Exam Code: H13-622
Exam Name: Huawei Certified Network Professional- Constructing Big Data Solution
Certification Provider: Huawei
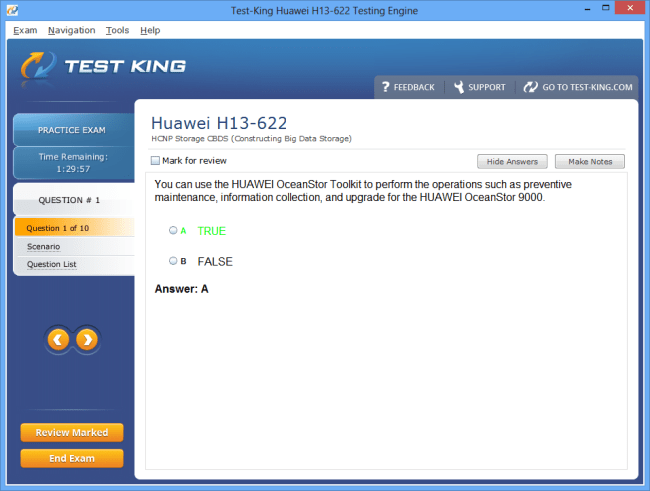
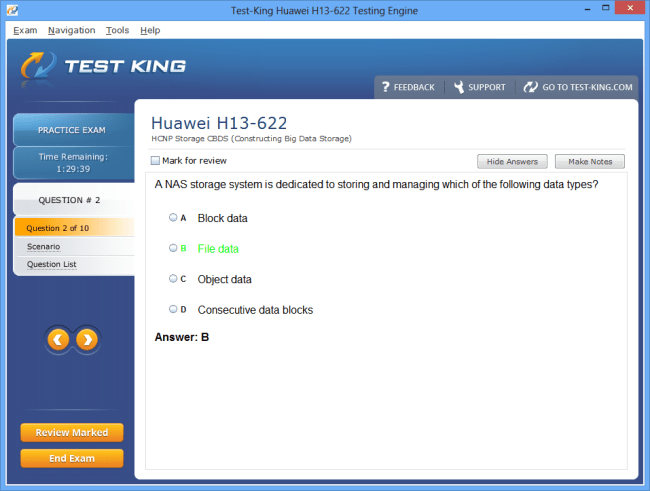
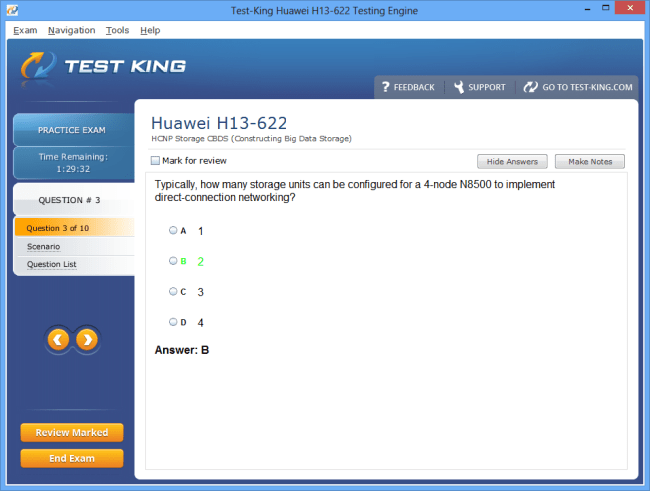
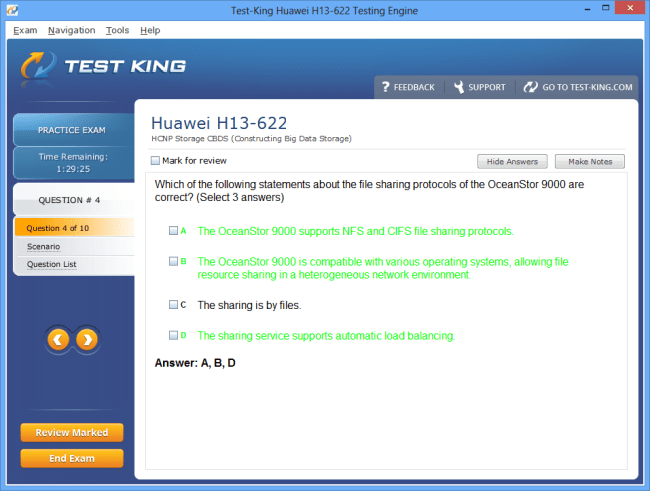
H13-622 Exam Product Screenshots
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get the products after purchase?
All products are available for download immediately from your Member's Area. Once you have made the payment, you will be transferred to Member's Area where you can login and download the products you have purchased to your computer.
How long can I use my product? Will it be valid forever?
Test-King products have a validity of 90 days from the date of purchase. This means that any updates to the products, including but not limited to new questions, or updates and changes by our editing team, will be automatically downloaded on to computer to make sure that you get latest exam prep materials during those 90 days.
Can I renew my product if when it's expired?
