibrant spectrum of career avenues in data analytics, statistical programming, and business intelligence. Professionals who earn this credential often find themselves at the confluence of technical expertise and strategic decision-making, bridging the gap between raw data and actionable insights. This certification serves as an emblem of proficiency, demonstrating a solid grasp of SAS programming, data manipulation, and statistical analysis, which are invaluable in industries ranging from healthcare to finance, retail, and government sectors.
Exploring the Pathways and Prospects in Data Analytics
Individuals embarking on this journey frequently discover that their enhanced capabilities allow them to approach problems with analytical acumen and a methodical mindset. Organizations increasingly rely on certified professionals to extract meaningful patterns from complex datasets, develop predictive models, and maintain data integrity across various platforms. The skill set associated with this certification transcends simple coding; it encompasses understanding data structures, validating inputs, managing large datasets, and integrating statistical procedures into business processes. These abilities make certified programmers indispensable in environments where data-driven strategies shape outcomes.
The demand for SAS certified professionals often correlates with the proliferation of data across enterprises. As companies accumulate vast amounts of transactional and operational data, the need for individuals who can efficiently manage, cleanse, and analyze this information becomes paramount. A SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 possesses the expertise to perform intricate data transformations, generate detailed reports, and create data visualizations that elucidate trends previously obscured. This expertise allows businesses to make evidence-based decisions, optimize operational efficiency, and enhance predictive capabilities.
Job Roles and Responsibilities
Certified professionals often pursue roles such as data analyst, statistical programmer, business analyst, or reporting specialist. As a data analyst, one is expected to design, implement, and interpret analytical models, transforming unstructured data into coherent narratives that guide business decisions. Statistical programmers leverage the certification to create reproducible workflows, automate reporting processes, and ensure the accuracy of datasets, enabling seamless integration of analytical outputs into corporate strategies. Business analysts use their programming knowledge to extract insights that inform marketing campaigns, financial forecasts, and operational improvements, while reporting specialists develop dashboards and visual summaries that make complex datasets accessible to decision-makers.
In addition to core roles, many SAS certified individuals explore niche positions that blend programming with domain-specific knowledge. For example, healthcare analytics requires proficiency in SAS to process patient records, clinical trial data, and epidemiological datasets, contributing to policy development and treatment optimization. Financial institutions employ certified programmers to monitor transactional data, identify trends, and develop risk mitigation strategies, while retail and e-commerce sectors rely on SAS expertise to analyze customer behavior, optimize inventory, and forecast demand with remarkable precision.
The responsibilities in these roles extend beyond basic programming. Certified professionals often engage in validating data accuracy, constructing complex queries, and performing multi-level analyses that require both technical skill and critical thinking. They also participate in cross-functional projects, collaborating with IT teams, statisticians, and business managers to translate analytical results into actionable strategies. The ability to communicate technical findings in accessible language is equally valued, as it ensures that analytical insights drive practical business decisions rather than remain confined to spreadsheets or code repositories.
Salary Expectations and Growth Trajectories
Professionals with the SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential often experience a significant boost in earning potential. Entry-level positions typically offer competitive salaries, reflecting the technical expertise and reliability of certified individuals. With experience and demonstrated proficiency, professionals may ascend to senior analyst roles, statistical programming lead, or managerial positions, each accompanied by commensurate financial rewards. The career trajectory is often accelerated by the acquisition of complementary skills such as advanced analytics, machine learning, or data visualization tools, which amplify the value of the SAS certification in a diverse set of industries.
Growth opportunities are not limited to traditional corporate environments. Freelancing and consultancy roles provide alternative pathways for SAS certified programmers to apply their skills across multiple projects, industries, and geographies. These roles often afford greater flexibility, exposure to varied datasets, and the opportunity to work with global clients, further enriching professional experience. Additionally, the certification often serves as a foundation for advanced SAS credentials, enabling professionals to specialize in areas such as predictive modeling, business intelligence, or advanced analytics, thereby expanding their career horizons.
Navigating Industry Demands and Emerging Trends
As industries evolve, SAS certified professionals are increasingly positioned at the forefront of emerging trends in data analytics. Organizations seek individuals capable of harnessing sophisticated statistical techniques, ensuring compliance with data governance protocols, and integrating diverse data sources for comprehensive analysis. The certification signals that the professional possesses the methodological rigor and technical dexterity required to manage these challenges. In sectors like finance, healthcare, and pharmaceuticals, this expertise directly translates into improved outcomes, whether through fraud detection, treatment efficacy analysis, or operational optimization.
Moreover, the global expansion of data-driven decision-making underscores the importance of SAS certified expertise. Multinational corporations rely on consistent analytical methodologies, and a certified base programmer can standardize processes, enhance reproducibility, and ensure that insights are valid across diverse markets. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud-based data platforms increasingly intersect with SAS programming, creating opportunities for certified professionals to participate in innovative projects that redefine industry standards.
Enhancing Professional Value
The professional value of a SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 is reinforced not only by technical competence but also by the ability to synthesize analytical findings into strategic recommendations. Organizations recognize that while raw data may be abundant, actionable intelligence depends on interpretation, visualization, and communication. Certified programmers develop a nuanced understanding of data structures, statistical techniques, and reporting mechanisms that allow them to bridge the gap between data science and business acumen. This dual capability elevates their role from mere data handler to strategic partner in decision-making processes.
In addition, certified professionals often demonstrate enhanced problem-solving abilities and methodological discipline. Their training equips them to design efficient workflows, troubleshoot data inconsistencies, and implement best practices in programming. These skills contribute to operational efficiency, reduce error rates, and enhance the credibility of analytical outputs. As industries become increasingly competitive, organizations place premium value on individuals who can combine technical mastery with strategic insight, making SAS certified programmers highly sought after in both local and international markets.