Yes, when the 90 days of your product validity are over, you have the option of renewing your expired products with a 30% discount. This can be done in your Member's Area.
Please note that you will not be able to use the product after it has expired if you don't renew it.
How often are the questions updated?
We always try to provide the latest pool of questions, Updates in the questions depend on the changes in actual pool of questions by different vendors. As soon as we know about the change in the exam question pool we try our best to update the products as fast as possible.
How many computers I can download Test-King software on?
You can download the Test-King products on the maximum number of 2 (two) computers or devices. If you need to use the software on more than two machines, you can purchase this option separately. Please email support@test-king.com if you need to use more than 5 (five) computers.
What is a PDF Version?
PDF Version is a pdf document of Questions & Answers product. The document file has standart .pdf format, which can be easily read by any pdf reader application like Adobe Acrobat Reader, Foxit Reader, OpenOffice, Google Docs and many others.
Can I purchase PDF Version without the Testing Engine?
PDF Version cannot be purchased separately. It is only available as an add-on to main Question & Answer Testing Engine product.
What operating systems are supported by your Testing Engine software?
Our testing engine is supported by Windows. Andriod and IOS software is currently under development.
Top Huawei Exams
- H12-811 - HCIA-Datacom V1.0
- H13-611 - HCIA-Storage
- H19-301 - Huawei Certified Pre-sales Associate-IP Network(Datacom)-ENU
- H13-624_V5.5 - HCIP-Storage V5.5
- H12-821 - HCIP-Datacom-Core Technology V1.0
- H12-831 - HCIP-Datacom-Advanced Routing & Switching Technology
- H19-308 - HCSA-Presales-Storage V4.0
- H12-891 - HCIE-Datacom
- H11-861_V4.0 - HCIP-Collaboration V4.0
- H35-210_V2.5 - HCIA-Access V2.5
- H12-711_V4.0 - HCIA-Security V4.0
- H19-110_V2.0 - HCSA-Sales-Storage V2.0
- H12-841_V1.5 - HCIP-Datacom-Campus Network Planning and Deployment V1.5
- H12-725_V4.0 - HCIP-Security V4.0
- H19-338_V3.0 - HCSP-Presales-Storage V3.0
- H13-629 - HCIE-Storage
- H19-101_V6.0 - HCSA-Sales-IP Network V6.0
- H12-311 - Huawei Certified ICT Associate-WLAN
H13-622 Exam Overview: Core Skills Required for Huawei Big Data Professionals
In today’s technology-driven landscape, the exponential growth of data has necessitated a sophisticated approach to managing, processing, and extracting actionable insights from vast information repositories. Enterprises now face unprecedented challenges as data volume, velocity, and variety increase, making traditional systems insufficient. Huawei has positioned itself at the forefront of big data solutions, offering enterprises robust frameworks that integrate cloud computing, distributed storage, and advanced analytics. The H13-622 certification is a gateway for professionals seeking to demonstrate proficiency in constructing these solutions, ensuring they possess both theoretical understanding and practical capabilities.
The certification emphasizes not only the technological aspects but also the strategic importance of data governance and solution architecture in enterprise environments. Candidates are expected to be adept at understanding distributed systems, designing scalable architectures, and implementing secure and efficient data pipelines. The knowledge required spans storage optimization, real-time data processing, and integration with artificial intelligence applications. This breadth of knowledge underscores the criticality of cultivating a holistic understanding of big data ecosystems.
Introduction to Huawei Big Data Solutions and Certification
Huawei’s approach to big data solutions emphasizes modularity and interoperability. Professionals certified through H13-622 are trained to construct environments where multiple technologies coexist seamlessly. These technologies include Hadoop clusters for batch processing, Spark frameworks for accelerated computation, and hybrid storage solutions that combine relational and non-relational databases. Such configurations allow organizations to handle massive datasets while ensuring rapid access and analytical performance. Knowledge of these ecosystems is indispensable for architects tasked with designing sustainable and resilient infrastructures.
Another key focus of the certification is cloud architecture. Huawei Cloud provides a comprehensive suite of services that supports big data workloads, including data warehousing, object storage, and real-time analytics platforms. Professionals must understand how to design workflows that leverage cloud-native features without compromising security or operational efficiency. This requires a nuanced understanding of cloud orchestration, resource allocation, and multi-tenant isolation. Mastery of these concepts ensures that data pipelines remain robust under fluctuating demands and that enterprises can derive insights with minimal latency.
Data governance is increasingly a pivotal aspect of big data projects. The certification expects candidates to grasp frameworks for maintaining data quality, lineage, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Implementing policies for data retention, access control, and metadata management is essential to ensure that enterprises can trust their datasets while avoiding legal or operational pitfalls. Knowledge of governance mechanisms also complements skills in data integration, as professionals must ensure that data flowing across various systems retains consistency and veracity.
Security considerations are tightly interwoven with governance and architecture. Huawei’s big data solutions emphasize encryption, role-based access, and audit mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access and ensure traceability. Candidates are trained to anticipate vulnerabilities in distributed networks and to apply mitigation strategies effectively. Understanding threat modeling, risk assessment, and resilience testing forms a core component of the competencies assessed in the H13-622 examination.
The H13-622 exam does not merely evaluate rote knowledge; it tests applied understanding. Professionals are expected to conceptualize complex big data environments, optimize workflows, and troubleshoot performance bottlenecks. Scenario-based questions often require candidates to evaluate trade-offs between latency, storage cost, and computational efficiency. For example, designing a hybrid architecture that balances on-premise resources with cloud capabilities demands insight into network topology, data replication strategies, and failover mechanisms.
One of the unique aspects of the certification is its emphasis on integration. Big data environments rarely exist in isolation; they interact with enterprise applications, IoT systems, and analytical platforms. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to construct solutions that accommodate heterogeneous data sources, including structured transaction data, semi-structured logs, and unstructured multimedia content. This necessitates familiarity with diverse ingestion frameworks, schema mapping, and transformation techniques that preserve semantic fidelity while enabling rapid analytics.
Performance optimization is another critical area of focus. Professionals must understand parallel processing, memory management, and indexing strategies that accelerate computation without incurring unnecessary operational overhead. Techniques such as partitioning, caching, and query optimization are evaluated not in isolation but in the context of real-world scenarios. Candidates need to appreciate the subtle interactions between resource allocation, processing algorithms, and network throughput to design efficient and resilient systems.
The scope of H13-622 extends to predictive analytics and machine learning integration. Professionals are expected to design pipelines capable of feeding clean, structured datasets into AI models. Understanding feature engineering, data normalization, and model deployment pipelines ensures that insights derived from analytical models are both reliable and actionable. These skills bridge the gap between raw data collection and strategic business decisions, reflecting the exam’s focus on practical application.
Understanding the underlying infrastructure is essential for candidates preparing for the certification. Huawei big data solutions often utilize distributed storage clusters that require synchronization, redundancy, and fault tolerance. Concepts such as replication factor, data block allocation, and consistency models are essential to ensure reliability. Candidates must also grasp the operational implications of node failure, network partitioning, and load balancing, as these factors directly influence system performance and data availability.
The examination also emphasizes workflow orchestration and automation. Professionals need to design pipelines that schedule and monitor jobs efficiently, manage dependencies, and handle exceptions gracefully. Workflow tools enable the orchestration of complex processes, reducing manual intervention and minimizing human error. Mastery of these tools is indispensable for constructing enterprise-grade big data solutions that are both scalable and maintainable.
Data analytics forms a substantial component of the required knowledge. Candidates must understand both descriptive and diagnostic analytics, utilizing reporting and visualization platforms to derive insights. Knowledge of query languages, analytical frameworks, and visualization techniques allows professionals to communicate findings effectively to stakeholders. This ensures that data-driven decisions are grounded in accurate interpretation and meaningful patterns, reinforcing the value of big data investments.
Enterprise deployment considerations are equally emphasized. Professionals must assess requirements for storage capacity, processing throughput, and network bandwidth before designing solutions. Budgetary constraints, operational overhead, and regulatory compliance shape the architecture choices, requiring candidates to think beyond technical feasibility toward strategic alignment with business objectives. Evaluating trade-offs between cost, performance, and maintainability is a recurrent theme in the H13-622 certification assessment.
Interdisciplinary understanding is also tested. Professionals are expected to integrate knowledge of database management, network protocols, distributed computing, and cloud engineering. This integration ensures that solutions are coherent, efficient, and adaptable to evolving technological landscapes. Candidates must appreciate how each component interacts with the others, as small misconfigurations can propagate into substantial performance or security issues.
Real-world case studies provide practical context. Candidates often encounter scenarios where they must design a solution for a large retail enterprise, a telecommunications provider, or a financial institution. These cases require considering data ingestion from multiple channels, optimizing storage for heterogeneous data types, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations, and enabling real-time analytical capabilities. By addressing such scenarios, professionals demonstrate their ability to translate theoretical concepts into tangible outcomes.
Monitoring and maintenance are fundamental aspects of big data solutions that H13-622 assesses. Professionals must establish monitoring systems that track cluster health, job performance, and resource utilization. Logging, alerting, and automated recovery mechanisms ensure that operational anomalies are detected and resolved promptly. Candidates must appreciate the subtleties of performance tuning, capacity planning, and lifecycle management to maintain optimal system functionality over time.
The certification also explores future-oriented technologies. Huawei invests in AI-assisted data operations, edge computing, and high-performance computing integration. Professionals are expected to understand emerging trends, such as federated learning, data mesh architectures, and hybrid cloud deployments. Awareness of these developments allows certified individuals to design solutions that remain relevant and scalable in rapidly evolving technological environments.
Collaboration and team dynamics are implicit components of professional competence. Constructing big data solutions often involves interdisciplinary teams, including data engineers, network specialists, and business analysts. Candidates must demonstrate understanding of workflow collaboration, communication of technical concepts, and adherence to project management practices. This ensures that solutions are implemented effectively and align with strategic business goals.