Future Prospects and Opportunities
Looking ahead, the demand for SAS certified professionals is likely to persist and expand as data-driven strategies become further ingrained in organizational operations. Certified programmers are well-positioned to explore leadership roles in analytics departments, serve as mentors to junior analysts, or transition into specialized domains such as predictive modeling or big data analytics. The flexibility of the skill set allows professionals to adapt to shifting market demands, embrace new analytical tools, and participate in high-impact projects that influence organizational direction.
The versatility of the certification also facilitates cross-industry mobility. Professionals may transition between sectors such as finance, healthcare, marketing, or government, leveraging their foundational SAS skills to address unique challenges in each domain. This adaptability is especially valuable in an era where data proliferation is ubiquitous and the need for structured, accurate, and interpretable analytics spans virtually every industry. By combining SAS proficiency with critical thinking and domain awareness, certified programmers can continually expand their influence and explore innovative career pathways that align with both personal ambitions and industry needs.
Expanding Horizons in Analytics and Programming
Earning the SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential provides an individual with a remarkable leverage in the data analytics and business intelligence arena. This certification validates proficiency in fundamental SAS programming, encompassing data manipulation, report generation, and the application of statistical methods to real-world datasets. Professionals equipped with this credential often find themselves sought after by organizations that rely heavily on precise, reproducible, and interpretable data for strategic planning. The certification acts as a gateway to a labyrinth of opportunities, enabling certified programmers to carve a niche in domains where analytical acuity meets organizational strategy.
Individuals who obtain this certification often report that their ability to manage complex datasets transforms their approach to problem-solving. They develop a meticulous methodology to scrutinize data, detect anomalies, and implement corrective measures, ensuring the integrity of their analytical outputs. In environments where decisions are increasingly guided by empirical evidence, these programmers become pivotal contributors, translating vast amounts of data into actionable intelligence. The role demands both technical competence and cognitive dexterity, requiring professionals to harmonize logical reasoning with statistical insight.
Organizations across industries, ranging from finance to pharmaceuticals, healthcare to retail, increasingly rely on professionals who can manipulate data with finesse. A SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 is adept at preparing datasets for analysis, automating repetitive processes, and generating reports that facilitate decision-making at multiple organizational levels. By understanding and applying efficient coding practices, certified programmers ensure that data pipelines remain robust, scalable, and adaptable to changing business requirements. This combination of technical prowess and analytical reasoning significantly enhances the professional’s value in competitive labor markets.
Career Roles and Functional Responsibilities
Certified programmers often gravitate toward roles such as data analyst, clinical data manager, business intelligence analyst, or statistical programmer. In the role of a data analyst, individuals are responsible for extracting insights from large and often unstructured datasets, employing statistical procedures to identify trends, correlations, and anomalies. Clinical data managers utilize SAS to manage patient data, ensure adherence to regulatory standards, and facilitate the reporting of trial results in a precise and reliable manner. Business intelligence analysts leverage programming skills to integrate data from disparate sources, crafting comprehensive dashboards and visualizations that guide strategic decisions. Statistical programmers focus on implementing reproducible workflows, performing quality checks, and producing analytic outputs that are critical for evidence-based decision-making.
The functional responsibilities of certified programmers are both multifaceted and dynamic. These professionals often engage in data cleaning, transformation, and validation, ensuring datasets are coherent, accurate, and reliable. They construct complex queries to retrieve specific information, perform comparative analyses to detect trends, and interpret statistical outputs to provide strategic recommendations. Additionally, they collaborate closely with cross-functional teams, bridging the gap between technical data handling and executive decision-making. Communication skills become paramount, as the ability to convey intricate findings in accessible language enhances the impact of their analyses.
Beyond conventional roles, SAS certified programmers frequently explore specialized positions that combine domain knowledge with programming expertise. Healthcare analytics, for instance, requires professionals to process electronic medical records, laboratory results, and clinical trial datasets, contributing to improved patient outcomes and regulatory compliance. In financial services, programmers employ SAS to monitor transactional patterns, detect anomalies, and develop predictive models that mitigate risk. Retail and e-commerce enterprises utilize certified programmers to analyze customer behaviors, optimize supply chains, and forecast demand, thus enhancing operational efficiency and profitability.
Earning Potential and Career Progression
Professionals with the SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential often witness a substantial uplift in compensation. Entry-level roles offer competitive salaries, reflecting the technical acumen and reliability that certified programmers bring to an organization. With accumulated experience, individuals often transition to senior analyst roles, data management leadership positions, or managerial tracks in analytics departments, accompanied by increased financial rewards. Career progression is further amplified by complementary skills, such as advanced statistical modeling, predictive analytics, or data visualization, which bolster the professional’s versatility and marketability.
SAS certified professionals also have the flexibility to pursue independent consulting or freelance opportunities. These avenues allow individuals to apply their expertise across various industries and projects, providing exposure to diverse datasets, business challenges, and strategic objectives. Freelancing offers not only financial benefits but also the chance to cultivate a broader understanding of industry practices and emerging analytical trends. The certification acts as a credential of credibility, signaling to clients and employers that the professional possesses both methodological rigor and practical SAS programming competence.
Career advancement is additionally influenced by the acquisition of higher-level SAS certifications or specialized training in analytics. By building on the foundational knowledge validated by the base programmer credential, professionals can specialize in areas such as predictive analytics, machine learning, or advanced data integration, thereby expanding the range of roles and responsibilities they can assume. This continuous learning trajectory enhances both personal and organizational value, positioning the certified programmer as a pivotal contributor in increasingly data-centric environments.