In summary, the H13-622 certification equips professionals with a comprehensive skill set that spans theoretical knowledge, practical implementation, and strategic planning. Candidates are trained to construct resilient, scalable, and efficient big data solutions within Huawei’s ecosystem, integrating storage, processing, analytics, and governance capabilities. Mastery of distributed systems, cloud architecture, data security, and performance optimization ensures that certified individuals can meet the growing demands of enterprise data environments. The certification represents a significant milestone for professionals seeking to validate their expertise in constructing Huawei big data solutions and contributing to data-driven organizational transformation.
Core Knowledge Areas for H13-622 Exam
The H13-622 certification is designed to ensure that professionals possess a profound understanding of the multifaceted big data ecosystem within Huawei’s technological framework. Success in the exam demands mastery over a variety of concepts, ranging from distributed computing to real-time data processing, and the ability to integrate them seamlessly into enterprise-grade solutions. Candidates are expected to internalize not only the mechanics of data systems but also the strategic imperatives that drive their design, deployment, and optimization.
One of the foundational elements of this knowledge framework is understanding the Hadoop ecosystem and its applications in large-scale data environments. Hadoop serves as a versatile platform for distributed storage and computation, allowing massive datasets to be processed efficiently across clusters of commodity hardware. Professionals must comprehend how Hadoop’s underlying components, such as the Hadoop Distributed File System and MapReduce processing paradigm, function together to provide resilience, fault tolerance, and scalability. Beyond the basics, the exam evaluates the candidate’s grasp of ecosystem enhancements, including YARN for resource management and Hadoop’s integration with other analytical tools to accelerate data workflows.
Spark is another integral technology assessed in H13-622, offering in-memory computation that dramatically enhances processing speed for iterative algorithms and complex queries. Candidates are expected to differentiate scenarios in which Spark’s resilient distributed datasets outperform traditional batch processing, and understand how to optimize cluster resources to maximize throughput. Knowledge of Spark streaming is crucial for implementing real-time analytics pipelines that respond to data as it is generated, a capability increasingly demanded by enterprises seeking instantaneous insights from IoT devices, social media streams, or transaction logs.
Data storage and management constitute another critical dimension of expertise. Professionals must navigate both traditional relational databases and emerging NoSQL paradigms, understanding when each is appropriate based on data structure, access patterns, and consistency requirements. This includes familiarity with columnar storage, document-based solutions, and key-value stores, alongside hybrid configurations that leverage the strengths of multiple systems. Optimizing storage strategies for performance, cost, and reliability is an essential skill, and candidates are expected to analyze trade-offs between disk throughput, memory usage, and network latency when designing these systems.
Efficient data processing lies at the heart of constructing big data solutions. Batch processing remains a fundamental technique, enabling the systematic analysis of historical data sets for trend identification, predictive modeling, and compliance reporting. However, enterprises increasingly require real-time or near-real-time processing to derive actionable insights promptly. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to implement streaming pipelines, handle high-velocity data, and employ micro-batch strategies or event-driven architectures that balance latency with resource efficiency. Understanding frameworks for both batch and streaming processing is pivotal for developing flexible, responsive solutions.
Security and compliance are paramount in enterprise data environments and form an integral part of the H13-622 curriculum. Professionals must understand mechanisms for safeguarding sensitive data, including encryption protocols, access controls, and auditing procedures. Beyond technical safeguards, candidates must appreciate regulatory frameworks and internal governance policies that dictate data handling practices. Implementing these measures ensures not only protection against unauthorized access but also compliance with national and international standards, which is vital for enterprises operating in regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and telecommunications.
Optimization of performance and scalability is another dimension of expertise evaluated in the exam. Professionals are expected to diagnose bottlenecks, balance workloads across distributed nodes, and fine-tune memory and storage allocations to maintain high throughput. This includes strategies such as data partitioning, caching, indexing, and query optimization, which collectively enhance system responsiveness and efficiency. Candidates must also consider how cluster size, network topology, and hardware specifications influence the overall architecture, demonstrating holistic insight into resource utilization and operational sustainability.
Understanding data integration techniques is essential for constructing cohesive systems from heterogeneous data sources. Professionals are expected to implement pipelines that ingest structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, harmonizing these sources into a unified framework for analysis. This involves knowledge of ETL processes, schema mapping, data cleaning, and transformation techniques that ensure semantic fidelity and analytical reliability. Integration is not solely a technical challenge; it also requires an understanding of workflow orchestration, error handling, and data lineage to maintain traceability and operational continuity.
The exam also evaluates proficiency in leveraging cloud-native features to construct scalable, resilient solutions. Huawei Cloud offers a suite of services for data storage, analytics, and orchestration, and candidates must understand how to deploy and manage workloads across these platforms. This includes concepts such as virtual resource allocation, containerization, automated scaling, and fault tolerance in distributed cloud environments. Professionals must demonstrate the ability to design hybrid architectures that harmonize on-premises and cloud resources, ensuring seamless data flow and operational agility.
Analytics forms a core component of the H13-622 knowledge areas. Candidates must be proficient in data interpretation, utilizing both descriptive and diagnostic techniques to extract meaningful insights. This involves query formulation, aggregation strategies, statistical analysis, and visualization methods that allow stakeholders to comprehend complex datasets effectively. Analytical proficiency ensures that big data infrastructures do more than store and process information—they enable decision-making and strategic planning by translating raw data into actionable intelligence.
The exam emphasizes the importance of maintaining data quality throughout its lifecycle. Professionals must understand methodologies for monitoring accuracy, completeness, and consistency across distributed systems. Implementing automated validation, anomaly detection, and error correction protocols ensures that the data remains reliable for analytical or operational purposes. High-quality data is fundamental for feeding predictive models, deriving accurate insights, and ensuring that enterprise decision-making is informed by credible information.
Knowledge of operational monitoring and fault management is another essential skill. Candidates are expected to deploy tools and practices for tracking cluster performance, resource utilization, and job execution. Alerting systems, log analysis, and automated recovery mechanisms form part of this operational competency, allowing professionals to maintain system stability and prevent downtime. Understanding the subtleties of distributed environments, including node failures, network partitioning, and workload redistribution, ensures that data solutions remain robust under stress.
Candidates are also evaluated on their understanding of data modeling principles. Structuring data for optimal storage, retrieval, and analysis requires careful consideration of relationships, hierarchies, and indexing. Professionals must design schemas that accommodate growth, maintain query performance, and facilitate analytical processing. This includes both relational and non-relational modeling, along with hybrid strategies that balance normalization with performance optimization. Effective data modeling underpins the construction of coherent, scalable, and efficient big data systems.
Real-world application scenarios are integral to the H13-622 examination. Professionals are often presented with challenges such as designing an architecture for a telecommunications company, a financial institution, or an e-commerce enterprise. These scenarios require integration of multiple technologies, evaluation of storage and processing trade-offs, and implementation of security and governance policies. Candidates must demonstrate both technical proficiency and strategic judgment in tailoring solutions to organizational objectives.
Emerging technologies are also woven into the knowledge requirements. Candidates must stay informed about advancements in machine learning integration, AI-assisted analytics, edge computing, and federated data architectures. Understanding these trends allows professionals to design solutions that are forward-compatible and able to adapt to the evolving landscape of enterprise data management. This foresight is critical for constructing infrastructures that remain relevant, efficient, and resilient over time.
In addition, collaboration within cross-functional teams is an implicit skill. Constructing big data solutions requires coordination among data engineers, system architects, network specialists, and business analysts. Professionals must understand workflow dependencies, communicate technical constraints effectively, and align architectural decisions with business goals. This interdisciplinary competence ensures that solutions are not only technically sound but also operationally effective and strategically aligned.
Operational efficiency is further enhanced through automation and orchestration. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to construct pipelines that schedule, monitor, and manage data workflows with minimal manual intervention. This reduces human error, accelerates processing, and ensures reproducibility in analytical results. Automation complements monitoring and optimization strategies, forming a cohesive approach to managing complex data ecosystems.
Finally, candidates are expected to exhibit analytical foresight and problem-solving acumen. Constructing big data solutions often involves addressing unexpected challenges, from network latency issues to sudden spikes in data volume. Professionals must diagnose, strategize, and implement solutions that maintain system stability while optimizing performance. This ability to adapt dynamically and troubleshoot effectively is a hallmark of competence recognized by the H13-622 certification.
The H13-622 certification ultimately equips professionals with a sophisticated and multidimensional skill set. Knowledge spans distributed computing, data storage, processing, analytics, governance, security, cloud architecture, and emerging technologies. Mastery in these areas ensures that professionals can construct resilient, scalable, and efficient big data solutions capable of meeting the growing demands of enterprise data environments. By integrating theoretical understanding with applied expertise, candidates demonstrate their readiness to contribute to transformative data initiatives within Huawei’s ecosystem.
Practical Skills Required for Constructing Big Data Solutions
Constructing big data solutions within Huawei’s ecosystem requires a convergence of technical proficiency, strategic insight, and operational dexterity. The H13-622 certification emphasizes not only understanding theoretical principles but also demonstrating practical skills that translate into real-world implementations. Professionals are expected to navigate complex environments, optimize workflows, and ensure resilience while accommodating dynamic enterprise requirements. This necessitates a comprehensive grasp of system design, data modeling, processing pipelines, and cloud integration.
Designing and deploying big data architectures is one of the fundamental skills evaluated. Candidates must conceptualize frameworks that balance storage, computation, and network resources effectively. This involves mapping data flow from ingestion through processing to analytical outputs, while considering constraints such as latency, throughput, and operational cost. A deep understanding of distributed computing principles allows professionals to partition workloads across multiple nodes, implement redundancy, and maintain consistency. Scalability considerations are critical, as enterprise data volumes expand unpredictably, demanding elastic architectures capable of accommodating growth without degrading performance.