Responding to Industry Needs and Emerging Analytics Trends
In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations seek professionals who can leverage sophisticated analytical techniques while maintaining data integrity and compliance. SAS Certified Base Programmers for SAS 9 are particularly suited to meet these demands due to their ability to manage complex datasets, automate repetitive workflows, and generate reproducible outputs. Industries such as healthcare, finance, and pharmaceuticals rely heavily on certified programmers to ensure regulatory adherence, maintain accuracy in reporting, and provide insights that guide critical decisions. These capabilities are not merely technical; they reflect a disciplined approach to data stewardship, analytical reasoning, and strategic implementation.
The expansion of data-driven decision-making globally further amplifies the demand for SAS certified expertise. Multinational organizations require consistent analytical standards across geographically diverse operations, and certified programmers play a central role in ensuring reproducibility, accuracy, and comparability of data outputs. As technologies such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and machine learning intersect with traditional data analysis, certified professionals are uniquely positioned to bridge conventional SAS programming with innovative computational methods. This confluence of expertise creates opportunities to contribute to high-impact projects, shaping the future of data analytics across multiple sectors.
Elevating Professional Value Through Analytical Mastery
Possessing the SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential signifies more than technical proficiency; it reflects an individual’s capability to synthesize data into actionable intelligence. Organizations recognize that strategic decisions are only as effective as the insights that underpin them, and certified programmers excel in translating raw datasets into meaningful narratives. Their training in data validation, statistical procedures, and reporting equips them to identify trends, detect anomalies, and optimize workflows with a methodical and efficient approach. The professional’s value is therefore measured not solely by coding ability but by the capacity to contribute to organizational decision-making and operational excellence.
Certified programmers also cultivate analytical rigor, problem-solving acumen, and methodological discipline, which collectively enhance their professional credibility. They implement best practices in data handling, minimize errors, and ensure the robustness of analytical outputs. The ability to navigate complex datasets, perform reproducible analyses, and present findings in an intelligible manner positions SAS certified professionals as indispensable contributors in modern organizations. As industries continue to emphasize data-driven strategies, these professionals become central to ensuring that analytical insights are both reliable and actionable.
Expanding Career Trajectories and Opportunities
The SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential provides a versatile platform for professionals to explore diverse career pathways. Certified programmers may ascend to leadership positions within analytics departments, mentor junior colleagues, or transition into specialized domains such as predictive modeling, advanced analytics, or business intelligence. The flexibility of the skill set allows them to adapt to evolving industry requirements, embrace new technologies, and participate in projects that influence strategic organizational outcomes.
Mobility across industries further enhances the appeal of this certification. Professionals can leverage their foundational SAS skills to transition between finance, healthcare, marketing, government, or other sectors, applying their expertise to unique datasets and domain-specific challenges. This adaptability ensures that certified programmers remain relevant in a competitive and rapidly changing job market. By coupling technical proficiency with analytical insight, they are well-positioned to continue expanding their influence, exploring innovative opportunities, and contributing meaningfully to the organizations they serve.
Professional Growth and Specialized Roles in Data Analytics
Obtaining the SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential signifies a commitment to precision, analytical rigor, and technical competence in the field of data analytics. This certification demonstrates mastery in SAS programming, encompassing data manipulation, management, and reporting, as well as the application of fundamental statistical techniques. Individuals who earn this credential often find themselves entering a professional ecosystem where their skills are highly valued for extracting meaningful insights, validating data accuracy, and contributing to strategic decisions across diverse industries.
The analytical expertise conferred by this certification extends far beyond routine programming. Certified programmers cultivate a deep understanding of data structures, data cleaning methodologies, and reproducible workflows, which equips them to handle complex datasets with efficiency and accuracy. In practice, this means identifying irregularities, creating streamlined processes for data transformation, and ensuring that reporting outputs are both reliable and interpretable. Organizations increasingly rely on these professionals to convert raw, often unstructured information into actionable intelligence, making them pivotal in shaping operational strategies and policy decisions.
Industries ranging from finance and healthcare to retail, manufacturing, and government increasingly prioritize the skills of certified SAS programmers. Financial institutions depend on these professionals to monitor transaction patterns, detect anomalies, and implement predictive models that mitigate risks. Healthcare organizations employ certified programmers to manage electronic health records, clinical trial data, and epidemiological datasets, ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards. In retail and e-commerce, the ability to analyze consumer behavior, forecast demand, and optimize supply chains gives certified professionals a critical role in strategic planning and operational efficiency.
Roles and Responsibilities in Analytics and Business Intelligence
SAS Certified Base Programmers often take on positions such as data analyst, reporting specialist, statistical programmer, or business intelligence analyst. In the role of a data analyst, the professional is expected to conduct detailed explorations of large datasets, identify trends and patterns, and communicate findings to stakeholders in a clear and actionable manner. Reporting specialists focus on generating dashboards, comprehensive reports, and visual summaries that translate intricate datasets into meaningful insights for decision-makers. Statistical programmers develop reproducible and automated workflows, implement quality control processes, and ensure the integrity of analytical outputs that guide organizational strategies.
The responsibilities of certified programmers frequently extend into multidisciplinary collaboration. These professionals work alongside statisticians, IT teams, and business managers to interpret results, refine analytical models, and ensure that insights align with organizational objectives. Effective communication is as critical as technical competence; the ability to articulate complex findings to non-technical stakeholders enhances the impact of their work. The role demands a balance between meticulous data handling and the capacity to derive strategic insights, creating a unique professional profile that blends technical precision with analytical intuition.
Specialized roles further expand the opportunities available to SAS certified professionals. In clinical research, for example, certified programmers manage trial data, validate results, and support regulatory submissions. Their work ensures that critical decisions regarding treatment efficacy, safety, and regulatory compliance are based on accurate and reliable information. In the financial sector, they implement complex algorithms to monitor investments, detect fraud, and support risk management frameworks. In retail, their expertise informs customer segmentation, marketing strategies, and inventory management, illustrating the versatility and applicability of SAS skills across industries.
Financial Rewards and Career Advancement
SAS Certified Base Programmers are recognized for the value they bring to organizations, and this recognition often translates into competitive salaries. Entry-level positions provide an attractive starting point for professionals entering the field, reflecting the demand for technical proficiency and analytical competence. As experience accumulates, professionals can progress to senior analyst roles, data management leadership positions, or specialized roles in statistical programming, each offering enhanced financial compensation and increased responsibility. The acquisition of complementary skills, such as advanced analytics, predictive modeling, or business intelligence tools, can further elevate earning potential and career mobility.
Beyond traditional corporate roles, certified programmers frequently explore consultancy and freelance opportunities. These paths allow professionals to work on diverse projects across industries, providing exposure to different datasets, analytical challenges, and business contexts. Freelancing not only offers flexibility and financial rewards but also enhances professional adaptability and problem-solving capabilities. The SAS certification serves as a credential of credibility in these contexts, signaling to clients and employers alike that the professional possesses both technical expertise and a disciplined approach to analytical work.
Career trajectories are also shaped by the pursuit of additional SAS credentials and specialized training. By building upon the foundation established by the base programmer certification, professionals can transition into predictive analytics, data science, or advanced statistical programming roles. This progressive skill development allows individuals to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving data landscape, where emerging technologies such as machine learning, artificial intelligence, and cloud-based analytics are increasingly integrated with traditional SAS workflows. Professionals who embrace continuous learning and adapt their skills accordingly can access high-impact positions and influence strategic organizational decisions.
Aligning Skills with Industry Evolution
The evolving demands of data-centric industries underscore the importance of SAS certified professionals. Organizations seek individuals capable of managing complex data pipelines, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, and integrating multiple data sources to produce coherent and actionable insights. Professionals with the SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential are uniquely equipped to meet these expectations due to their rigorous training in data validation, statistical procedures, and efficient coding practices. Their work supports the production of reliable outputs that inform high-stakes decisions, ranging from clinical trials to financial investments.
Emerging trends in analytics and data management further enhance the relevance of SAS certification. As enterprises increasingly adopt data-driven strategies, certified programmers contribute to building reproducible and scalable workflows, designing automated reporting systems, and implementing best practices for data governance. The integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and predictive modeling with SAS programming expands the professional’s toolkit, allowing them to participate in innovative projects and maintain strategic relevance. The global emphasis on standardized analytical processes also amplifies the value of certified programmers, who can harmonize methodologies across diverse operational contexts.
Amplifying Professional Impact
The value of a SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 is measured not only by technical skill but also by the ability to translate analytical findings into actionable strategies. Certified programmers develop an acute understanding of data integrity, statistical principles, and reporting standards, enabling them to identify trends, uncover anomalies, and provide recommendations that shape organizational outcomes. Their work ensures that analytical insights are both reliable and strategically relevant, positioning them as indispensable contributors in any data-driven environment.
Analytical discipline, problem-solving capability, and methodological rigor define the professional identity of certified SAS programmers. They implement structured workflows, ensure reproducibility of analyses, and reduce the risk of errors in complex data manipulations. These attributes enhance both operational efficiency and organizational confidence in the insights generated. As industries continue to emphasize evidence-based decision-making, certified programmers occupy a central role, bridging the gap between technical data processing and strategic business insight.
Exploring New Frontiers and Future Roles
The SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential provides a versatile foundation for exploring diverse career pathways and evolving professional roles. Certified programmers may ascend to managerial positions within analytics teams, lead cross-functional projects, or transition into specialized areas such as predictive analytics, big data management, or advanced statistical modeling. The flexibility of the skill set allows them to adapt to shifting industry landscapes, integrate emerging technologies, and contribute meaningfully to innovative projects with organizational impact.
Cross-industry mobility further amplifies career potential for SAS certified professionals. By leveraging foundational SAS skills, individuals can transition across sectors including healthcare, finance, government, marketing, and technology, applying their expertise to unique datasets and domain-specific challenges. This adaptability ensures that professionals remain relevant in an increasingly competitive job market. By combining technical competence with analytical insight, SAS certified programmers position themselves as strategic assets, capable of driving organizational success and shaping the future of data-driven decision-making.
Navigating Professional Landscapes in Data Analytics and Statistical Programming
Earning the SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential establishes a professional’s expertise in foundational SAS programming and positions them to explore a wide array of opportunities in analytics and business intelligence. The certification attests to proficiency in data manipulation, validation, reporting, and statistical procedures, equipping professionals with the skills needed to handle complex datasets with accuracy and efficiency. In today’s data-driven ecosystem, organizations increasingly seek individuals who can transform raw information into meaningful insights that drive strategic decisions, operational efficiency, and predictive analysis.
Certified SAS programmers often describe the transformative impact of the credential on their professional perspective. They develop a refined analytical mindset, capable of interpreting intricate data patterns and implementing robust workflows that ensure reproducibility and accuracy. This competency allows organizations to mitigate risks, streamline operations, and derive actionable intelligence from diverse datasets. By applying rigorous data validation, efficient coding practices, and statistical analysis, certified programmers bridge the gap between computational proficiency and strategic insight, establishing themselves as indispensable contributors to organizational decision-making.
Industries spanning healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, and government have a pronounced demand for certified SAS programmers. Financial institutions rely on these professionals to monitor transaction data, detect anomalies, and generate predictive models that guide investment decisions. Healthcare organizations utilize certified programmers to manage patient records, process clinical trial datasets, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements. In retail and e-commerce, SAS expertise is applied to analyze consumer behavior, optimize supply chains, and anticipate market trends. The versatility of these skills allows certified professionals to influence operational outcomes across a broad spectrum of sectors, demonstrating the universal value of analytical competence.