Data modeling is integral to constructing robust solutions. Professionals must create schemas that facilitate efficient querying, support analytical workloads, and accommodate evolving data structures. This requires awareness of relational, non-relational, and hybrid models. Designing for normalization, indexing, and partitioning ensures that storage utilization is optimized and access performance is maximized. Candidates are also expected to handle semi-structured and unstructured data, transforming logs, multimedia content, and sensor streams into analyzable formats without compromising data fidelity.
Implementing ETL processes forms another core skill area. Extracting data from diverse sources, transforming it for analytical consistency, and loading it into target repositories demands precision and foresight. Professionals must design pipelines that handle high data volumes while preserving integrity and performance. This includes employing techniques such as data cleansing, validation, deduplication, and schema evolution management. Optimization strategies, such as parallel transformations and incremental loading, ensure that pipelines operate efficiently under fluctuating workloads.
Efficient handling of massive datasets requires mastery of storage architectures, indexing strategies, and query optimization techniques. Candidates must understand data partitioning, replication, and caching mechanisms that reduce latency and enhance throughput. Storage strategies are evaluated not solely on technical correctness but also on their operational sustainability. For instance, professionals need to determine when to prioritize storage cost efficiency versus computational speed, and how to allocate resources dynamically across nodes to maintain consistent performance.
Integrating cloud-native solutions with on-premise infrastructure is increasingly essential in enterprise environments. Professionals are expected to design hybrid architectures that leverage Huawei Cloud’s capabilities while maintaining critical workloads on local servers. This involves resource orchestration, virtual environment management, and ensuring seamless data movement across environments. Understanding containerization, automated scaling, and workload balancing is crucial to optimize performance while minimizing operational complexity. This skill ensures that organizations can maintain agility and resilience in the face of unpredictable demands.
Troubleshooting and optimizing big data workflows is another vital competency. Professionals must identify bottlenecks, diagnose systemic issues, and implement corrective measures efficiently. This requires proficiency in monitoring system performance, analyzing job execution metrics, and understanding interdependencies within complex pipelines. Candidates are expected to employ proactive strategies such as predictive maintenance, automated failover, and adaptive resource allocation. These measures ensure minimal disruption in operations and consistent delivery of insights to decision-makers.
Data security and compliance are inseparable from practical skills in constructing solutions. Professionals must implement encryption, access control, and auditing mechanisms to safeguard sensitive information. Additionally, they must ensure that systems adhere to regulatory mandates, including data retention policies, privacy laws, and internal governance frameworks. This requires both technical and operational knowledge to enforce security at multiple layers of architecture, including storage, network, and application tiers. Incorporating security as an intrinsic component of solution design rather than an afterthought is a hallmark of certified competence.
Performance tuning is an area where practical expertise is rigorously evaluated. Candidates are expected to optimize query execution, balance cluster workloads, and leverage caching and indexing to minimize latency. This involves understanding the subtleties of distributed resource allocation, such as the impact of node heterogeneity, network congestion, and job scheduling algorithms. Fine-tuning solutions ensures that analytical workflows remain responsive even as data volumes and complexity increase, providing consistent reliability for enterprise decision-making.
Workflow orchestration is a critical component of big data operations. Professionals must implement pipelines that automate task scheduling, manage dependencies, and handle exceptions effectively. Orchestration ensures that complex workflows execute seamlessly, reducing manual intervention and minimizing errors. Candidates must demonstrate knowledge of techniques for error recovery, job prioritization, and resource management to maintain continuous and predictable data processing, even in high-pressure operational environments.
Monitoring and alerting systems are indispensable in maintaining solution stability. Professionals are expected to deploy mechanisms that track cluster health, job performance, and resource utilization. These systems allow rapid detection of anomalies, proactive mitigation of performance degradation, and documentation of operational events for future analysis. Integrating monitoring with automation ensures that issues are resolved quickly, sustaining high availability and minimizing disruption to business operations.
Analytics integration is another essential skill. Professionals must enable data pipelines to feed structured and transformed data into analytical engines for visualization, predictive modeling, and business intelligence. Understanding how to prepare datasets for machine learning, generate features, and optimize input for model training ensures that organizations can leverage insights effectively. Candidates are expected to design pipelines that support iterative analysis, maintain data lineage, and allow reproducibility of results, which is critical for strategic decision-making.
Operational maintenance extends to cluster management, capacity planning, and lifecycle oversight. Professionals must anticipate growth, plan resource allocation, and implement strategies for scaling infrastructure efficiently. This includes predicting workload spikes, balancing computational loads, and provisioning storage in alignment with performance targets. Proper maintenance ensures long-term sustainability, minimizing system failures and maximizing the value of big data investments.
Collaboration and communication skills complement technical competencies. Constructing big data solutions requires coordination across multiple teams, including data engineers, architects, network specialists, and business analysts. Professionals must understand the dependencies, communicate design decisions clearly, and document operational procedures to ensure cohesive project execution. Interdisciplinary coordination reduces errors, accelerates deployment, and ensures that solutions align with organizational objectives.