Professional Roles and Responsibilities
SAS Certified Base Programmers frequently occupy roles such as data analyst, statistical programmer, business intelligence analyst, or reporting specialist. Data analysts focus on exploring datasets to uncover trends, correlations, and anomalies, translating findings into strategic recommendations. Statistical programmers implement reproducible workflows, automate reporting processes, and ensure the integrity of complex data outputs, while business intelligence analysts consolidate information from multiple sources to develop dashboards and visualizations that facilitate decision-making. Reporting specialists craft structured summaries and analytical presentations that convey key insights to non-technical stakeholders, ensuring that data-driven strategies are effectively communicated.
The responsibilities of certified programmers extend beyond technical execution. Professionals often collaborate with statisticians, IT teams, and business managers to ensure alignment between analytical outcomes and organizational objectives. Effective communication is essential, as the ability to present complex findings in accessible terms enhances the utility of analytical insights. Certified programmers are expected to exercise critical thinking, problem-solving, and methodological rigor, allowing them to identify inefficiencies, optimize workflows, and contribute to high-stakes decision-making processes. This multifaceted role positions them as both technical experts and strategic partners in organizational development.
Specialized opportunities further expand the scope of career paths available to SAS certified professionals. In clinical research, certified programmers manage large-scale trial data, ensuring regulatory compliance and facilitating accurate reporting of outcomes. In finance, they develop risk models, detect fraudulent activity, and analyze transactional data for strategic investment insights. Retail and marketing sectors leverage certified programmers to segment customer populations, analyze purchasing behavior, and forecast demand patterns, providing actionable insights that drive profitability. Across these domains, the SAS certification ensures that professionals can deliver precise, reproducible, and impactful analyses that support organizational goals.
Compensation and Advancement Opportunities
Professionals holding the SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential often experience significant advantages in terms of compensation and career growth. Entry-level positions offer competitive salaries, reflecting the high demand for technically proficient individuals capable of handling complex datasets. As experience accumulates, professionals can progress to senior analyst roles, managerial positions, or leadership tracks in analytics departments, accompanied by increased remuneration and responsibility. The acquisition of complementary skills, such as advanced analytics, predictive modeling, and data visualization, further enhances earning potential and broadens the spectrum of career opportunities.
SAS certified programmers also benefit from flexible career paths that extend beyond traditional employment. Freelancing, consulting, and contract-based opportunities enable professionals to apply their expertise across multiple industries and projects, fostering adaptability and exposure to diverse datasets and analytical challenges. These roles often offer financial incentives, professional autonomy, and the ability to cultivate a robust portfolio of accomplishments. The SAS certification serves as a symbol of credibility in these contexts, signaling both methodological expertise and practical proficiency in data analysis and programming.
Continual professional development further enriches career progression. By building upon the foundational knowledge validated by the base programmer certification, professionals can pursue advanced SAS credentials, specialize in predictive analytics, or explore areas such as machine learning and big data management. This ongoing skill enhancement allows certified programmers to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving analytical landscape, positioning them for high-impact roles that influence strategic decision-making and organizational performance.
Adapting to Industry Dynamics and Emerging Trends
The growing emphasis on data-driven decision-making underscores the need for professionals capable of navigating complex analytical landscapes. Certified SAS programmers are particularly well-suited to this environment due to their mastery of data validation, reporting, and statistical procedures. Organizations increasingly rely on these professionals to ensure that analytical outputs are accurate, reproducible, and strategically relevant. Their expertise allows companies to implement evidence-based strategies, enhance operational efficiency, and anticipate market or industry shifts with a high degree of confidence.
Emerging trends in technology and analytics further enhance the relevance of SAS certification. The integration of machine learning, artificial intelligence, and cloud-based analytics with traditional SAS workflows creates opportunities for certified programmers to participate in innovative projects and contribute to organizational transformation. Global enterprises value standardized analytical practices, and certified professionals play a critical role in ensuring consistency and reliability across diverse operations and datasets. By remaining adaptable and embracing technological advances, SAS certified programmers maintain their strategic value and continue to open new avenues for professional impact.
Elevating Professional Value Through Analytical Competence
The SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential represents more than technical skill; it reflects a professional’s ability to synthesize complex datasets into actionable insights that inform decision-making. Certified programmers develop expertise in validating data, applying statistical methods, and producing structured outputs that are both accurate and interpretable. Their work supports evidence-based strategies, mitigates operational risks, and contributes to organizational efficiency. The combination of technical mastery and analytical acumen enhances professional credibility, making certified programmers sought-after contributors in data-driven environments.
Methodological discipline, problem-solving capacity, and analytical precision define the professional identity of SAS certified programmers. They implement robust workflows, ensure reproducibility of analyses, and minimize errors in data processing, thereby reinforcing the reliability of organizational insights. By combining technical proficiency with strategic understanding, certified programmers are positioned to influence decision-making at multiple levels, bridging the gap between computational execution and actionable intelligence.
Expanding Horizons and Future Prospects
The SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential equips professionals with a versatile foundation to explore evolving career paths. Certified programmers may advance into leadership roles, oversee analytics teams, or transition into specialized domains such as predictive modeling, business intelligence, or big data analytics. The adaptability of SAS programming skills enables professionals to navigate changing industry requirements, integrate emerging technologies, and contribute meaningfully to projects that shape organizational strategies.