In addition, candidates must be proficient in integrating emerging technologies. Huawei’s big data environment increasingly incorporates artificial intelligence, machine learning, and edge computing. Professionals must design solutions capable of feeding AI pipelines, supporting federated learning scenarios, and integrating data streams from edge devices. Knowledge of these innovations ensures that architectures remain future-proof, capable of handling both current and anticipated enterprise requirements.
Real-world application scenarios often test problem-solving acumen. Professionals may be asked to design solutions for financial institutions, retail chains, or telecommunication providers, balancing multiple objectives including security, cost, performance, and compliance. These scenarios assess the candidate’s ability to synthesize knowledge across architecture, storage, processing, analytics, and governance. The ability to conceptualize and implement solutions that are both technically robust and strategically aligned is a defining feature of certified professionals.
Integration of heterogeneous data sources is an expected skill. Enterprises often possess structured databases, semi-structured logs, and unstructured multimedia content. Professionals must design pipelines that harmonize these disparate sources into cohesive, analyzable datasets. This involves schema mapping, transformation, and validation to ensure that data remains consistent and interpretable across platforms. Effective integration facilitates actionable insights and supports decision-making processes at various organizational levels.
Automation and optimization go hand in hand in practical applications. Candidates are expected to implement workflows that self-adjust based on processing demands, detect anomalies automatically, and recover from failures without manual intervention. Automation not only enhances efficiency but also reduces operational risks, allowing organizations to focus resources on analytical tasks and strategic initiatives rather than routine maintenance.
Finally, an understanding of enterprise constraints and strategic objectives informs the practical implementation of solutions. Professionals must balance technical feasibility with cost efficiency, regulatory compliance, and performance expectations. Decision-making involves evaluating trade-offs between storage solutions, processing frameworks, and deployment models, ensuring that architectures provide value while remaining operationally sustainable. Mastery of these practical skills signifies readiness to construct Huawei big data solutions that are resilient, scalable, and effective in real-world enterprise contexts.
Tools, Platforms, and Technologies Tested in H13-622 Exam
The H13-622 certification evaluates not only theoretical knowledge and practical skills but also proficiency in a diverse set of tools, platforms, and technologies integral to constructing Huawei big data solutions. Professionals are expected to demonstrate an in-depth understanding of how these instruments interact to facilitate storage, processing, analytics, orchestration, and security across distributed environments. Mastery of these technologies enables enterprises to derive actionable insights efficiently while maintaining resilience, scalability, and compliance.
Huawei’s big data tools form the foundation of technological proficiency tested in the exam. These tools provide comprehensive support for data storage, computing, and analytical tasks. Candidates are expected to understand the functionalities of distributed storage systems, including mechanisms for redundancy, fault tolerance, and efficient retrieval. Professionals must be capable of configuring clusters, managing node allocation, and optimizing storage layouts to maximize performance. Understanding the interplay between storage and computational frameworks ensures that resources are utilized efficiently while maintaining operational continuity.
Data analytics and visualization platforms are pivotal for interpreting complex datasets. Professionals must be proficient in deploying analytical pipelines that extract meaningful insights from structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Visualization tools enable stakeholders to comprehend patterns, trends, and anomalies in intuitive formats. Candidates are expected to design dashboards, generate reports, and support decision-making processes by transforming raw data into actionable intelligence. Integrating visualization with analytical frameworks ensures that enterprises can respond to emergent business needs with agility.
Automation and orchestration technologies are essential for managing complex workflows in distributed environments. Candidates are expected to implement pipelines that schedule, monitor, and execute jobs efficiently, reducing manual intervention and minimizing errors. This includes handling task dependencies, error recovery, and dynamic allocation of resources based on workload fluctuations. Mastery of orchestration tools allows professionals to maintain system responsiveness and reliability, particularly in high-velocity data environments where downtime can have significant operational consequences.
Monitoring and management platforms are integral for sustaining cluster health and operational efficiency. Professionals must deploy tools that track system performance, detect anomalies, and provide real-time metrics on resource utilization. These systems enable proactive intervention, ensuring that performance bottlenecks, node failures, or unexpected workload spikes are addressed promptly. Candidates are expected to analyze monitoring data, fine-tune configurations, and implement automated corrective measures to maintain optimal functionality.
Integration with cloud-native services constitutes another dimension of technological competence. Huawei Cloud offers scalable storage, computing, and analytics capabilities that support big data workloads. Professionals must understand how to deploy and orchestrate cloud resources, configure virtual environments, and implement elastic scaling strategies. This includes knowledge of containerization, multi-tenant isolation, and workload migration between on-premises and cloud infrastructures. Proficiency in cloud integration ensures that architectures are flexible, cost-effective, and resilient under varying operational demands.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are increasingly incorporated into Huawei big data solutions. Candidates are expected to prepare pipelines capable of feeding clean, structured datasets into AI models, supporting predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and recommendation systems. Knowledge of feature engineering, model deployment, and iterative optimization ensures that AI-driven insights are both reliable and actionable. Professionals must understand how to integrate machine learning frameworks seamlessly into existing big data infrastructures, balancing computational requirements with analytical outcomes.