Cross-industry mobility further amplifies professional prospects. Individuals can leverage their foundational SAS skills to transition between sectors such as healthcare, finance, government, marketing, and technology, applying their expertise to diverse datasets and domain-specific challenges. This flexibility ensures sustained relevance in competitive and rapidly evolving job markets. By coupling technical mastery with analytical insight, SAS certified programmers position themselves as strategic assets capable of driving organizational success, influencing business strategy, and contributing to the advancement of data-centric decision-making.
Unlocking Professional Potential in Data Analytics and Statistical Programming
Achieving the SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential marks a significant milestone in a professional’s journey toward mastery in data analytics and statistical programming. This certification validates essential competencies in SAS programming, including data manipulation, reporting, and basic statistical analysis, positioning professionals to make substantial contributions across various industries. The credential demonstrates an individual’s ability to manage datasets efficiently, generate accurate reports, and implement reproducible analytical workflows, which are highly valued in organizations that rely on data-driven decision-making.
Certified programmers often find that their perspective on problem-solving is transformed through the rigor of the certification process. They acquire a meticulous approach to analyzing data, detecting inconsistencies, and applying corrective methods to ensure the integrity of outputs. These capabilities enable organizations to rely on professionals for critical analysis, whether in financial forecasting, healthcare research, retail strategy, or operational optimization. The certification equips individuals with both technical proficiency and analytical insight, allowing them to navigate complex datasets while providing actionable intelligence to decision-makers.
Industries such as finance, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, and government increasingly prioritize professionals who can interpret and manipulate large volumes of data with precision. In financial organizations, certified programmers are tasked with monitoring transactions, developing predictive models, and identifying anomalous patterns that could indicate risk or fraud. Healthcare institutions utilize certified SAS programmers to analyze patient records, clinical trial datasets, and population-level health data, ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards while facilitating evidence-based decisions. In retail and e-commerce, professionals leverage SAS skills to assess consumer behavior, forecast demand, and optimize inventory management, demonstrating the adaptability of their expertise across diverse business contexts.
Career Roles and Responsibilities
Professionals with the SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential often pursue roles such as data analyst, statistical programmer, reporting specialist, or business intelligence analyst. Data analysts are responsible for exploring large datasets, identifying trends, correlations, and patterns, and communicating insights in a manner that informs strategic decision-making. Statistical programmers develop reproducible analytical workflows, automate reporting processes, and ensure that datasets are accurate, reliable, and consistent. Business intelligence analysts integrate data from multiple sources, transforming complex information into dashboards, visualizations, and summaries that enable executives to make informed decisions. Reporting specialists focus on structuring and presenting analytical outputs in ways that convey essential insights clearly and effectively.
The scope of responsibilities extends beyond technical execution, often encompassing collaboration with multidisciplinary teams. Certified programmers work with statisticians, IT personnel, and business managers to interpret results, refine analytical models, and align outputs with organizational objectives. Effective communication is essential for translating complex findings into actionable strategies, and certified professionals are trained to convey insights in accessible, data-driven narratives. The combination of technical expertise and analytical judgment allows these individuals to address organizational challenges, optimize operations, and support decision-making processes at multiple levels.
Specialized opportunities further broaden the potential roles available to SAS certified programmers. In clinical research, for instance, they manage trial datasets, validate findings, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, contributing to informed healthcare decisions. In the finance sector, their skills are applied to monitor investment portfolios, detect anomalies, and develop predictive models that guide strategic initiatives. Retail and marketing applications of SAS programming include analyzing purchasing behavior, segmenting customer populations, and forecasting trends to optimize sales strategies and enhance operational efficiency. These diverse applications illustrate the versatility and strategic value of the certification in multiple professional domains.
Compensation and Career Growth
Professionals holding the SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential frequently experience enhanced compensation and accelerated career growth. Entry-level positions offer competitive remuneration, reflecting the demand for individuals with technical proficiency and analytical capabilities. As experience accumulates, professionals may advance to senior analyst roles, managerial positions, or leadership tracks within analytics departments, accompanied by increased responsibility and financial reward. Further professional development, such as learning advanced analytics, predictive modeling, or business intelligence tools, can significantly enhance earning potential and broaden the range of available career opportunities.
The certification also provides avenues for non-traditional career paths, including consulting, freelance analytics, and project-based roles. These opportunities allow professionals to apply their skills across industries, exposing them to diverse datasets, business challenges, and analytical methodologies. Freelancing offers flexibility, professional autonomy, and opportunities to cultivate a comprehensive portfolio of work, while the certification ensures credibility and trust with clients and organizations. By leveraging the SAS credential, professionals can demonstrate methodological rigor and technical expertise, both of which are highly valued in flexible, project-driven roles.
Continuous learning further shapes career trajectories for certified programmers. By building upon the foundational knowledge provided by the base programmer certification, individuals can pursue advanced SAS credentials, specialize in predictive analytics, or explore emerging areas such as machine learning and big data management. This ongoing skill development ensures that certified professionals remain competitive in a fast-evolving analytical landscape, opening doors to high-impact projects and leadership opportunities that influence organizational strategy and operational effectiveness.
Adapting to Industry Trends and Emerging Technologies
The contemporary emphasis on data-driven decision-making has elevated the demand for professionals who can manage complex datasets, ensure reproducibility of analyses, and provide actionable insights. SAS Certified Base Programmers for SAS 9 are particularly well-positioned to fulfill these needs due to their proficiency in data validation, statistical analysis, and structured reporting. Organizations rely on these individuals to maintain accuracy, optimize workflows, and translate intricate datasets into insights that support operational efficiency, strategic planning, and risk mitigation.
Emerging technologies and evolving analytical paradigms further enhance the relevance of SAS certification. The integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud-based analytics into traditional SAS workflows allows certified programmers to contribute to innovative projects that redefine business processes. Global organizations also value standardized analytical methods, and SAS certified professionals play a critical role in ensuring consistency, reliability, and scalability of analytical outputs across diverse operational contexts. By staying attuned to technological advancements and industry trends, certified programmers maintain their strategic value and remain at the forefront of the data analytics profession.
Amplifying Professional Impact
The professional impact of a SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 extends beyond technical skill. Certified programmers develop the ability to synthesize complex datasets, identify patterns, and deliver actionable insights that guide decision-making. Their expertise in validating data, applying statistical procedures, and producing reproducible analytical outputs ensures that organizations can rely on their analyses to inform strategy, mitigate risk, and enhance operational efficiency. This combination of technical mastery and analytical insight solidifies the professional’s role as a trusted contributor within any organization.
Analytical discipline, methodological rigor, and problem-solving capabilities define the identity of certified SAS programmers. They design workflows that minimize errors, ensure reproducibility, and optimize data processing efficiency. Their ability to interpret complex datasets and communicate findings effectively positions them as key contributors to organizational decision-making. As industries increasingly prioritize evidence-based strategies, the professional contributions of certified programmers are both strategic and indispensable, bridging the gap between raw data and actionable intelligence.
Expanding Horizons and Career Flexibility
The SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential equips professionals with the versatility to explore diverse career paths. Certified programmers may advance into managerial positions, lead cross-functional analytics initiatives, or specialize in domains such as predictive modeling, advanced statistical analysis, or business intelligence. The adaptability of SAS programming skills allows professionals to navigate shifting industry requirements, integrate emerging analytical tools, and contribute meaningfully to high-impact projects with strategic implications.
Cross-industry mobility further expands career opportunities for certified programmers. By leveraging foundational SAS skills, professionals can transition across sectors including healthcare, finance, government, marketing, and technology, applying their expertise to domain-specific challenges and diverse datasets. This flexibility ensures sustained relevance in competitive job markets and enables certified programmers to continuously expand their professional influence. Combining technical proficiency with analytical insight, SAS certified professionals position themselves as strategic assets capable of shaping organizational success, guiding decision-making, and advancing the field of data-driven analytics.
Expanding Expertise and Professional Horizons
Obtaining the SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential represents a transformative step for professionals seeking to elevate their careers in analytics, data management, and business intelligence. This certification validates mastery in SAS programming fundamentals, including data manipulation, reporting, statistical analysis, and workflow automation, establishing a strong foundation for more advanced analytical pursuits. In an increasingly data-driven landscape, certified programmers are highly sought after for their ability to extract actionable insights, ensure data integrity, and deliver structured, reproducible analytical outputs that directly support strategic decision-making.
Certified SAS programmers often find that the credential enhances both their analytical and professional acumen. They develop an aptitude for managing complex datasets, detecting inconsistencies, and applying corrective strategies to maintain data reliability. This precision enables organizations to trust their analytical outputs for operational planning, financial forecasting, regulatory compliance, and strategic initiatives. Beyond mere technical execution, the certification fosters a mindset that integrates computational rigor with critical thinking, empowering professionals to translate raw data into coherent, actionable intelligence.
The demand for SAS certified professionals spans diverse industries, including finance, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, and government. Financial institutions utilize certified programmers to monitor transactions, develop predictive models, and detect anomalies that inform risk management and investment strategies. Healthcare organizations rely on SAS expertise to analyze patient records, manage clinical trial data, and support evidence-based decision-making while adhering to regulatory standards. In retail and e-commerce, certified programmers assess consumer behaviors, forecast demand trends, optimize supply chains, and drive operational efficiency. The versatility of these skills ensures that professionals remain relevant across multiple organizational contexts.
Professional Roles and Responsibilities
Certified SAS programmers frequently occupy roles such as data analyst, business intelligence analyst, statistical programmer, or reporting specialist. Data analysts explore large datasets to identify trends, correlations, and patterns, presenting findings in a manner that supports strategic planning and decision-making. Statistical programmers create reproducible workflows, automate reporting processes, and validate data integrity, ensuring that analytical outputs remain consistent and reliable. Business intelligence analysts consolidate information from multiple sources, producing dashboards, visualizations, and summaries that make complex data comprehensible to non-technical stakeholders. Reporting specialists focus on structuring analytical outputs to communicate key insights effectively, enhancing the impact of data-driven strategies.
Beyond technical execution, the responsibilities of certified programmers often include collaboration with cross-functional teams. Professionals work closely with statisticians, IT personnel, and business managers to refine analytical models, interpret results, and align outputs with organizational objectives. Effective communication skills are critical, as translating intricate analytical findings into actionable recommendations ensures that insights are applied efficiently across business operations. Certified programmers therefore act as both technical experts and strategic contributors, bridging the gap between raw data and informed decision-making.
Specialized roles further expand the opportunities available to certified programmers. In clinical research, SAS professionals manage trial data, validate outcomes, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, supporting informed healthcare decisions. In finance, they implement risk models, detect fraudulent activity, and provide predictive insights that guide investment strategies. In retail and marketing, certified programmers segment customer populations, analyze purchasing patterns, and forecast trends to optimize operations and drive profitability. These diverse applications illustrate the adaptability of SAS skills across industries and highlight the strategic value of certification.
Compensation and Career Progression
SAS Certified Base Programmers often enjoy enhanced compensation and accelerated career growth. Entry-level roles offer competitive salaries, reflecting the technical expertise and analytical skills demanded by employers. As experience accumulates, professionals may progress to senior analyst roles, data management leadership positions, or managerial tracks within analytics departments, accompanied by increased responsibility and financial reward. Additional skill acquisition, such as advanced analytics, predictive modeling, or data visualization, can further elevate earning potential and broaden career opportunities.