Data security and governance tools are fundamental in ensuring compliance and protecting sensitive information. Professionals must implement encryption mechanisms, access control protocols, and auditing frameworks to safeguard data integrity and confidentiality. Candidates are also expected to utilize governance platforms for managing metadata, monitoring data lineage, and enforcing regulatory compliance. Mastery of these tools ensures that big data solutions not only function efficiently but also adhere to organizational policies and legal requirements.
Operational optimization tools support performance tuning and workload balancing. Candidates must leverage these platforms to analyze job execution, optimize query performance, and allocate resources dynamically across distributed nodes. Techniques such as caching, partitioning, and indexing are evaluated in the context of practical scenarios, requiring professionals to make strategic decisions that balance latency, throughput, and cost. Optimization ensures that enterprise workloads are processed efficiently while maintaining system reliability.
The H13-622 exam also assesses knowledge of real-time data processing platforms. Professionals must implement streaming pipelines capable of handling continuous data flows from IoT devices, transaction logs, or user interactions. Candidates are expected to design architectures that manage event ingestion, transformation, and storage while minimizing latency. Real-time processing platforms require integration with monitoring, orchestration, and analytics tools to ensure that operational and analytical objectives are met concurrently.
Data integration technologies are critical for constructing cohesive environments from heterogeneous sources. Professionals must employ tools that facilitate ETL processes, schema mapping, data validation, and transformation. These tools ensure that structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data are harmonized into unified datasets suitable for analysis. Understanding integration mechanisms allows candidates to maintain data consistency, enable efficient analytics, and support complex workflows across multiple platforms.
Enterprise deployment tools are part of the technological landscape candidates must navigate. Professionals are expected to manage clusters, configure high-availability mechanisms, and optimize network topologies to sustain performance. Deployment tools enable scaling of resources, load balancing, and automated provisioning, ensuring that infrastructures remain resilient and responsive. Knowledge of these tools allows professionals to translate design blueprints into operational realities efficiently.
Data archival and lifecycle management platforms are also important. Professionals must implement strategies for managing historical datasets, including compression, tiered storage, and retrieval optimization. Lifecycle management ensures that operational storage is utilized effectively while retaining the ability to access historical data for analytical or compliance purposes. Candidates must balance storage costs with performance requirements, applying policies that support both efficiency and accessibility.
Collaboration tools are implicitly evaluated through scenario-based tasks. Constructing big data solutions involves coordinating across teams, including data engineers, analysts, and network specialists. Professionals must use platforms that facilitate workflow sharing, version control, and documentation of operational procedures. These tools enable seamless communication and ensure that solution implementation aligns with organizational goals while maintaining technical coherence.
The exam emphasizes end-to-end data pipeline construction using integrated toolchains. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to ingest data, process it through distributed frameworks, analyze outcomes, and visualize insights while maintaining governance, security, and performance standards. Mastery of these technologies ensures that professionals can construct robust, scalable, and intelligent big data environments capable of meeting enterprise demands.
Emerging technologies such as federated learning, edge computing integration, and AI-assisted analytics are increasingly incorporated into Huawei solutions. Candidates must understand how these innovations interact with traditional data platforms, enabling low-latency processing at the network edge, enhanced analytical capabilities, and distributed intelligence. Knowledge of these advanced technologies allows professionals to design forward-looking solutions that remain relevant as enterprise data landscapes evolve.
Operational troubleshooting is another focus area. Professionals are expected to identify and resolve bottlenecks, resource contention, and workflow failures using monitoring and diagnostic tools. This includes analyzing job execution logs, detecting anomalies in data flows, and implementing corrective actions without interrupting critical services. Effective troubleshooting ensures that enterprise solutions remain reliable under dynamic and high-demand conditions.
Scenario-based evaluation is prevalent in the exam, requiring candidates to deploy tools in contexts such as large-scale financial analytics, e-commerce data processing, or telecommunication monitoring. Professionals must design architectures, implement workflows, and integrate analytical and visualization platforms to solve complex problems. These exercises assess both technological knowledge and the ability to apply it practically under enterprise constraints.
Workflow automation tools allow professionals to reduce manual intervention while enhancing reliability. Candidates must implement schedules, dependency management, and exception handling, ensuring continuous operation of data pipelines. Automation complements orchestration, optimization, and monitoring, forming a cohesive system that maximizes efficiency, minimizes error rates, and supports business objectives.
Conclusion
Understanding the interoperability of various tools and platforms is crucial. Professionals must demonstrate how to integrate storage systems, processing engines, analytical frameworks, visualization platforms, and governance tools into coherent, high-performing infrastructures. This ensures that the enterprise can harness data strategically, maintain resilience, and adapt to evolving technological and business demands. Mastery of these tools and platforms represents a defining competency for professionals undertaking the H13-622 certification.