Certified programmers also have the flexibility to pursue consulting, freelancing, or project-based engagements. These roles allow professionals to apply their expertise across multiple industries, providing exposure to diverse datasets, business challenges, and analytical methodologies. Freelancing offers professional autonomy, flexibility, and the ability to cultivate a comprehensive portfolio of work. The SAS certification enhances credibility in these contexts, signaling methodological rigor and technical proficiency that are highly valued by clients and organizations alike.
Continued professional development shapes career trajectories for certified programmers. Building upon the foundational skills validated by the base programmer credential, professionals can pursue advanced SAS certifications, specialize in predictive analytics, or explore emerging areas such as machine learning, big data management, or business intelligence. This ongoing skill enhancement ensures that certified programmers remain competitive in a rapidly evolving analytical landscape and positions them to assume high-impact roles that influence strategic organizational outcomes.
Adapting to Industry Demands and Emerging Technologies
The demand for SAS certified professionals is heightened by the growing reliance on data-driven decision-making across industries. Organizations require individuals capable of managing large, complex datasets, ensuring the reproducibility of analyses, and delivering actionable insights. Certified programmers meet these needs through proficiency in data validation, structured reporting, and statistical methodologies. Their work enables organizations to implement evidence-based strategies, optimize operations, and mitigate risk, providing a critical foundation for informed decision-making.
Emerging technologies and evolving analytics paradigms enhance the relevance of SAS certification. Integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud-based analytics with traditional SAS programming enables certified professionals to contribute to innovative projects that redefine organizational practices. Global enterprises value standardized analytical processes, and SAS certified programmers play a pivotal role in maintaining consistency, reliability, and scalability of data outputs across diverse operational environments. By embracing technological advancements and industry trends, certified professionals sustain their strategic value and remain at the forefront of the analytics profession.
Amplifying Professional Impact
SAS Certified Base Programmers possess the ability to translate complex datasets into meaningful insights that inform strategic decisions. Their expertise in data validation, statistical procedures, and structured reporting ensures that organizations can rely on analytical outputs to guide operations, optimize performance, and support long-term planning. By combining technical mastery with analytical insight, certified programmers elevate their professional impact, serving as trusted contributors whose work directly influences organizational success.
Analytical discipline, methodological rigor, and problem-solving acumen define the identity of certified SAS programmers. They implement efficient workflows, ensure reproducibility, and minimize errors in data processing, reinforcing the reliability of organizational insights. Their capacity to interpret complex datasets and communicate findings effectively positions them as critical contributors to evidence-based strategies, bridging the gap between technical data handling and actionable business intelligence.
Expanding Career Horizons and Future Opportunities
The SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential provides a versatile foundation for exploring diverse career pathways. Certified programmers may advance into leadership roles, oversee analytics teams, or specialize in predictive modeling, business intelligence, or advanced statistical analysis. The adaptability of SAS programming skills allows professionals to navigate shifting industry landscapes, integrate emerging analytical technologies, and contribute meaningfully to high-impact projects with strategic significance.
Cross-industry mobility further broadens professional opportunities for certified programmers. By leveraging foundational SAS skills, individuals can transition across healthcare, finance, government, marketing, technology, and other sectors, applying their expertise to domain-specific challenges and unique datasets. This flexibility ensures that certified professionals remain relevant in competitive job markets and can continuously expand their professional influence. By combining technical proficiency with analytical insight, SAS certified programmers establish themselves as strategic assets capable of guiding organizational success and advancing data-driven decision-making.
Conclusion
The SAS Certified Base Programmer for SAS 9 credential empowers professionals to excel in a data-centric world, providing the technical foundation, analytical skill, and strategic insight necessary to thrive in diverse industries. Certified programmers are uniquely positioned to navigate complex datasets, deliver reliable and actionable insights, and influence organizational strategies across finance, healthcare, retail, government, and beyond. The certification not only enhances career prospects and earning potential but also fosters versatility, professional credibility, and adaptability in a rapidly evolving analytical landscape. By integrating technical mastery with analytical acumen, SAS certified professionals secure roles as pivotal contributors, bridging the gap between raw data and informed decision-making, while continuously expanding their horizons for future growth and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get the products after purchase?
All products are available for download immediately from your Member's Area. Once you have made the payment, you will be transferred to Member's Area where you can login and download the products you have purchased to your computer.
How long can I use my product? Will it be valid forever?
Test-King products have a validity of 90 days from the date of purchase. This means that any updates to the products, including but not limited to new questions, or updates and changes by our editing team, will be automatically downloaded on to computer to make sure that you get latest exam prep materials during those 90 days.
Can I renew my product if when it's expired?
Yes, when the 90 days of your product validity are over, you have the option of renewing your expired products with a 30% discount. This can be done in your Member's Area.
Please note that you will not be able to use the product after it has expired if you don't renew it.
How often are the questions updated?
We always try to provide the latest pool of questions, Updates in the questions depend on the changes in actual pool of questions by different vendors. As soon as we know about the change in the exam question pool we try our best to update the products as fast as possible.
How many computers I can download Test-King software on?
You can download the Test-King products on the maximum number of 2 (two) computers or devices. If you need to use the software on more than two machines, you can purchase this option separately. Please email support@test-king.com if you need to use more than 5 (five) computers.
What is a PDF Version?
PDF Version is a pdf document of Questions & Answers product. The document file has standart .pdf format, which can be easily read by any pdf reader application like Adobe Acrobat Reader, Foxit Reader, OpenOffice, Google Docs and many others.
Can I purchase PDF Version without the Testing Engine?
PDF Version cannot be purchased separately. It is only available as an add-on to main Question & Answer Testing Engine product.
What operating systems are supported by your Testing Engine software?
Our testing engine is supported by Windows. Andriod and IOS software is currently under development.


